How Fuel Oil Burners Work: Boilers and Their Operation - 1956 - CharlieDeanArchives
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the operation of boiler burners, detailing how they mix air and fuel oil for combustion. It highlights different types of burners, including mechanical atomizing and steam atomizing burners, and explains their functioning components, such as atomizers and forced draught blowers. The video emphasizes the importance of controlling fuel and air supply for optimal performance, demonstrating how adjustments to pump and blower speeds affect firing rates. Viewers are encouraged to consult official Navy publications for comprehensive information on various burner types used in naval applications.
Takeaways
- 🔥 Different types of burners, including mechanical and steam atomizers, play a crucial role in boiler operations.
- 💧 The atomizer reduces fuel oil to fine mist-like particles for efficient combustion.
- 🌬️ Forced draught blowers provide strong air blasts essential for mixing with atomized oil.
- ⚙️ Firing rates can be controlled by adjusting the flow of fuel oil and air supplied to the burner.
- 🔄 The sprayer plate atomizes oil, and its capacity may need to be changed based on firing rate requirements.
- 📏 Varying the speed of forced draught blowers is the primary method to control air supply to the burner.
- 🔄 In return flow burners, excess oil returns to the pump while only a portion is combusted.
- 🚀 Rotary cut burners utilize centrifugal force to mix oil with air for optimal atomization.
- 💨 Steam atomizing burners mix high-pressure steam with low-pressure oil for enhanced combustion efficiency.
- 📚 Official Navy publications provide detailed information on the types of burners used in ships.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the burners in a boiler?
-The primary function of the burners in a boiler is to provide a combustible mixture of air and fuel oil that is burned in the boiler furnace.
How do mechanical atomizing burners operate?
-Mechanical atomizing burners operate by atomizing fuel oil in different ways, typically using mechanical methods such as pressure atomization, rotary cup atomization, or steam atomization.
What role do forced draught blowers play in the burning process?
-Forced draught blowers send a strong blast of air to the burner, facilitating the mixing of air with the atomized fuel oil, which is essential for combustion.
How is fuel oil atomized in the burner?
-Fuel oil is atomized by being forced through an atomizer nozzle where it is broken down into fine mist-like particles by the sprayer plate, which creates a hollow cone of mist.
What is the function of the sprayer plate in a burner?
-The sprayer plate in a burner helps to atomize the oil by making it rotate at high speed, which breaks the oil into smaller particles that can be mixed with air for combustion.
How do you control the firing rate of a burner?
-The firing rate of a burner is controlled by varying the amount of fuel oil and air supplied to it, adjusting the pump pressure on the fuel oil lines and the speed of the forced draught blowers.
What happens to the oil that is not burned in the burner?
-The oil that is not burned in the burner returns to the fuel oil pump, allowing for recycling of the unused oil.
What are the types of mechanical atomizers mentioned in the script?
-The types of mechanical atomizers mentioned include pressure type atomizers, return flow pressure atomizers, and rotary cup atomizers.
What is the significance of maintaining constant pressure on the oil entering the burner?
-Maintaining constant pressure on the oil entering the burner ensures optimal atomization and consistent fuel delivery, which is critical for stable combustion.
What adjustments must be made when changing the firing rate of the burner?
-When changing the firing rate of the burner, corresponding adjustments must be made to both the fuel oil flow and the air supply to maintain the correct combustion mixture.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Boiler Control Systems
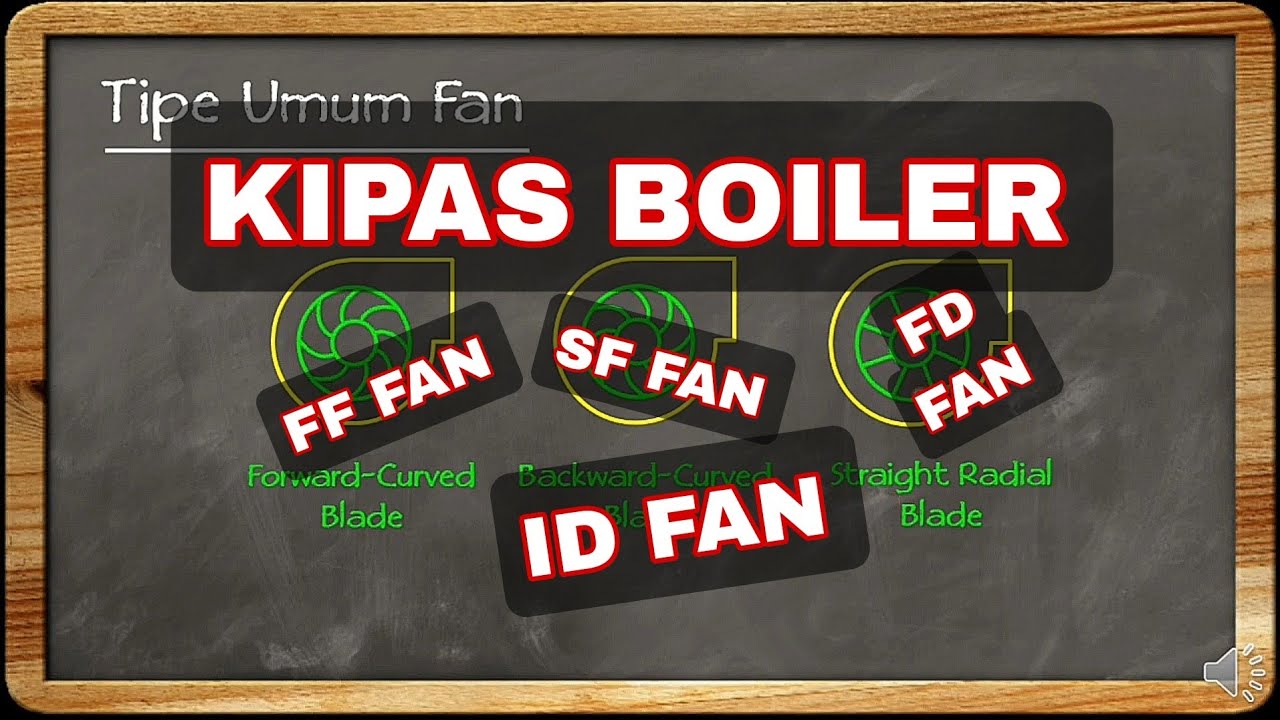
Boiler Fan #FAN #CENTRIFUGAL #BOILER #PABRIKSAWIT #OPERATOR #KIPASANGIN #PMKS #DRAFT #CONTROL #FIRE
Engine Fuel Systems Part 1 - Aircraft Gas Turbine Engines #19

Combustion Chambers Part 2 - Aircraft Gas Turbine Engines #09

Komponen dan Cara Kerja Sistem Bahan Bakar Bensin

Mengenal dan Belajar BOILER/Ketel uap
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
