How to Use an Oscilloscope
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive guide to using an oscilloscope, a key tool for analyzing electrical circuits. It covers the oscilloscope’s functions, including how to measure amplitude, frequency, and transient signals. The tutorial explains the setup process, including the use of 10x probes, adjusting settings like vertical and horizontal scales, and configuring triggers for accurate measurements. The video also highlights how to capture and save waveform data, while offering purchasing tips based on essential oscilloscope specifications like bandwidth, rise time, and sample rate. Ideal for beginners, the guide simplifies complex concepts to help users get started with oscilloscope measurements.
Takeaways
- 😀 Oscilloscopes are vital tools for analyzing and debugging electrical circuits by visualizing waveforms and measuring signal parameters like amplitude, frequency, and transients that a multimeter cannot capture.
- 😀 Modern digital oscilloscopes use an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) to sample signals and display waveforms, unlike older cathode ray models that used an electron beam.
- 😀 Probes come in various types, with the most common being passive voltage probes, which measure the voltage difference between the ground clip and probe tip.
- 😀 The 10x probe setting reduces the signal by a factor of 10, minimizing the effect of the probe on high-frequency circuits. Always use this setting for accurate measurement.
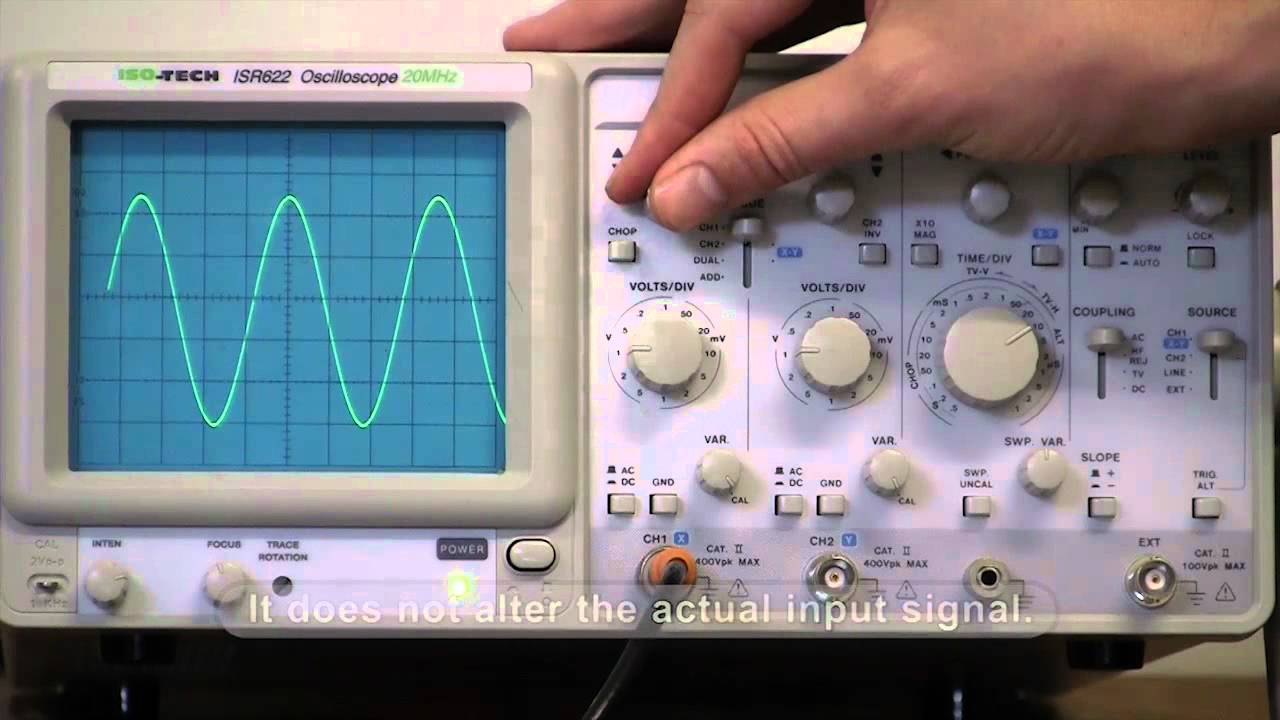
- 😀 The oscilloscope's vertical controls adjust the voltage scale for each channel, while horizontal controls manage the time scale for both channels simultaneously.
- 😀 The trigger section of the oscilloscope determines when to start measuring, essential for stabilizing signals and ensuring consistent waveform capture.
- 😀 To achieve clear measurements, you should adjust the oscilloscope's vertical and horizontal scales, as well as the trigger level, to stabilize periodic waveforms.
- 😀 For non-periodic signals or quick events, use the oscilloscope's single sweep mode, which captures just one cycle of a signal upon detecting a rising or falling edge.
- 😀 Many oscilloscopes offer automatic measurements like peak-to-peak voltage, frequency, and time intervals, but manual measurements with cursors can be used for more precision.
- 😀 Key oscilloscope specifications to consider when purchasing include bandwidth (at least five times the signal frequency), rise time, sampling rate, and resolution to ensure accurate measurements.
- 😀 USB oscilloscopes are a cost-effective alternative to traditional models, offering portability and sufficient performance for most basic measurement tasks.
Q & A
What is the primary function of an oscilloscope?
-An oscilloscope is used to analyze and debug electrical circuits by displaying real-time waveforms of electrical signals, allowing you to measure parameters like amplitude, frequency, and transient signals.
