Siklon Tropis
Summary
TLDRThis script provides an in-depth explanation of tropical cyclones, their formation, and their impact on regions such as Indonesia. It details the process by which tropical cyclones form over warm ocean waters, reaching up to 200 km in radius, and becoming destructive weather events with high winds and heavy rainfall. The script also explains the different names for tropical cyclones depending on the region, and highlights the crucial role of monitoring centers like BMKG in issuing early warnings to mitigate damage. Notable examples of past cyclones in Indonesia are also included.
Takeaways
- 🌪️ Tropical cyclones are intense storms with a radius of 150-200 km, capable of causing significant damage through strong winds, heavy rain, and storm surges.
- 🌍 The names for tropical cyclones vary by location: 'typhoon' in the Northwest Pacific, 'hurricane' in the Atlantic, and 'cyclone' in the South Pacific and Indian Ocean.
- 🌡️ Tropical cyclones form over warm ocean waters with a surface temperature of at least 26.5°C, which fuels their development.
- 💨 As a tropical cyclone intensifies, it forms a low-pressure system surrounded by convection clouds, leading to higher wind speeds and a more organized structure.
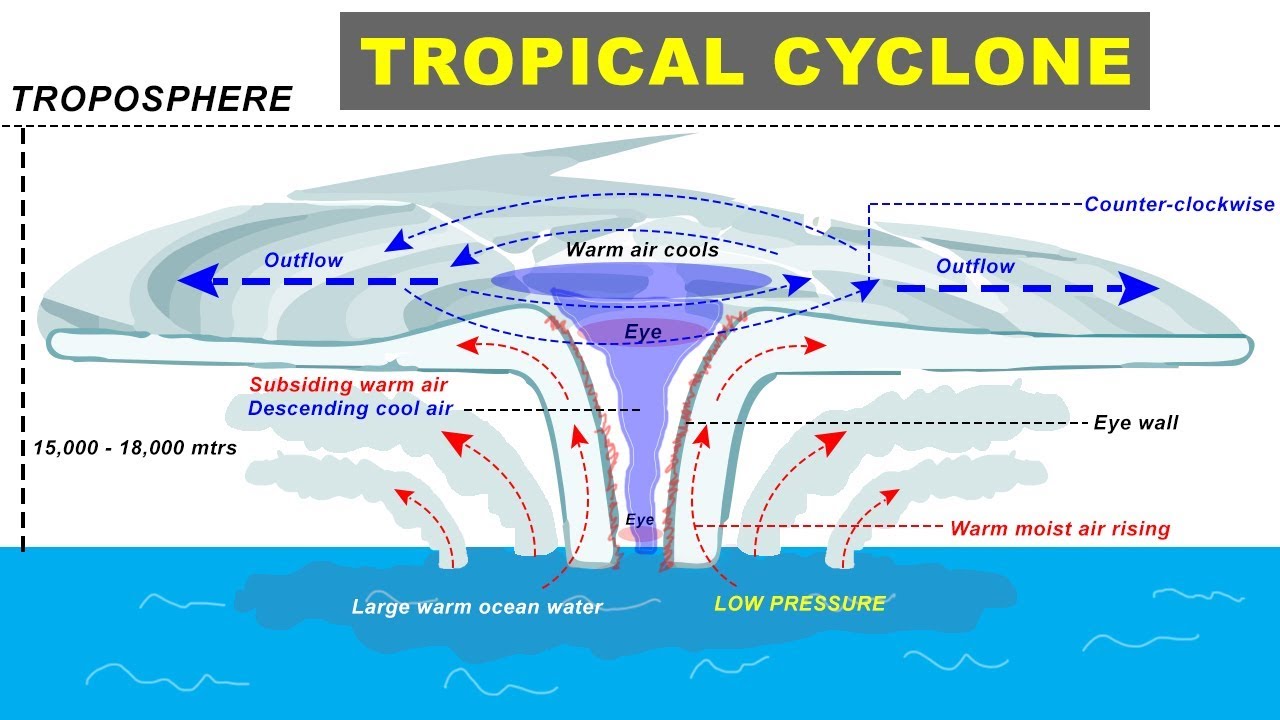
- 🌪️ Once matured, tropical cyclones feature a calm center, known as the 'eye', surrounded by the most dangerous part, the 'eye wall', which has the strongest winds and heaviest rainfall.
- ⏳ Tropical cyclones can last between three to eighteen days, typically weakening after they make landfall or move into cooler waters.
- 🌏 The majority of tropical cyclones occur in the Northern Hemisphere, particularly between 10° and 20° latitude, with approximately 60% of these storms happening in this region.
- 🇮🇩 While tropical cyclones rarely form near the equator (0° to 10° latitude), they still impact countries like Indonesia, such as Cyclone Cempaka and Cyclone Rossi.
- 🚨 Indonesia has a Tropical Cyclone Warning Center within the BMKG (Meteorological, Climatological, and Geophysical Agency) that monitors and issues early warnings for cyclones affecting the region.
- 📱 To stay updated on tropical cyclones, individuals can visit the BMKG website or use the BMKG Info app on their smartphones for real-time information and alerts.
Q & A
What is a tropical cyclone?
-A tropical cyclone is a powerful storm with a large radius of up to 150-200 km. It can bring strong winds, heavy rainfall, and cause flooding, high waves, and storm surges.
What are the different names for a tropical cyclone depending on its location?
