Boiler Control Systems
Summary
TLDRThis transcript outlines the key components of boiler control systems, focusing on combustion control, burner management, and level control. It explains the objectives of combustion control systems, including regulating fuel oil and combustion air supply based on boiler load, as well as the importance of cascade control for stability. The burner management system is highlighted for its role in firing and shutting off burners in sequence. Additionally, the trip system is discussed for safety during emergencies, while the level control system ensures accurate measurement of water levels and feed water flow. Overall, it emphasizes the intricate balance required for optimal boiler operation.
Takeaways
- 🔥 The main objectives of combustion control systems include supplying fuel oil based on boiler load and managing air supply for optimal combustion.
- ⚙️ Cascade control systems enhance stability by using a master controller that processes steam pressure and flow signals to adjust air and fuel oil supply.
- 🔄 Slave controllers react to variations from the master controller, maintaining steady conditions for efficient combustion.
- 🛠️ Tuning of the cascade control system involves setting slave controllers in manual mode for adjustments and switching back to auto after proper tuning.
- 🔥 A burner management system sequences the firing and shutting off of burners based on boiler load, optimizing performance across varying conditions.
- ⚠️ Safety is critical; a trip system is installed to automatically shut off burners in response to critical signals like flame failure or high pressure.
- 💧 An automatic level control system is essential for maintaining proper water levels in boilers with different steam production characteristics.
- 📉 For low steam production and high water content, the level control system primarily focuses on measuring water levels to regulate feed water flow.
- 🔍 Monitoring steam consumption against feed water supply is crucial to avoid pressure drops and maintain system stability.
- 🧑🔧 Following the operating manual's instructions is essential for safe and effective tuning of both master and slave controllers.
Q & A
What is the primary goal of the combustion control system in a boiler?
-The primary goal of the combustion control system is to supply fuel oil according to the boiler load, ensuring efficient combustion and managing the combustion air supply based on fuel consumption.
How does a cascade control system function in boiler operations?
-A cascade control system comprises a master controller that receives steam pressure and flow signals, with slave controllers (air and fuel oil) adjusting to variations in the master controller's output to maintain stable combustion.
What safety measures are included in the burner management system?
-The burner management system includes a sequence for firing and shutting off burners based on boiler load, as well as pressure limit settings to prevent hazards to personnel and equipment.
What does the trip system monitor, and what actions does it take?
-The trip system monitors signals such as flame failure, combustion air failure, and water levels. In case of an emergency, it activates a shutdown procedure to prevent hazards.
What are the differences in level control systems for boilers with high vs. low steam production?
-For boilers with low steam production and high water content, the level control system focuses primarily on measuring water levels and controlling feed water flow. In contrast, for high steam production and low water content, it relies on steam consumption signals alongside water level measurements.
Why is it important to tune the slave controller in manual mode during normal operation?
-Tuning the slave controller in manual mode allows for precise adjustments according to the specifications in the operating manual, ensuring optimal performance before switching back to automatic mode.
What is the role of the high-low selector in the combustion control system?
-The high-low selector allows for adjusting airflow before increasing fuel oil flow when boiler load rises, and vice versa when reducing load, thereby optimizing combustion efficiency.
What happens to the master controller during the firing of the boiler?
-The master controller must remain in manual mode during the firing of the boiler to ensure stability and control while the slave controllers are in automatic or remote setpoint mode.
How does the level control system respond to changes in steam consumption?
-A sudden increase in steam consumption leads to a pressure drop in the steam-water drum, which increases the water level. The system compares steam consumption with feed water supply to manage changes effectively.
What instructions should be followed when tuning the master controller?
-When tuning the master controller, it should be done with the slave controller in auto mode, following detailed instructions in the manual, as each burner has a limited capacity within an optimum range.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

FAMILIARIZATION OF ENGINE CONTROL CONSOLE | Electrician leckyjake

Strategi pengendalian lanjut (bag. 1)

Ch.1 - The Nature of Management Control Systems
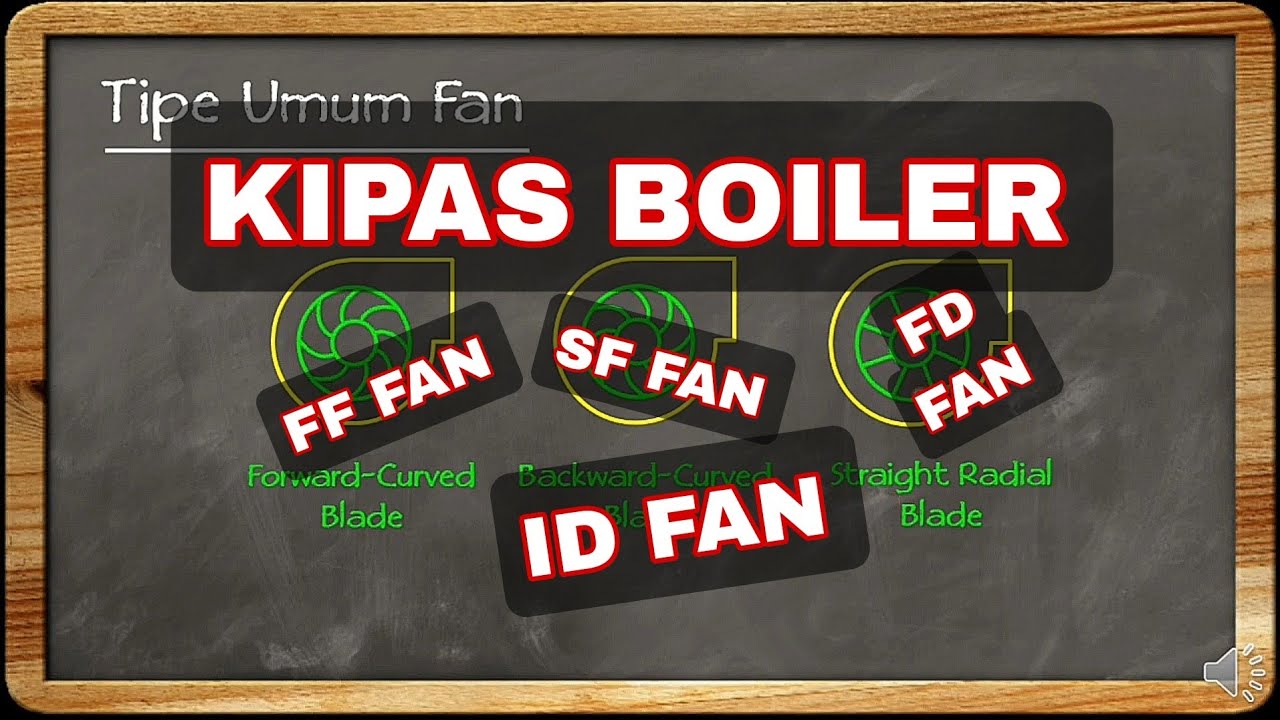
Boiler Fan #FAN #CENTRIFUGAL #BOILER #PABRIKSAWIT #OPERATOR #KIPASANGIN #PMKS #DRAFT #CONTROL #FIRE
IoT levels and Deployment Templates - Level 1 to Level 6

0902 Componen of Internal Control compressed
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)