Membaca Tegangan dan Frekuensi Sinyal Generator dengan Oscilloscope
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial provides a detailed guide on how to use an oscilloscope to measure key electrical parameters such as voltage and frequency from a signal generator. The instructor demonstrates the process of setting up the oscilloscope to read peak voltage, peak-to-peak voltage, RMS voltage, and frequency, with clear examples and step-by-step instructions. The lesson also covers essential concepts such as calibration, adjusting oscilloscope settings, and performing calculations for accurate readings. Ideal for learners looking to understand and master oscilloscope measurements, this video emphasizes both theoretical knowledge and practical application.
Takeaways
- 😀 Understanding the oscilloscope and frequency generator setup is essential for accurately measuring voltage and frequency signals.
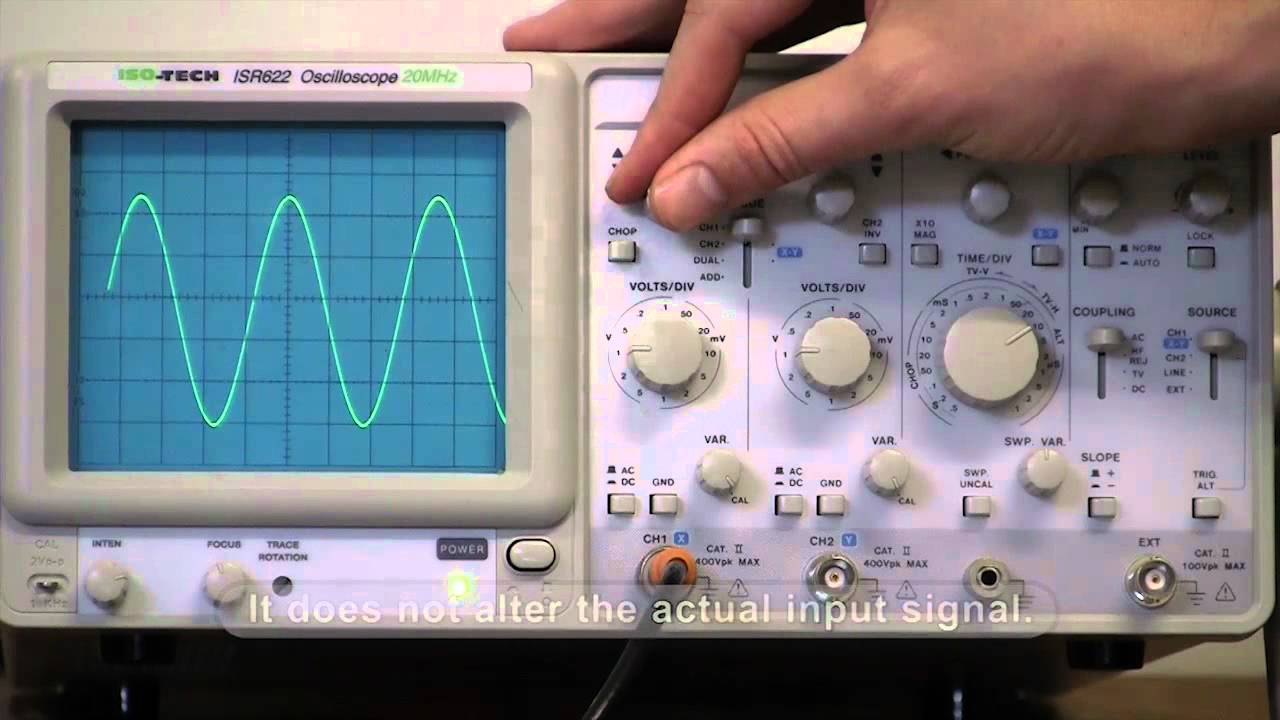
- 😀 The sine wave output from the frequency generator should be set to a peak-to-peak amplitude of 10V and a frequency of 50 Hz.
- 😀 The oscilloscope settings need to be adjusted to ensure proper voltage and time readings, including the voltage divisions (volts per division) and time divisions (seconds per division).
- 😀 To measure peak voltage, focus on the vertical scale and calculate the voltage from the center to the peak of the waveform.
- 😀 To measure peak-to-peak voltage, measure from the highest peak to the lowest trough, ensuring all peaks are accounted for.
- 😀 The RMS voltage is calculated by dividing the peak voltage by the square root of 2, providing a representation of the effective voltage of the waveform.
- 😀 When measuring the frequency, focus on the horizontal scale (time per division) to capture one full wave cycle without truncating it.
- 😀 The period is the time taken for one complete cycle of the wave, measured by counting the number of divisions across one full cycle on the oscilloscope screen.
- 😀 The frequency is the reciprocal of the period, calculated as 1 divided by the period in seconds.
- 😀 It’s important to adjust the oscilloscope’s time divisions (timer setting) to display one complete waveform accurately, ensuring reliable frequency measurements.
- 😀 Practicing with different waveforms and settings on the oscilloscope will help improve measurement accuracy and confidence in signal analysis.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of the frequency generator in the context of this lesson?
-The frequency generator is used to create electrical signals with a specified frequency and amplitude, which can then be measured and analyzed using the oscilloscope.
How do you set the amplitude of the frequency generator in this lesson?
-The amplitude is set by adjusting the frequency generator's voltage level. In the example, the amplitude is set to 10 volts peak-to-peak, which is achieved by selecting the appropriate voltage setting on the generator.
