The Ingenious Design of Strain Gauges
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the fascinating world of strain gauges, essential devices in engineering that measure deformation under load to ensure structural integrity. By understanding strain as the change in length relative to original length, the video explains how electrical resistance strain gauges operate through changes in resistance when bonded to surfaces. It covers the importance of gauge factor, temperature compensation, and the use of rosettes for comprehensive strain measurement. The video highlights practical applications in load cells and emphasizes the significance of these tools in various engineering fields, providing a comprehensive overview of their functionality and importance.
Takeaways
- 📏 Strain gauges are essential tools for measuring how objects deform under loading, crucial for the integrity of structures and mechanical systems.
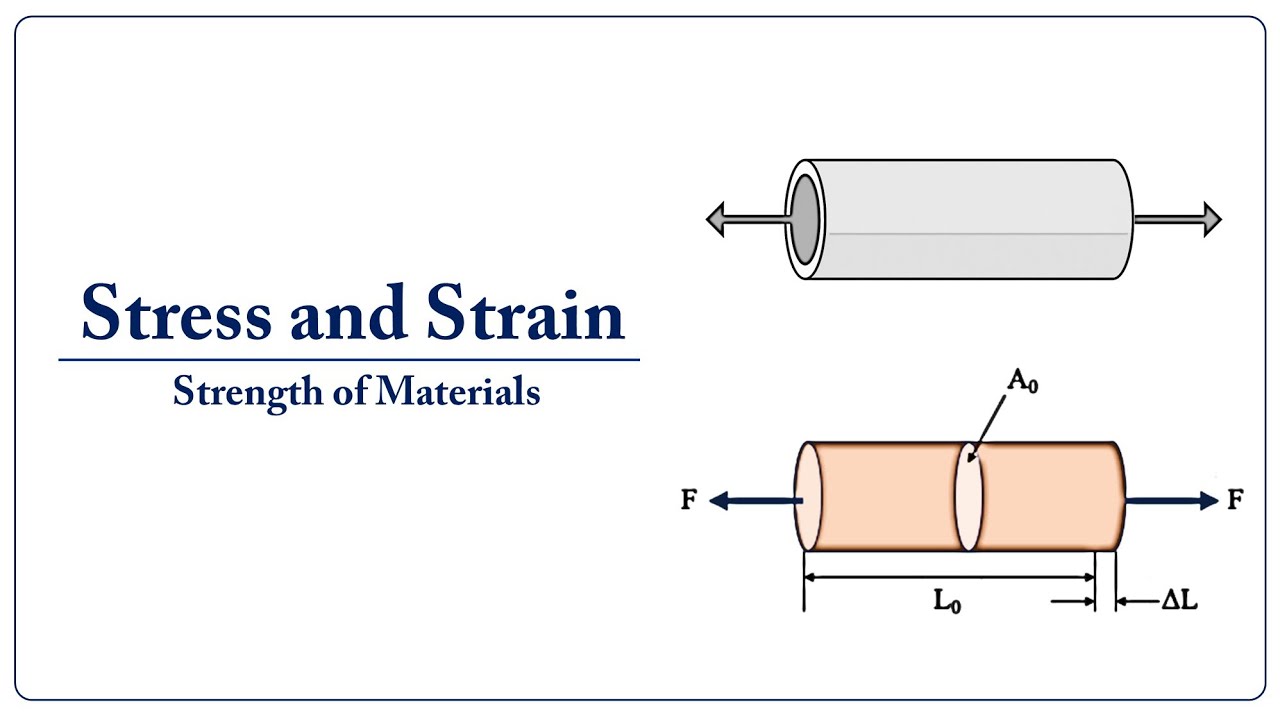
- 🔍 Strain is defined as the change in length (Delta-L) divided by the original length (L) of an object.
- ⚡ The most common strain gauge design is the electrical resistance strain gauge, which measures changes in electrical resistance as an object deforms.
- 🧪 Strain gauges consist of a conductive foil grid bonded to an insulating plastic film, designed to maximize sensitivity while minimizing errors from transverse loads.
- 📈 The sensitivity of strain gauges is defined by the Gauge Factor (K), representing the relative change in resistance per unit strain.
- 🌡️ Constantan is the most popular material for strain gauges due to its stable gauge factor across a wide temperature range, making it reliable for accurate measurements.
- 🛠️ Wheatstone bridges are used to measure very small changes in resistance in strain gauges, allowing for precise strain calculations.
- 🌡️ Temperature compensation is important to avoid measurement errors caused by differential thermal expansion between the strain gauge and the test material.
- 📏 Strain gauges can only measure normal strain in one direction, so multiple gauges (strain gauge rosettes) are often used to capture full strain information at a point.
