BAB 2 KEANEKARAGAMAN HAYATI | GEOGRAFI SMA KELAS XI | KURIKUKUM MERDEKA
Summary
TLDRThis video focuses on a geography lesson for 11th-grade students under the 'Merdeka Curriculum'. It covers Indonesia's biodiversity, highlighting the distribution of flora and fauna across different regions. The lesson discusses various ecosystems, the factors affecting species distribution (like climate and geography), and the importance of conserving biodiversity. Specific examples include Indonesia's different flora regions, such as Sumatra, Kalimantan, and Papua, and fauna types like Asiatic, Australasian, and transitional species. The video concludes with insights on sustainable practices, conservation efforts, and the value of biodiversity for ecological balance and human well-being.
Takeaways
- 🌍 The video is a geography lesson for 11th grade, based on the Merdeka Curriculum, focusing on biodiversity in Indonesia.
- 🌿 The topics covered include the distribution of flora and fauna, their benefits, and efforts for conservation.
- 🗺️ Indonesia's geographic position significantly influences the distribution of its flora and fauna.
- 🦕 During the Jurassic period, the Earth had two major landmasses: Laurasia and Gondwana.
- 🌱 Indonesia has diverse flora, including 4,000 species of trees, 1,500 species of ferns, and 5,000 species of orchids.
- 🌳 Flora distribution is divided into three subregions: Indonesia-Malaysia, Wallacea, and Australia, with distinct flora in each region.
- 🐘 The fauna in Indonesia is classified into Asiatic, Australasian, and transitional types, with specific animals for each region.
- 🌧️ Climate, soil, topography, and biotic factors are essential in determining the distribution of fauna across Indonesia.
- 🏞️ Biodiversity conservation efforts include maintaining ecological balance and developing economic values, such as the Grojogan Sewu nature park and Cibodas Botanical Garden.
- 👥 Local wisdom plays a significant role in the sustainable management of the environment, as seen in practices by the Baduy people, the Subak system in Bali, and farming traditions in West Kalimantan.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The video discusses biodiversity in Indonesia, specifically focusing on the distribution of flora and fauna, their benefits, conservation efforts, and successful conservation practices.
How is Indonesia's geographical location important for the distribution of flora and fauna?
-Indonesia's geographical location influences the distribution of flora and fauna, as its position leads to the presence of different subregions, each with unique environmental conditions affecting species distribution.
What are the three subregions for flora distribution in Indonesia?
-The three subregions for flora distribution are Indonesia-Malaysia (Sumatra, Java, Kalimantan), the Wallacean region (Sulawesi, East Nusa Tenggara, Maluku), and the Australian subregion (Papua).
What are some examples of flora found in the Sumatra and Kalimantan regions?
-Examples of flora in Sumatra and Kalimantan include Rafflesia arnoldii, Meranti, and Damar trees. The region features tropical rainforests and mangrove forests.
What factors influence the distribution of fauna in Indonesia?
-Factors influencing the distribution of fauna in Indonesia include climatic conditions, edaphic (soil-related) factors, physiographic (landform) factors, and biotic factors (interactions with living organisms).
What are the three types of fauna distribution in Indonesia?
-The three types of fauna distribution are Asiatic fauna (in the western part), Australian fauna (in the eastern part), and transitional fauna (found between the Asiatic and Australian regions).
Can you give examples of species found in the Asiatic fauna region?
-In the Asiatic fauna region, which includes Sumatra, Java, Bali, and Kalimantan, examples include orangutans, tigers, elephants, crocodiles, and various species of birds such as owls and mynas.
What are the benefits of conserving flora and fauna in Indonesia?
-Conserving flora and fauna helps maintain ecological balance, provides aesthetic and economic value, and ensures sustainable benefits for human well-being, including ecosystem services and potential economic use.
What are some examples of successful conservation areas in Indonesia?
-Examples of successful conservation areas include Grojogan Sewu Nature Park (Central Java), Baluran National Park (East Java), and Juanda Forest Park (West Java).
What is an example of local wisdom in Indonesia that supports environmental conservation?
-One example is the Subak system in Bali, which manages water resources sustainably without harming the environment. Another example is the traditional Baduy community, which divides land into different zones to preserve nature.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

