Formation of Cyclone | Tornadoes Vs Cyclones Vs Hurricanes | UPSC Mains GS1
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script delves into the formation and impact of tropical cyclones, particularly in the Indian Ocean region. It discusses the conditions necessary for cyclone formation, such as warm ocean temperatures and atmospheric pressure, and the stages of cyclone development. The script also explains the difference between tropical and temperate cyclones, and how they are named in various regions, such as typhoons in East Asia and hurricanes in the Caribbean. The video aims to educate viewers on the science behind these natural phenomena and their significance in the UPSC Prelims and Mains examinations.
Takeaways
- 🌀 Cyclones are a common natural phenomenon in the Arabian Sea, often bringing heavy rainfall but sometimes causing significant destruction.
- 🏞️ The most devastating cyclones in India are those that impact the western coast, with Cyclone Taukte in 2021 being a prime example, causing widespread damage and displacement.
- 💧 Cyclones bring not only strong winds but also torrential rain, which can lead to flooding and disrupt infrastructure.
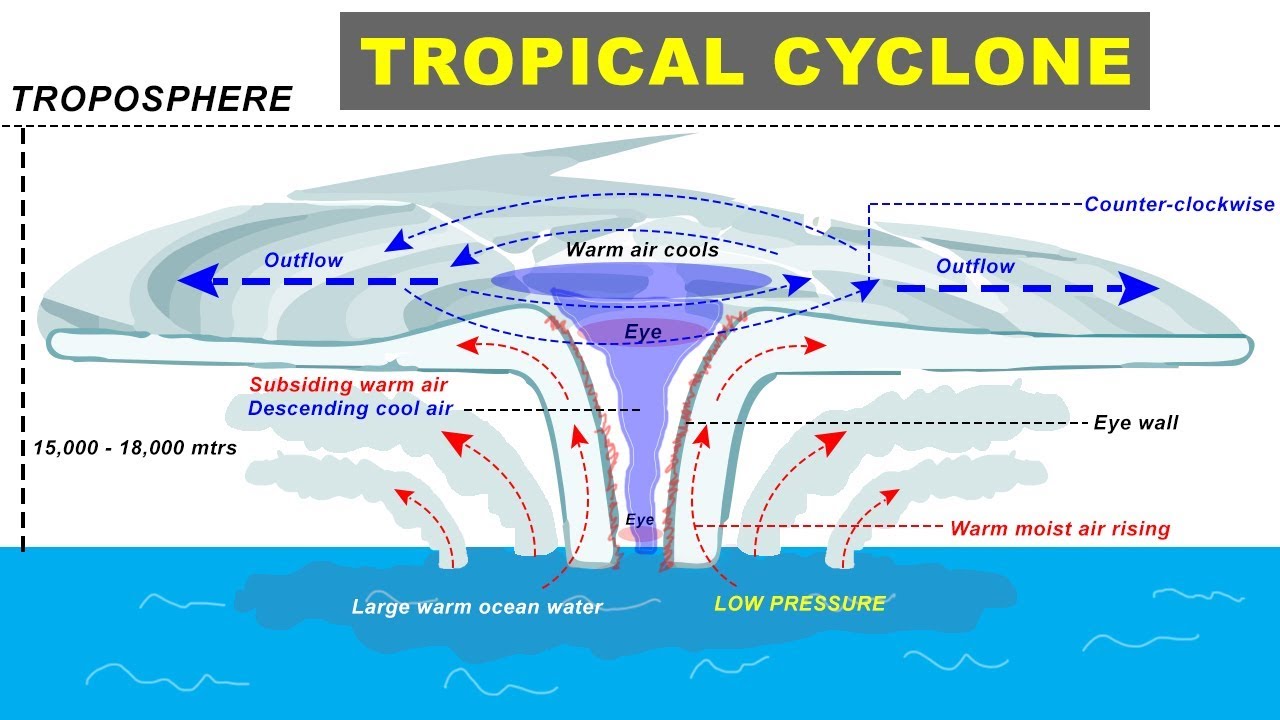
- 🌍 The formation of cyclones is influenced by several factors including warm ocean temperatures, atmospheric pressure, and the Coriolis effect.
- 🔁 The process of cyclone formation involves three stages: the initial formation, the intensification where the cyclone gathers moisture and strengthens, and the dissipation stage where it loses energy and eventually fades.
- 🌡️ Warm ocean surface temperatures play a crucial role in cyclone formation, as they provide the necessary heat energy to fuel the system.
- 🌪️ Cyclones are categorized into two main types: Tropical Cyclones, which form near the equator, and Extratropical Cyclones, which form at mid to high latitudes.
- 🌎 In the Indian Ocean region, all cyclones are referred to as tropical cyclones, while in other regions like the Caribbean, they are known as hurricanes.
- ⏱️ The life cycle of a cyclone involves the development of a low-pressure system over warm waters, the organization of thunderstorms, and the eventual dissipation as it moves over land or cooler waters.
- 🌤️ The消散 of a cyclone is marked by the central eye filling in with clouds and the decrease in wind speed as it moves over land or loses its heat source.
Q & A
What is a cyclone, and how is it formed?
-A cyclone is a rotating, organized system of clouds and thunderstorms that forms over large water bodies, typically oceans. It is created due to low atmospheric pressure, high temperatures (above 27°C), and the Coriolis force. These conditions lead to the rise of warm, moist air, which forms the cyclone's structure.
What are the key conditions necessary for cyclone formation?
-Three main conditions are necessary for cyclone formation: (1) a large water body like an ocean, (2) water temperatures above 27°C to create a low-pressure zone, and (3) the presence of the Coriolis force, which helps initiate the cyclone's circular movement.