-A tropical cyclone is called a 'tropical storm' or 'cyclone' when it forms in the Indian Ocean, a 'typhoon' when it forms in the Northwest Pacific Ocean, and a 'hurricane' when it forms in the Atlantic Ocean.
Where do tropical cyclones typically form?
-Tropical cyclones typically form over warm sea waters in tropical regions where the surface sea temperature exceeds 26.5°C.
What is the role of warm sea surface temperatures in the formation of a tropical cyclone?
-Warm sea surface temperatures provide the energy necessary to form low-pressure systems, leading to the development of convective clouds, which are the primary ingredients for forming a tropical cyclone.
What is the 'eye' of a tropical cyclone?
-The 'eye' of a tropical cyclone is a relatively calm area at the center, where wind speeds are low, and there are no clouds. It is surrounded by the eye wall, where the highest winds and heaviest rains occur.
How does the structure of a tropical cyclone change as it matures?
-As a tropical cyclone matures, it becomes more stable, with a well-defined circular pattern and a low-pressure center. The maximum wind speed increases, and the storm can reach wind speeds exceeding 60 km/h.
How long does a tropical cyclone typically last?
-The lifespan of a tropical cyclone usually ranges from three days to 18 days.
Where do most tropical cyclones occur on Earth?
-Most tropical cyclones occur in the Northern Hemisphere, particularly between latitudes 10° and 20° from the equator. About 60% of tropical cyclones happen in the Northern Hemisphere.
What role does BMKG play in monitoring tropical cyclones in Indonesia?
-The Meteorological, Climatological, and Geophysical Agency (BMKG) in Indonesia monitors tropical cyclones and issues early warnings related to their impact in the region. They use their Tropical Cyclone Warning Center to provide information and alerts.
Can tropical cyclones form near the equator?
-Tropical cyclones rarely form near the equator, especially between 0° and 10° latitude. However, cyclones have been observed close to the equator, such as Tropical Cyclone Femei, which formed near the Malay Peninsula.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Formation of Cyclone | Tornadoes Vs Cyclones Vs Hurricanes | UPSC Mains GS1
Tropical Cyclone, Hurricane, Storm Formation explained | Cyclone Biparjay in Arabian Sea, Gujarat

How Typhoons Are Formed | Animation

Geography of South Asia: Physical Characteristics

Explained | How are Cyclones formed | Hurricanes and Cyclones | Curious DNA

How Cyclones are Formed? | Animation Video | OnlyIAS
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