What is the difference between an analog and a digital oscilloscope?
-In an analog oscilloscope, the signal deflects an electron beam across a phosphorescent screen, whereas in a digital oscilloscope, the signal is sampled by an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) and displayed as a waveform on a screen.
What do the '1X' and '10X' settings on oscilloscope probes mean?
-'1X' means the probe directly measures the signal without attenuation, whereas '10X' reduces the signal by a factor of 10 to minimize the probe's impact on the circuit, especially at higher frequencies.
Why should you calibrate the probe using the compensation screw?
-Calibration is essential to ensure accurate waveform measurements. The compensation screw adjusts the internal capacitor of the probe, which helps eliminate distortion or errors in the waveform, especially for high-frequency signals.
What does the 'DC coupling' setting on an oscilloscope do?
-The 'DC coupling' setting allows the oscilloscope to measure both AC and DC components of the signal, displaying the entire waveform, including any DC offset.
How does the trigger section of the oscilloscope help stabilize waveforms?
-The trigger section controls when the oscilloscope starts measuring, typically set to a specific part of the signal (like a rising edge). This prevents the waveform from jittering or moving erratically on the screen.
What should you do if the waveform appears unstable or jittery?
-If the waveform is unstable, adjust the trigger level to indicate when the oscilloscope should start measuring, ensuring it begins at a consistent point of the signal.
What is the importance of the oscilloscope’s bandwidth rating?
-The bandwidth rating indicates the maximum frequency the oscilloscope can measure accurately. It is recommended that the oscilloscope's bandwidth be at least five times higher than the frequency of the signal you're measuring for optimal accuracy.
How do you capture non-periodic signals with an oscilloscope?
-To capture non-periodic signals, set the oscilloscope to 'single sweep' mode. This allows the oscilloscope to capture one snapshot of the signal based on a trigger condition, rather than continuously refreshing the display.
What is the role of the sample rate in an oscilloscope’s performance?
-The sample rate determines how frequently the oscilloscope samples the signal per second. A higher sample rate is necessary to accurately display high-frequency signals and sharp transitions.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Percobaan Pengukuran Tegangan Listrik Dengan Osiloskop | Praktikum Fisika Dasar 2

Membaca Tegangan dan Frekuensi Sinyal Generator dengan Oscilloscope

Pengukuran Besaran Listrik - Oscilloscope
How to use an oscilloscope with an A/C source

More Essentials about Circuits

Belajar Cara Menggunakan Oscilloscope Digital | Cara Kalibrasi Oscilloscope Digital
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
