1.4 Classification of latices
Summary
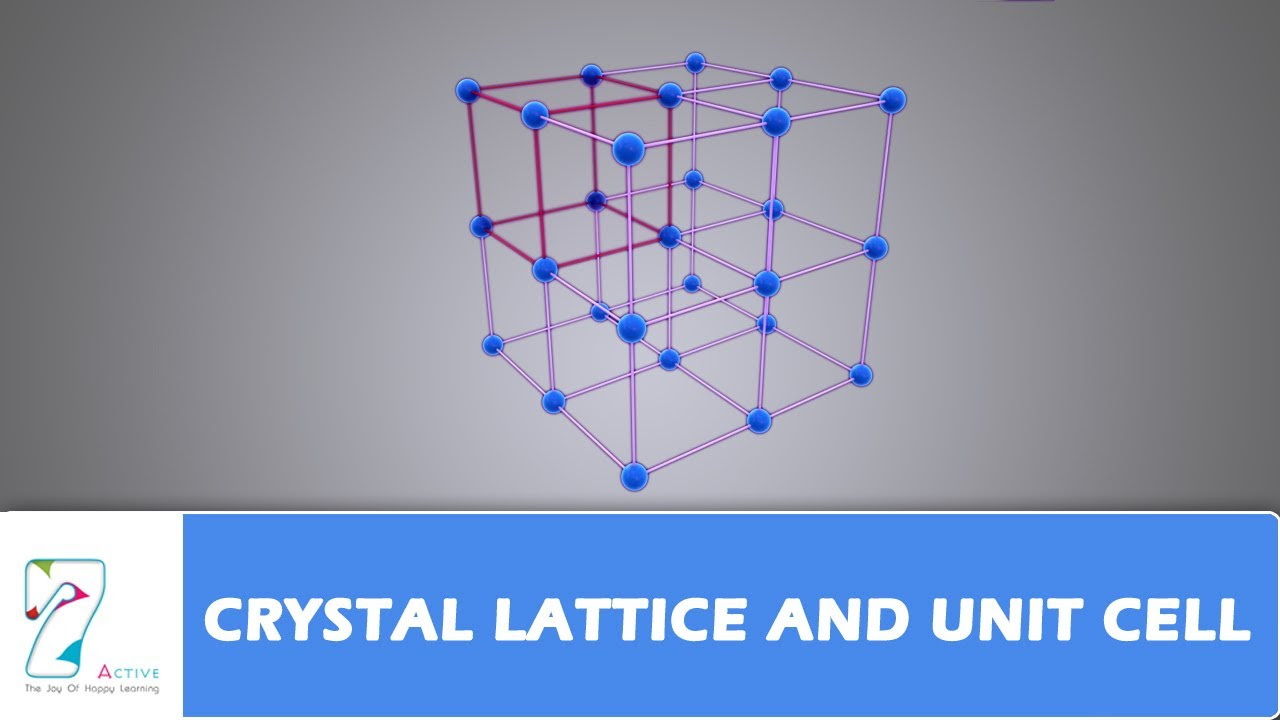
TLDRThis video explores the classification of crystal lattices, highlighting the seven crystal systems and the fourteen Bravais lattices. It details the characteristics of each system, such as cubic, tetragonal, and orthorhombic, and their respective unit cells. The video emphasizes the arrangement of lattice points, explaining terms like primitive, body-centered, face-centered, and end-centered lattices. It concludes by discussing the absence of certain expected lattices, setting the stage for further exploration in the next installment.
Takeaways
- 🔍 Lattices are defined as periodic arrangements of points in three-dimensional space, characterized by their axes and angles.
- 📏 There are seven crystal systems: cubic, tetragonal, orthorhombic, hexagonal, trigonal, monoclinic, and triclinic.
- 🧊 Each crystal system has a conventional unit cell that describes the geometry and symmetry of the lattice.
- ⚙️ Bravais lattices provide a more detailed classification within the crystal systems, with a total of fourteen types recognized.
- 🏗️ The 'p' or primitive/simple lattice has lattice points only at the corners of the unit cell.
- 🏢 The 'i' or body-centered lattice includes points at the corners and one additional point in the center of the unit cell.
- 🏠 The 'f' or face-centered lattice includes points at the corners and the centers of all faces of the unit cell.
- ⚖️ The 'c' or end-centered/base-centered lattice has points at corners and centers of only one pair of parallel faces.
- ❓ Edge-centered lattices do not exist because the points in this arrangement do not have equivalent surroundings.
- 🔄 The absence of certain potential Bravais lattices, such as cubic 'c' and tetragonal 'c', raises questions that will be explored in further discussions.
Q & A
What is a crystal defined as in the video?
-A crystal is defined as a periodic arrangement of atoms, represented by a lattice, which is a set of points arranged periodically in space.
What are the seven crystal systems mentioned in the video?
-The seven crystal systems are cubic, tetragonal, orthorhombic, hexagonal, trigonal (rhombohedral), monoclinic, and triclinic.
What is the significance of a unit cell in crystal systems?
-The unit cell is the smallest repeating unit that defines the structure of the crystal, with specific dimensions and angles that characterize each crystal system.
How are Bravais lattices classified?
-Bravais lattices are classified based on their lattice points, with types including primitive (P), body-centered (I), face-centered (F), and end-centered (C).
What distinguishes the body-centered cubic lattice from the simple cubic lattice?
-In the body-centered cubic lattice, there is an additional lattice point at the center of the cube, in addition to the corner points present in the simple cubic lattice.
Why are there only fourteen recognized Bravais lattices despite the potential for more?
-Only fourteen Bravais lattices are recognized due to the requirement of translational symmetry, meaning that points must be equivalent under translation, which is not the case for some configurations like edge-centered lattices.
What are the properties of the face-centered cubic lattice?
-The face-centered cubic lattice has lattice points at each corner of the cube and at the center of each face, leading to a denser packing of points compared to simple cubic lattices.
What is meant by 'primitive' in the context of Bravais lattices?
-Primitive refers to a lattice where lattice points are located only at the corners of the unit cell, with no additional points within the cell.
Can you explain what is meant by the term 'end-centered' lattice?
-An end-centered lattice has lattice points at the corners and at the centers of one pair of parallel faces, distinguishing it from face-centered lattices which have points on all faces.
What will be discussed in the next video according to the transcript?
-The next video will address why certain potential lattices, such as cubic C and tetragonal C, are absent from the list of recognized Bravais lattices.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
CRYSTAL LATTICE AND UNIT CELL

2A Conceitos básicos de simetria e cristalografia

56. Типы химических связей. Ковалентная связь

noc19-cy16 Lecture 06-Solid state Chemistry-Week 2 Lecture-1 Unit Cell

Solids, Its Properties, and the Intermolecular Forces | Crystalline Solids and Amorphous Solids

Aula 10 – Estruturas Cristalinas Cúbicas de Face Centrada, Corpo Centrado e Hexagonal Compacta.
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