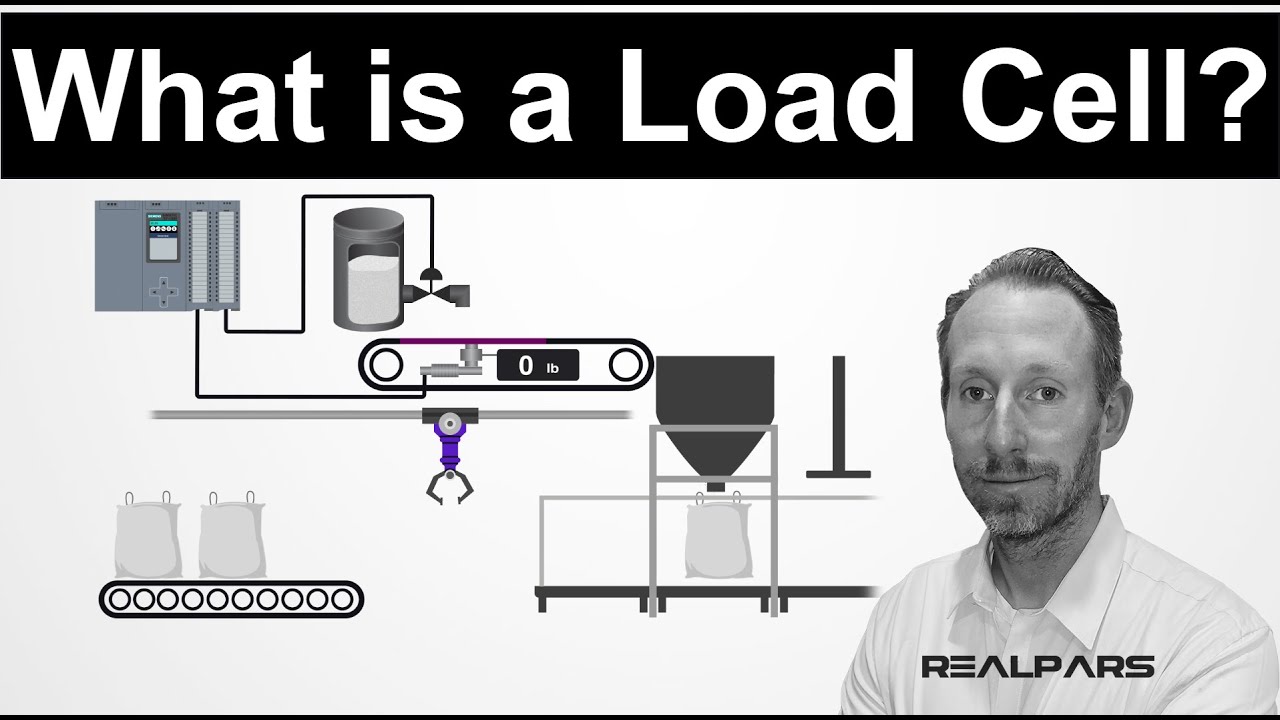
- ⚖️ Strain gauges have various applications, including in load cells, which accurately measure forces and are used in diverse engineering fields.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of a strain gauge?
-The primary purpose of a strain gauge is to measure the strain on the surface of an object, helping engineers monitor the structural integrity of materials and systems.
How is strain defined in the context of engineering?
-Strain is defined as the measure of deformation experienced by an object, calculated by dividing the change in length (Delta-L) by the original length (L) of the object.
What is the significance of the gauge factor in strain gauges?
-The gauge factor (K) represents the sensitivity of a strain gauge, defined as the relative change in resistance divided by the corresponding strain. A higher gauge factor indicates greater sensitivity to strain.
What are the three mechanisms that cause changes in electrical resistance of a strained conductor?
-The three mechanisms are: the reduction in the cross-sectional area of the conductor, the increase in length due to stretching, and changes to the resistivity of the material due to increased atomic spacing.
Why is Constantan commonly used as a material for strain gauges?
-Constantan is popular due to its moderate gauge factor, good corrosion resistance, excellent fatigue properties, and stable performance over a wide temperature range.
What is the Wheatstone bridge, and how does it relate to measuring strain?
-The Wheatstone bridge is an electrical circuit used to measure resistance changes in strain gauges. It allows for precise determination of resistance variations by balancing the circuit with known resistances.
What are the two main methods of temperature compensation for strain gauges?
-The two main methods are active compensation, which uses a dummy strain gauge to cancel out thermal expansion effects, and self-compensation, where the strain gauge is made from a material with a similar coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) to the test item.
What is a strain gauge rosette, and why is it used?
-A strain gauge rosette is a configuration of multiple strain gauges installed at specific angles to capture the strain state at a point. It allows for the measurement of normal strain in multiple directions, providing a complete understanding of the strain tensor.
How can Mohr's circle be used in conjunction with strain gauges?
-Mohr's circle is a graphical representation that allows engineers to visualize the strain state at a point. By plotting the normal strains from multiple gauges, it helps calculate principal strains and other critical strain characteristics.
What applications do load cells have in engineering?
-Load cells, which utilize strain gauges, are used to measure forces accurately in various applications, such as weighing products on assembly lines and measuring thrust in rocket engines.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)