INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH | Unit 1 Module 2 - Grade 10 Science Lesson | MELC-Based [TEACH]
Summary
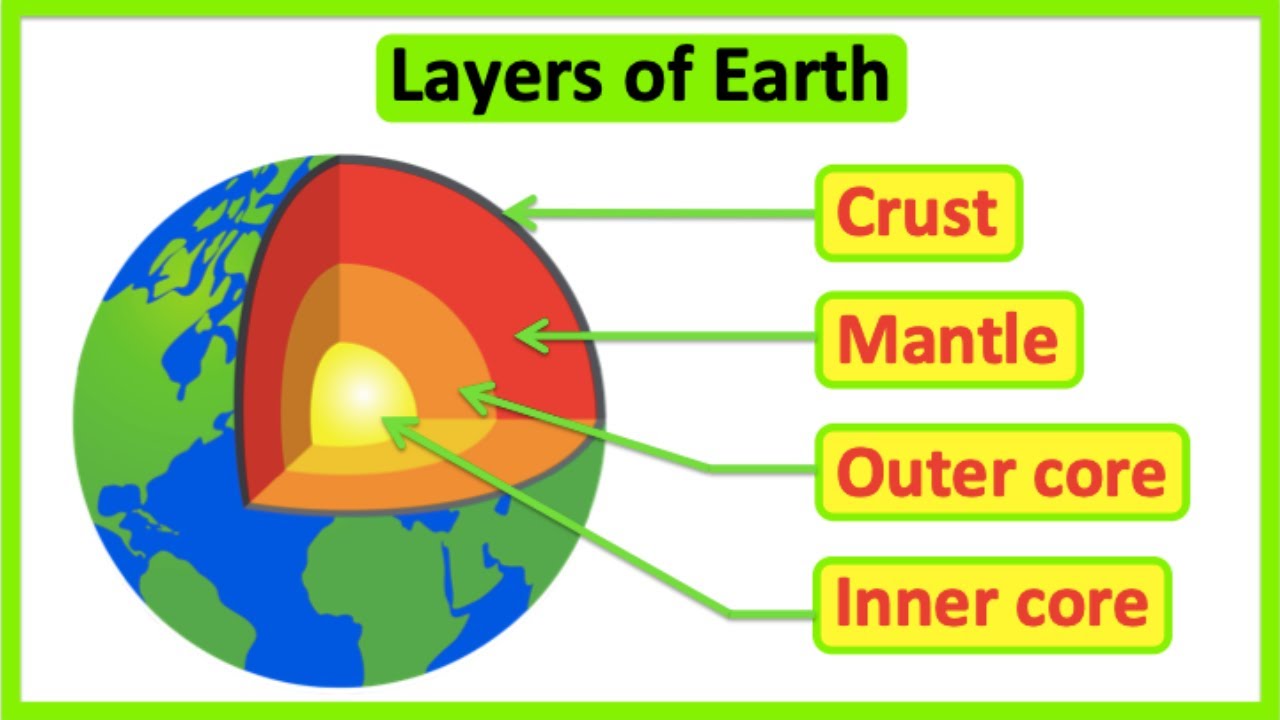
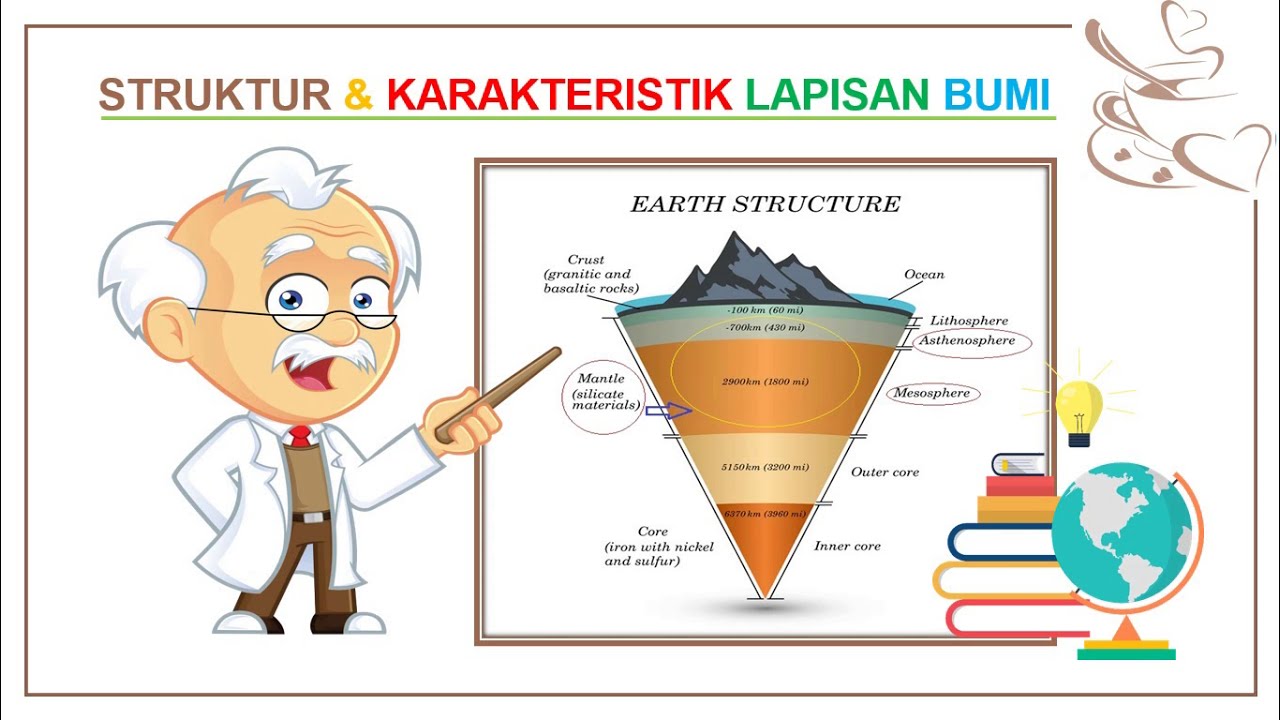
TLDRWelcome to CaViTeach, where today's lesson delves into Earth's internal structure, highlighting its five layers: the crust, mantle, outer core, inner core, and atmosphere. The inner core, made of iron and nickel alloy, is incredibly dense and hot at 5000°C, contrasting with the molten outer core at 2000°C. The mantle, composed of silicate rocks and divided into the upper, transition, and lower regions, is solid despite its extreme heat. The crust, Earth's thin outer layer, varies in thickness and composition, with continental crust being less dense than oceanic. This episode wraps up with a teaser for the next, focusing on the atmosphere.
Takeaways
- 🌐 The Earth has five concentric layers: crust, mantle (upper and lower), outer core, inner core, and atmosphere.
- 🔥 The inner core is the hottest part of the Earth with a temperature of about 5000°C, composed of solid iron and nickel alloy.
- 🌀 The outer core, with a temperature of around 2000°C, is made up of molten iron and nickel alloy, contributing to Earth's magnetic field.
- 🌍 The mantle, which makes up 80% of Earth's volume and 68% of its mass, is primarily composed of silicate rocks containing silicon, iron, oxygen, and magnesium.
- 🌡️ The asthenosphere, a layer within the mantle, is a soft and weak layer responsible for the movement of lithospheric plates, leading to earthquakes.
- 🏔️ The crust is the thinnest and outermost layer, divided into oceanic crust (7-10 km thick) and continental crust (35-40 km thick), with different compositions and densities.
- 🌋 The Mohorovicic Discontinuity marks the boundary between the crust and the mantle, while the Gutenberg Discontinuity is the boundary between the outer core and the lower mantle.
- 🧲 The Earth's magnetic field is believed to be generated by the movement of molten iron and nickel in the outer core.
- 🌌 The Lehmann Discontinuity is the boundary between the solid inner core and the molten outer core, discovered by Inge Lehmann.
- 🌬️ The atmosphere, the fifth layer, will be discussed in a future episode, highlighting the structure and composition of Earth's outermost layer.
Q & A
What are the five concentric layers of the Earth?
