What is Biochemistry? What do Biochemists study? 🦋 Biology
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces biochemistry as the study of life at the molecular level, highlighting the importance of carbon-based molecules in biological systems. It explains the structural hierarchy from atoms to multicellular organisms, and focuses on the key biological molecules—proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. Emphasizing the crucial role of 3D structures in determining the functions of these molecules, the video also touches on their interactions in processes like enzyme activity, DNA replication, and cellular functions. Overall, it presents biochemistry as the foundation of life itself.
Takeaways
- 😀 Biochemistry is the study of the molecules of life and their emergent properties that lead to biological function.
- 😀 Atoms like Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur (CHNOPS) make up 98% of living matter.
- 😀 Biological molecules form when atoms interact, creating bonds and chemical behavior.
- 😀 There are four main types of biological molecules: Proteins, Carbohydrates, Lipids, and Nucleic Acids.
- 😀 Proteins are polymers of amino acids that fold into 3D shapes to perform essential biological functions.
- 😀 The 3D structure of a biological molecule determines its function, similar to how a key fits a lock.
- 😀 Carbohydrates are sugars and polymers of sugars used for energy and building biological structures.
- 😀 Lipids, like fats and oils, are nonpolar molecules important for energy storage, cushioning, and cellular membranes.
- 😀 Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) store genetic information and are crucial for genetic processes.
- 😀 All biological molecules are carbon-based, with carbon atoms forming stable skeletons, and functional groups modifying their behavior.
- 😀 Biochemistry enables the understanding of complex cellular processes and interactions that sustain life.
Q & A
What is biochemistry and how does it relate to the chemistry of life?
-Biochemistry is the study of the molecules that make up living organisms and how these molecules interact to form life. While chemistry focuses on atoms and molecules in a lab setting, biochemistry explores how these interactions create living systems with emergent properties that cannot be predicted by individual molecules alone.
What are emergent properties in biochemistry?
-Emergent properties refer to new and unexpected characteristics that arise when biological molecules interact. These properties cannot be predicted by simply studying individual molecules in isolation. For example, when molecules combine to form complex structures like cells, the resulting behavior and functions are more than the sum of their parts.
What is the structural hierarchy in biology?
-The structural hierarchy in biology starts at the atomic level and progresses through molecules, cells, tissues, and organs. Ultimately, these structures work together to form a multicellular organism capable of complex processes like metabolism and reproduction.
What elements make up 98% of living matter on Earth?
-The elements that make up 98% of living matter on Earth are Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Nitrogen (N), Oxygen (O), Phosphorus (P), and Sulfur (S), collectively known as CHNOPS.
How do atoms form biological molecules?
-Atoms form biological molecules through chemical bonds, where they interact by sharing, gaining, or losing electrons. These interactions result in the creation of molecules such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids, which are essential for life processes.
Why is the 3D structure of biological molecules important?
-The 3D structure of biological molecules is crucial because it determines their function. Just like how a key must fit into a lock, the shape of a molecule allows it to perform its specific role in biological processes. For example, the 3D shape of a protein determines whether it can act as an enzyme, structural component, or signaling molecule.
What are the four main types of biological molecules?
-The four main types of biological molecules are: 1) Proteins, which are made of amino acids and carry out many functions, including catalysis and immune defense; 2) Carbohydrates, which provide energy and structural support; 3) Lipids, which are involved in energy storage and form the cell membrane; and 4) Nucleic acids, which store genetic information, such as DNA and RNA.
How do functional groups influence biological molecules?
-Functional groups are small chemical species, like hydroxyl (OH) or methyl (CH3), that attach to the carbon backbone of molecules. These groups participate in chemical reactions, affecting the molecule's reactivity and function, and play a role in determining the molecule's overall behavior in living systems.
What is the role of enzymes in biochemistry?
-Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions. They control the rates of biochemical reactions within cells, ensuring that processes like metabolism, DNA replication, and protein synthesis occur at the right pace and under appropriate conditions.
How do biochemistry and life processes connect?
-Biochemistry is the foundation of all life processes. The interactions between biological molecules, such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids, enable essential functions like energy production, cell division, and genetic inheritance. These molecular interactions are what allow life to sustain and reproduce.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Fundamentos Básicos de Sistemas Biológicos (Aula 1, parte 1)
BIOCHEMISTRY MODULE 1_Introduction to Biochemistry
Introduction to Pharmacology
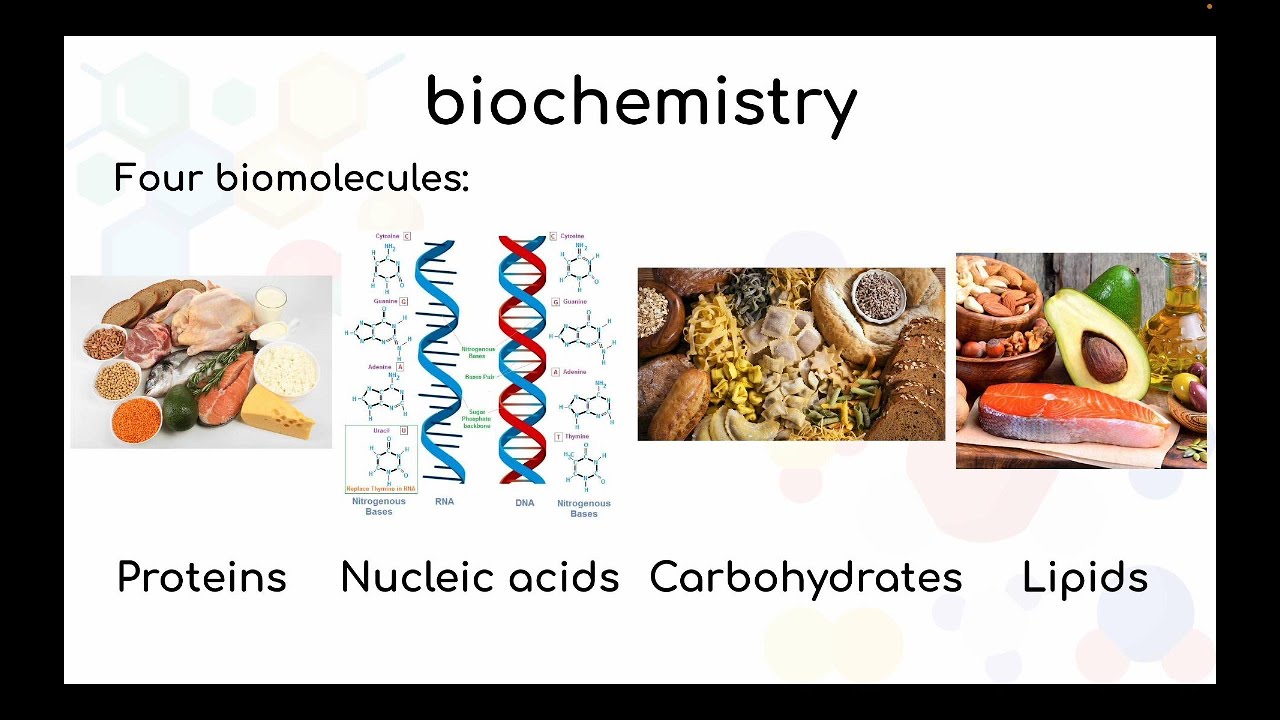
Introduction to Biochemistry: Definition, Scope, History, and Key Biomolecules

Biochemistry Water, PH and Buffers Part 1 tutorial

INTRODUÇÃO À BIOQUÍMICA - Bioquímica | Biologia com Samuel Cunha
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
