BBC Geography - Plate Tectonics
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the Earth's structure, highlighting the thin crust above a molten mantle and the intensely hot inner core. It explains the dynamics of tectonic plates, which are categorized into oceanic and continental types. Key geological processes at plate boundaries are described, including constructive boundaries that form volcanic islands, destructive boundaries leading to earthquakes and tsunamis, and collision boundaries that create mountain ranges like the Himalayas. Additionally, it covers conservative boundaries that can trigger significant earthquakes. Overall, the video illustrates how these geological processes shape our planet and pose potential dangers.
Takeaways
- 🌍 The Earth's core consists of a semi-molten mantle layer and an inner core with temperatures reaching approximately 5,500 degrees Celsius.
- 🪨 The Earth's crust, which protects us from the intense heat below, is relatively thin, measuring only 25 to 100 kilometers in thickness.
- 🍏 If the Earth were an apple, its crust would be comparable to the thickness of the apple's skin.
- ⚠️ The Earth's surface is not a single solid layer but consists of tectonic plates that move and shift.
- 🌊 There are two main types of tectonic plates: oceanic plates under the oceans and continental plates beneath landmasses.
- 🔥 Heat rising and falling beneath the plates creates convection currents that can move the plates, leading to geological activity.
- 🌋 Tectonic plate boundaries can lead to significant geological events; there are four primary types: constructive, destructive, collision, and conservative.
- 🇮🇸 At constructive plate boundaries, like in Iceland, two plates pull apart, allowing magma to rise and form shield volcanoes.
- 🇯🇵 In Japan, destructive plate boundaries cause one plate to sink beneath another, leading to subduction and powerful earthquakes and tsunamis.
- 🏔️ Collision plate boundaries, such as those that formed the Himalayas, occur when two continental plates collide, creating fold mountains.
- ⚡ Conservative plate boundaries, like those in California, involve plates sliding past each other, leading to earthquakes when they become stuck and then dislodge.
Q & A
What lies beneath the Earth's crust?
-Beneath the Earth's crust is the mantle, which contains a layer of semi-molten magma, and below that is the inner core with temperatures around 5,500 degrees Celsius.
How thick is the Earth's crust?
-The Earth's crust is relatively thin, ranging from 25 to 100 kilometers thick.
How can the Earth's crust be compared to an apple?
-If the Earth were an apple, the crust would be comparable to the skin of the apple, which is very thin in relation to the rest of the fruit.
What are tectonic plates?
-Tectonic plates are large, jagged pieces that make up the Earth's surface. They come in two types: oceanic plates, found under the oceans, and continental plates, which are thicker and found under land masses.
What causes tectonic plates to move?
-Tectonic plates move due to convection currents in the mantle beneath them, where heat rises and falls, causing the plates to pull apart or push together.
What happens at constructive plate boundaries?
-At constructive plate boundaries, also known as divergent boundaries, two tectonic plates pull apart, allowing magma to rise through the gap, forming shield volcanoes and creating islands like Iceland.
What is subduction?
-Subduction occurs at destructive plate boundaries, where an oceanic plate sinks beneath a less dense continental plate, often causing earthquakes and volcanic activity.
How did the Himalayan mountain range form?
-The Himalayan mountain range formed at collision plate boundaries, where two continental plates of the same density collided and pushed against each other, causing the Earth's crust to buckle and create fold mountains.
What is a conservative plate boundary?
-At conservative plate boundaries, tectonic plates slide past each other at different speeds or in opposite directions, leading to earthquakes when they get stuck and then dislodge.
What significant geological events are linked to plate boundaries?
-Significant geological events like earthquakes and tsunamis, such as the devastating 2011 tsunami in Japan, are linked to destructive plate boundaries and subduction processes.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH | Unit 1 Module 2 - Grade 10 Science Lesson | MELC-Based [TEACH]

Mexus education
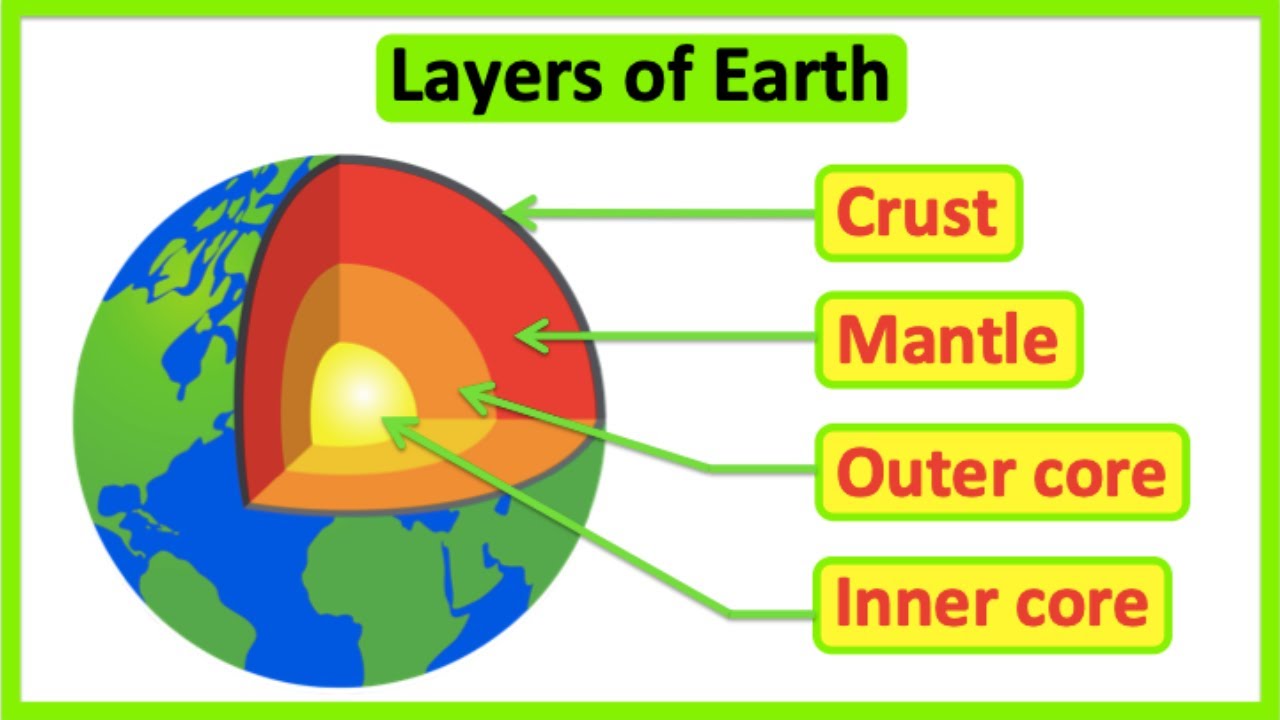
Layers of the Earth | Structure of the Earth | Educational Science Lesson

Structure Of The Earth | The Dr. Binocs Show | Educational Videos For Kids

THE GEOSPHERE | Educational Videos for Kids

Earth's Interior
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
