How to scalp Futures with the Depth of Market (DOM) For Beginners
Summary
TLDRThis video dives into scalping strategies in the S&P 500 futures market using order flow and the Depth of Market (DOM) tool. The presenter explains how scalpers target quick, small moves, typically 1-3 points, with tight risk management. The video covers key concepts like market orders, delta imbalances, and reactive buying or selling. By analyzing large market orders and delta shifts, traders can identify opportunities for scalping both with and against the trend. This comprehensive guide provides valuable insights into identifying and executing scalping trades efficiently.
Takeaways
- 💡 Scalping in futures trading involves short-term trades aiming for small price movements, typically lasting a point or two.
- 📊 Depth of Market (DOM) is a key tool for identifying scalping opportunities in the futures market, particularly with the S&P 500.
- ⚡ Scalping differs from day trading because it requires faster decision-making, as scalpers look for quick, minor price moves with limited risk.
- 📉 The risk in scalping is usually around $50-$100 per contract, with traders targeting a reward of about the same amount.
- 🔍 The DOM is crucial for tracking order flow, with scalpers focusing on market orders and delta to identify buy and sell pressure.
- 🛑 Scalpers look for large buy or sell orders and try to follow the momentum, whether by joining the trend or reacting to trapped traders.
- ⏱ Scalping requires quick reactions and precise entries, as small moves are targeted, and any delay can reduce profitability.
- 📉 Delta is used to measure the imbalance between buyers and sellers, with larger positive or negative delta values indicating key points of support or resistance.
- 🔄 Trapped traders are an important concept in scalping, as large negative or positive delta can indicate where traders are stuck, providing an opportunity for a quick move in the opposite direction.
- 🎯 Scalpers use very tight stop-losses and aim for small profits per trade, typically in the range of 1-3 points, and rely heavily on reading order flow and price reactions in real-time.
Q & A
What is scalping in the futures market?
-Scalping in the futures market is a trading strategy that involves taking very short-term positions, typically lasting for just a point or two. Traders aim to capture small, quick profits, usually with limited risk.
How does scalping differ from day trading?
-Scalping differs from day trading in that scalpers aim for very small, quick moves and are in and out of trades rapidly. Day traders, on the other hand, take longer positions and look for more substantial moves within a trading day.
What is the Depth of Market (DOM) and how is it used in scalping?
