DNA Ligation
Summary
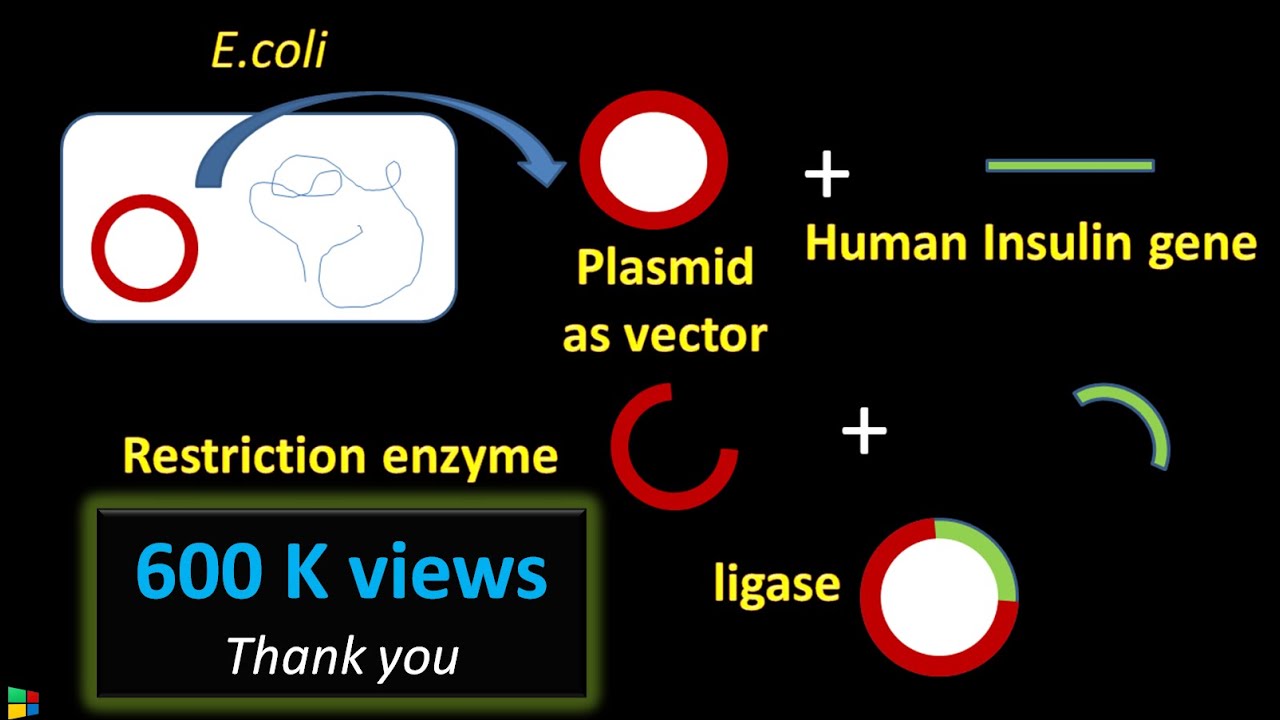
TLDRDNA ligation is a crucial step in molecular cloning, where DNA ligase forms a covalent bond between adjacent DNA fragments, such as a vector and a gene of interest. This process involves three key steps: ligase self-adenylation with ATP or NAD, transfer of the adenyl group to the donor strand, and the formation of a phosphodiester bond between the donor and acceptor strands, releasing AMP. T4 DNA ligase is the most commonly used enzyme, though there are various ligases from NEB suited to different applications. For selection guidance, users can visit NEBStickTogether.com and CloneWithNEB.com.
Takeaways
- 😀 DNA ligation is the process of forming a covalent bond between adjacent DNA fragments, often between a vector and a gene of interest.
- 😀 Ligation is typically the final step before transformation in the DNA cloning workflow.
- 😀 DNA ligase is used to join double-stranded DNA fragments with either blunt or cohesive ends, creating recombinant DNA plasmids.
- 😀 A DNA ligase catalyzes the formation of a phosphodiester bond between the five prime phosphate and three prime hydroxyl termini in duplex DNA.
- 😀 Ligation occurs in three steps: adenylation of ligase, transfer of the adenyl group to the donor strand, and phosphodiester bond formation with the release of AMP.
- 😀 The first step of ligation involves the ligase self-adenylating by reacting with free ATP or NAD.
- 😀 The second step is the transfer of the adenyl group to the five prime phosphorylated end of the donor strand.
- 😀 In the final step, the adenylated donor end forms a phosphodiester bond with the adjacent three prime hydroxyl acceptor, releasing AMP.
- 😀 T4 DNA ligase is the most commonly used ligase for cloning applications.
- 😀 NEB offers a range of DNA ligases, including master mix formats for convenience and easy application.
- 😀 For assistance in selecting the appropriate DNA ligase for specific ends and applications, refer to the NEB selection chart at NEBStickTogether.com.
Q & A
What is DNA ligation?
-DNA ligation is the process of forming a covalent bond between adjacent DNA fragments, typically a vector and a gene of interest, in molecular cloning.
Why is DNA ligation important in cloning?
-DNA ligation is a critical step in cloning as it connects the DNA fragments, creating recombinant DNA that can then be introduced into a host organism for further analysis or expression.
What is the role of DNA ligase in DNA ligation?
-DNA ligase catalyzes the formation of a phosphodiester bond between the 5' phosphate and 3' hydroxyl termini of adjacent DNA fragments, enabling their ligation into a stable recombinant molecule.
How does DNA ligase work in three steps?
-1) The ligase is adenylated by ATP or NAD. 2) The adenyl group is transferred to the 5' phosphorylated end of the donor strand. 3) The adenylated donor end reacts with the adjacent 3' hydroxyl acceptor to form the phosphodiester bond, releasing AMP.
What are cohesive and blunt ends in DNA ligation?
-Cohesive ends have single-stranded overhangs that can easily pair with complementary sequences, while blunt ends are directly adjacent, requiring ligation without overhangs.
Why is T4 DNA ligase commonly used for cloning?
-T4 DNA ligase is widely used because of its ability to efficiently ligate both cohesive and blunt-ended DNA fragments, making it versatile for a variety of cloning applications.
What other DNA ligases are available from NEB?
-NEB offers several DNA ligases, including those in convenient master mix formats, optimized for different end types and cloning applications.
How does the adenylation of DNA ligase facilitate ligation?
-Adenylation of the DNA ligase activates it, allowing it to transfer the adenyl group to the 5' phosphorylated end of the donor DNA, initiating the ligation process.
What is the significance of AMP release during DNA ligation?
-The release of AMP signifies the completion of the ligation reaction, as the phosphodiester bond is formed between the donor and acceptor DNA fragments.
Where can I find more information about NEB products for DNA ligation?
-For more details on NEB's DNA ligase products and other cloning tools, visit their website at CloneWithNEB.com.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)