How do cyclones impact coastal regions?
-Cyclones bring heavy rainfall, strong winds, and can cause widespread destruction in coastal areas. They lead to flooding, displacement of people, and damage to infrastructure. For instance, Cyclone Tauktae in 2021 displaced over 200,000 people and caused significant destruction in Gujarat, India.
What is the difference between a cyclone and an anticyclone?
-A cyclone is a system of low-pressure winds that rotate counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere. In contrast, an anticyclone is a high-pressure system where winds move in the opposite direction, causing more stable weather conditions.
How does the Coriolis force influence cyclones?
-The Coriolis force, generated by the Earth's rotation, deflects the path of moving air. In the Northern Hemisphere, it causes cyclone winds to rotate counterclockwise, while in the Southern Hemisphere, they rotate clockwise.
What are the stages of cyclone development?
-Cyclones develop in three stages: (1) Formation Stage – where warm air rises from the ocean surface, (2) Mature Stage – the cyclone grows in size and gathers moisture, and (3) Dissipation Stage – the cyclone loses energy and dissipates as it releases moisture as rainfall.
What are tropical cyclones, and where do they typically occur?
-Tropical cyclones form in the tropical regions between 0° to 30° latitude, in both hemispheres. They require warm ocean temperatures and are commonly seen in regions like the Indian Ocean, Southeast Asia, and the Caribbean.
What distinguishes tropical cyclones from temperate cyclones?
-Tropical cyclones form in low-latitude regions (0° to 30°) and are fueled by warm ocean waters. Temperate cyclones, also known as extratropical cyclones, form in higher latitudes (30° to 65°) and are driven by temperature differences rather than ocean heat.
How do cyclones differ in naming across regions?
-Cyclones are named differently based on their location. For instance, in the Indian Ocean, they are called 'cyclones,' in the Pacific region they are referred to as 'typhoons,' and in the Caribbean and the United States, they are known as 'hurricanes.'
Why is the eastern coast of India more prone to cyclones than the western coast?
-The eastern coast of India is more vulnerable to cyclones due to its geographical position facing the Bay of Bengal, where cyclones tend to form more frequently. The western coast, while not immune, faces fewer cyclones.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Siklon Tropis

Typhoon | Grade 8 Science DepEd MELC Quarter 2 Module 3

HAZARDS CAUSED BY HYDROMETEOROLOGICAL PHENOMENA / EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE / SCIENCE 11 - MELC 18

Explained | How are Cyclones formed | Hurricanes and Cyclones | Curious DNA
Tropical Cyclone, Hurricane, Storm Formation explained | Cyclone Biparjay in Arabian Sea, Gujarat

Geography of South Asia: Physical Characteristics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)