-The five concentric layers of the Earth are the crust, the mantle (divided into upper and lower portions), the outer core, the inner core, and the atmosphere.
What is the diameter of the Earth's inner core?
-The inner core has a diameter of approximately 2,600 kilometers.
What are the main constituents of the inner core?
-The inner core is primarily composed of an iron and nickel alloy.
What is the approximate temperature of the inner core?
-The inner core has an approximate temperature of 5,000 degrees Celsius.
Why is the inner core solid despite its high temperature?
-The inner core is solid due to extreme pressure, a phenomenon known as pressure freezing, which counteracts the melting effect of the high temperature.
How do scientists know that the inner and outer core are composed of iron and nickel alloy?
-Scientists deduce this composition from the Earth's magnetic field, which is generated by the movement of molten iron and nickel in the outer core, and from the density of the Earth, which is higher than that of crust rocks, suggesting denser materials like iron and nickel in the core.
What is the significance of the Lehmann Discontinuity?
-The Lehmann Discontinuity is the boundary between the inner and outer core, named after Inge Lehmann who discovered that the outer core is molten and the inner core is solid.
What is the mantle's composition and its role in the Earth's structure?
-The mantle is composed mostly of silicate rocks containing silicon, iron, oxygen, and magnesium. It makes up 80% of Earth's volume and 68% of its mass, serving as an intermediate zone between the crust and the core.
What is the Asthenosphere and its relation to plate tectonics?
-The Asthenosphere is a soft, weak, and partially molten layer of the upper mantle that causes the movement of lithospheric plates, leading to continental drift and earthquakes.
What are the two types of crust found on Earth and their main differences?
-There are two types of crust: continental crust, which is thicker and composed of less dense rocks like granite, and oceanic crust, which is thinner and made up of denser rocks like basalt.
What is the Mohorovicic Discontinuity and who is it named after?
-The Mohorovicic Discontinuity is the boundary between the crust and the mantle, named after the Croatian meteorologist and seismologist Andrija Mohorovicic.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)