What is the significance of the vertical direction (Volts/Div) setting on the oscilloscope?
-The vertical direction (Volts/Div) on the oscilloscope is used to adjust the scale for measuring the voltage of the signal. This setting determines how much voltage each division on the oscilloscope screen represents.
Why is it necessary to adjust the oscilloscope's time/div setting?
-The time/div setting controls the horizontal scale, allowing you to adjust the time span shown on the oscilloscope's screen. This ensures that a full waveform can be observed clearly and accurately, which is crucial for measuring the period and frequency.
What does RMS voltage represent, and how is it calculated in this lesson?
-RMS (Root Mean Square) voltage is a way of representing the effective value of a fluctuating voltage. It is calculated by dividing the peak voltage by the square root of 2. In the example, the RMS voltage is calculated as 5V ÷ √2, which equals approximately 3.6V.
How do you calculate peak-to-peak voltage from the oscilloscope reading?
-Peak-to-peak voltage is calculated by measuring the vertical distance from the positive peak to the negative peak on the oscilloscope screen. In the example, the total vertical distance is 10 divisions, each representing 1 volt, so the peak-to-peak voltage is 10V.
What is the method for determining the frequency of the signal on the oscilloscope?
-The frequency is determined by measuring the period of one full waveform (from one peak to the next) and calculating the inverse of the period. For example, if one period takes 20 milliseconds, the frequency is 50 Hz (1 ÷ 20ms = 50Hz).
What role does the horizontal direction (Time/Div) play in measuring the signal on the oscilloscope?
-The horizontal direction (Time/Div) adjusts the time scale, allowing you to capture one complete cycle of the waveform on the oscilloscope screen. This is essential for accurately measuring the signal's period and frequency.
How do you measure the peak voltage using the oscilloscope?
-The peak voltage is measured by counting the number of vertical divisions from the baseline (neutral point) to the positive peak of the signal. In the example, the peak voltage is calculated as 5 divisions, with each division representing 1 volt, so the peak voltage is 5V.
Why is it important to calibrate the frequency generator and oscilloscope?
-Calibration ensures that both the frequency generator and oscilloscope provide accurate and reliable measurements. It helps in setting precise values for frequency, amplitude, and time, which are crucial for correct signal analysis.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Petunjuk Penggunaan Osiloskop Analog

How to Read an Oscilloscope - GCSE and A Level Physics

Membaca dan Mengukur dengan Osiloskop
How to use an oscilloscope with an A/C source

Manejo de Equipos de Laboratorio de Electrónica Pt. 6 (Generador de Funciones y Osciloscopio)

Pengukuran Besaran Listrik - Oscilloscope
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)