-The Depth of Market (DOM) is a tool used to view the market orders for a specific asset, showing the buy and sell orders at different price levels. In scalping, traders use the DOM to identify where large buy or sell orders are positioned, allowing them to anticipate short-term price movements.
What are market orders and how do they impact scalping strategies?
-Market orders are trades executed immediately at the current market price. In scalping, large market orders can indicate strong buying or selling pressure, and traders use this information to make quick decisions, entering or exiting trades based on the flow of these orders.
What is the role of Delta in scalping using the DOM?
-Delta represents the difference between buy orders and sell orders at a specific price level. In scalping, large positive or negative Delta values can indicate imbalances in market pressure, helping traders predict whether prices will rise or fall.
How do traders use large Delta values to make scalping decisions?
-Traders look for large Delta values to spot potential areas of price reversals or continuations. For example, if there is a large negative Delta and buyers step in aggressively, it may indicate that sellers are trapped, and the price could reverse upward.
What is a ‘stuck short’ and how is it relevant to scalping?
-A 'stuck short' occurs when large sell orders are placed, but buyers counteract these orders, preventing the price from dropping further. In scalping, identifying 'stuck shorts' can signal potential upward moves, providing opportunities to go long.
How do scalpers manage risk in the S&P 500 futures market?
-In the S&P 500 futures market, scalpers typically manage risk by setting very tight stop-losses, often just a point or two, and aim for small profits, around $50 to $100 per contract. This helps limit exposure to market noise while capturing quick gains.
Why is it important for scalpers to act quickly on market entries and exits?
-Scalping relies on capturing very small price movements, so missing an optimal entry or exit can lead to missed profits or increased losses. Quick decision-making is essential for capitalizing on brief market opportunities and avoiding unfavorable price reversals.
What is the significance of observing large sell orders on the DOM?
-Large sell orders on the DOM indicate strong selling pressure. Scalpers may choose to enter short positions when these orders appear, expecting further downward price movements. Conversely, if these orders fail to push prices lower, it could signal a reversal.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
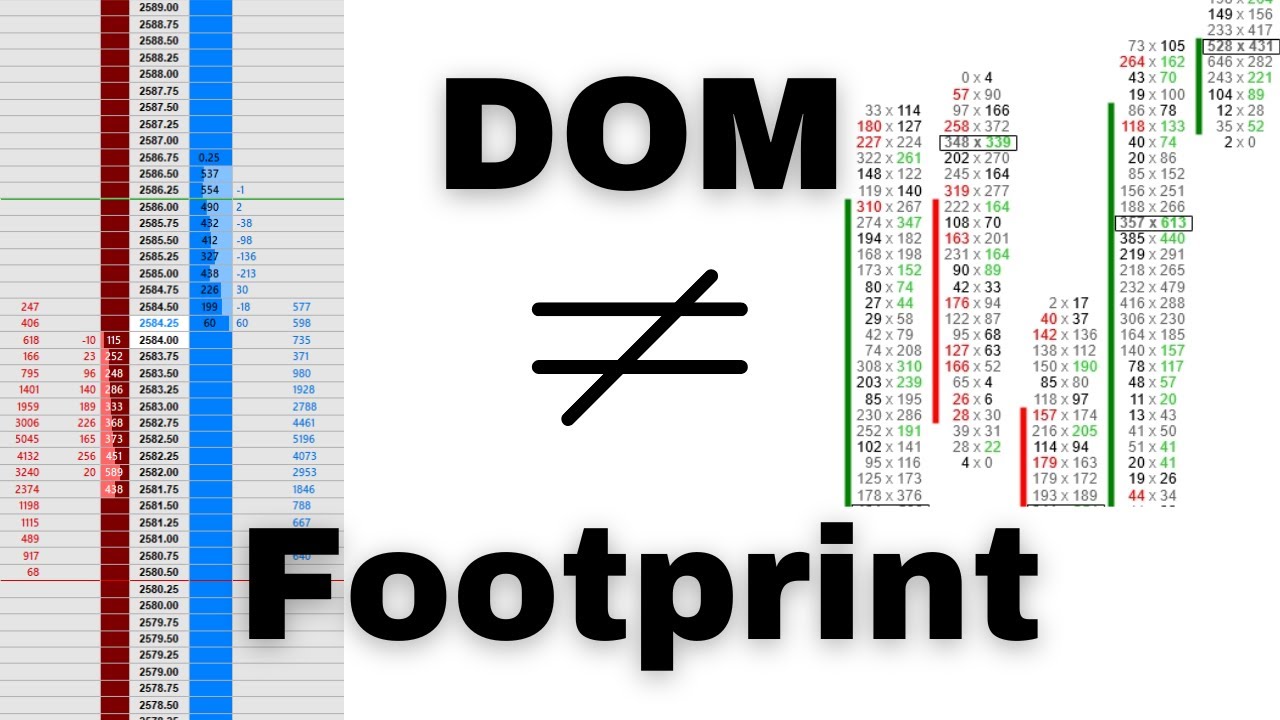
Understanding The Differences Between a DOM and Footprint Chart

How To Spot the Bottom of ICT's Market Maker Model

Stock Market Index | by Wall Street Survivor

⚠️WATCH BEFORE MONDAY 9 30am! #PLTR #SOFI #TSLA #NVDA

This Signal Appears Before EVERY Market Correction

The Only Day Trading Strategy You Need | BLITZ MODEL
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