SOAL LATIHAN BAB 4 LISTRIK MAGNET DAN SUMBER ENERGI ALTERNATIF (IPA Kelas 9 Kurikulum Merdeka)
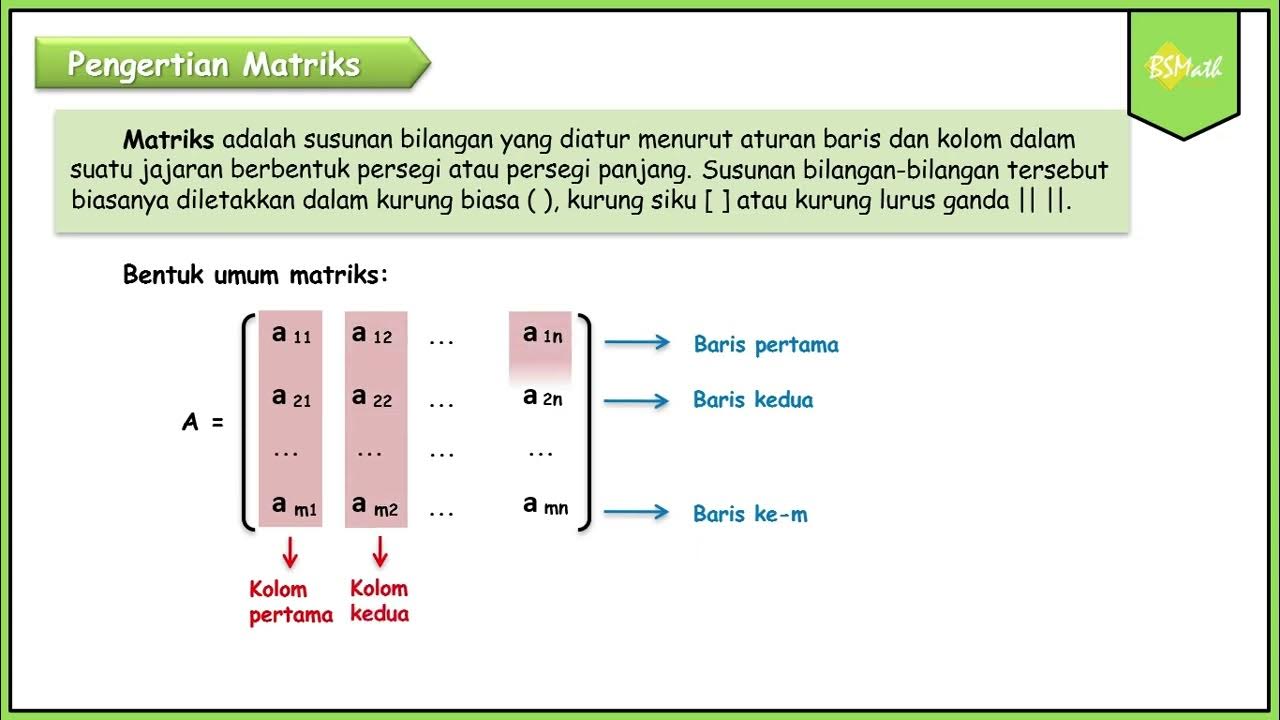
Pengertian Matriks - Matematika Tingkat Lanjut SMA Kelas XI Kurikulum Merdeka

Informatika kelas XI Kurikulum Merdeka

Pendidikan Pancasila Bab 1 : Mengenal Lingkungan Sekitar - Halaman 1-4 Kelas 4 Kurikulum Merdeka

Keragaman Hayati, bag 2 (Sebaran Bioma di Dunia) #kumer
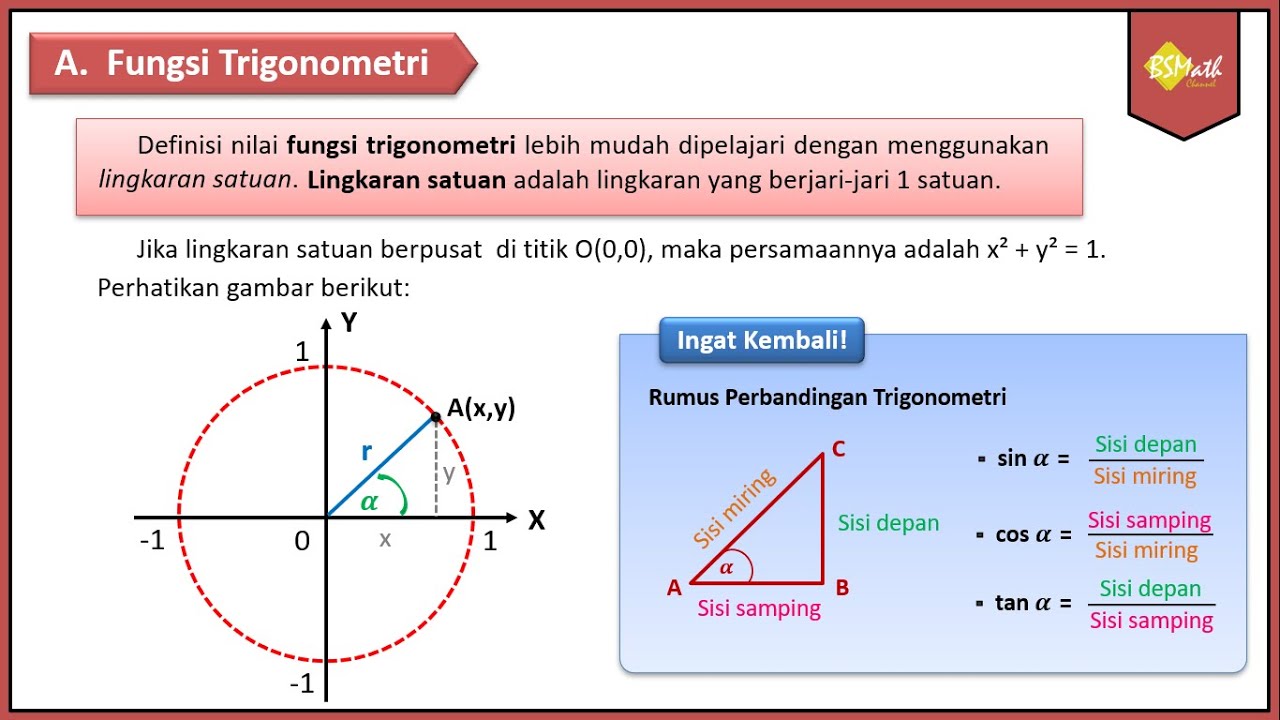
Tanda Fungsi Trigonometri Tiap Kuadran | Matematika Tingkat Lanjut SMA Kelas XI Kurikulum Merdeka
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
