TESOL/TEFL training: Teaching a Grammatical Structure
Summary
TLDRThis video script presents a lesson on teaching the second conditional in English, focusing on hypothetical or unreal situations. The teacher introduces the structure through a story about John, who dreams of being rich and buying luxuries like a car. Students practice forming sentences such as 'If he was rich, he would buy a car.' The lesson covers both positive and negative forms of the second conditional and emphasizes its use for expressing dreams or unlikely scenarios. Students then engage in interactive activities, including sentence rearranging and discussing hypothetical situations in groups, to reinforce their understanding of the structure.
Takeaways
- 😀 The lesson focuses on teaching the second conditional to students through a revision session.
- 😀 The structure being taught expresses unreal or unlikely situations, often referring to dreams or hypothetical scenarios.
- 😀 The teacher uses a scenario involving a character, John, to illustrate the structure: 'If he was rich, he would buy a car.'
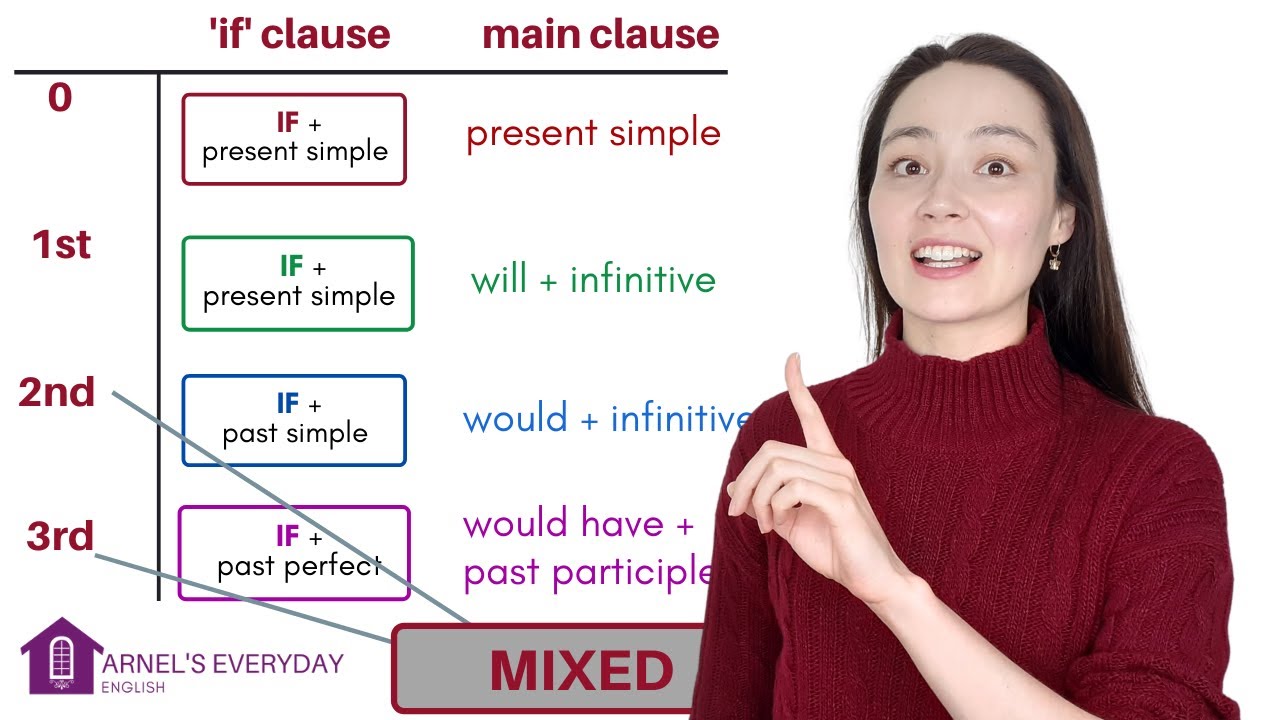
- 😀 The sentence structure follows the pattern: 'If + past tense, + would + base verb.'
- 😀 Students practice the structure by repeating sentences as a class and individually, reinforcing pronunciation and understanding.
- 😀 The lesson emphasizes the use of picture prompts to generate examples and stimulate conversation.
- 😀 The second conditional structure is explained as representing unreal situations, such as dreams or wishes.
- 😀 The teacher introduces a negative form, using the example: 'If she was rich, she wouldn't buy a car.'
- 😀 The class is encouraged to identify whether the situations are real or unreal, reinforcing their understanding of conditional forms.
- 😀 The second conditional is explicitly named and defined as the 'second conditional,' used for expressing unreal or unlikely situations.
- 😀 Students are tasked with a group activity involving mixed-up conditional sentences, encouraging collaboration and application of the learned structure.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the lesson in the transcript?
-The main focus of the lesson is teaching the second conditional structure, which is used to discuss unreal or unlikely situations, such as hypothetical scenarios or dreams.
How does the teacher introduce the second conditional to the students?
-The teacher introduces the second conditional by using the example of a man named John who dreams of being rich. The structure is modeled with sentences like 'If he were rich, he would buy a car.'
What activities are used to help students practice the second conditional?
-The activities include sentence repetition as a class and individually, reordering mixed-up sentences, and group discussions about hypothetical scenarios.
What is the key grammatical structure being taught in the lesson?
-The key grammatical structure is the second conditional, formed by 'if + past simple, would + base verb.' For example, 'If I were rich, I would buy a car.'
Why does the teacher use a lottery ticket as a visual aid?
-The teacher uses the lottery ticket as a visual aid to prompt discussion about what would happen if someone won the lottery, setting up a context to practice the second conditional.
What is the purpose of the controlled practice in the lesson?
-The controlled practice helps students practice forming correct second conditional sentences by rearranging mixed-up sentences, reinforcing both the structure and meaning of the grammar.
How does the teacher help students practice both positive and negative forms of the second conditional?
-The teacher provides examples of both positive and negative forms, such as 'If he were rich, he would buy a car' (positive) and 'If she were rich, she wouldn’t buy a car' (negative), and encourages students to repeat them.
What type of questions are used in the free practice section?
-In the free practice section, students are asked open-ended hypothetical questions such as 'What would you do if you were rich?' and 'What would you do if you found your boyfriend’s diary left open?'
How does the teacher explain the unreal or unlikely nature of second conditional sentences?
-The teacher explains that second conditional sentences express unreal, unlikely, or dream situations. For example, winning the lottery and becoming rich is an unlikely or hypothetical situation.
What are students asked to do during the group discussion activity?
-During the group discussion activity, students are asked to compare their answers about what they would do in hypothetical situations, such as what they would buy if they were rich or what they would do if they saw a partner’s diary.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Grade 9 English Q1 Ep7: Second Conditional

Episode 47 • Pro Business English With Second & Third Conditional • The Business English Podcast

Conditional Sentence type 0, 1, 2, 3

Grade 9 English Q1 Ep8: Third Conditional

Conditionals in English | Daily English Conversation
ALL CONDITIONALS | 0,1,2,3 and MIXED CONDITIONALS - English Grammar | if....
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
