AP7 MATATAG Q1 Week 1 LOKASYON AT PISIKAL NA KATANGIAN NG TIMOG SILANGANG ASYA with POWERPOINT
Summary
TLDRThe video script explains the physical characteristics and geography of Southeast Asia, highlighting its division into mainland and insular regions. It provides insights into the influence of Indian and Chinese cultures in the area and identifies the countries that make up both mainland and insular Southeast Asia. Countries like Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, and Vietnam are part of mainland Southeast Asia, while nations such as Indonesia, the Philippines, and Brunei belong to insular Southeast Asia. Malaysia is unique as it falls under both categories. The video also mentions the flags of the respective countries.
Takeaways
- 🌍 Continents are the largest landmasses on Earth, and there are seven of them: North America, South America, Europe, Africa, Asia, Australia, and Antarctica.
- 🌏 According to Alfred Wegener, continents were once connected in a supercontinent called Pangaea, but due to continental plate movements, they separated to form the current continents.
- ☀️ The word 'Asia' is derived from the terms 'Ajan' and 'Asu', meaning the place where the sun rises, or the East.
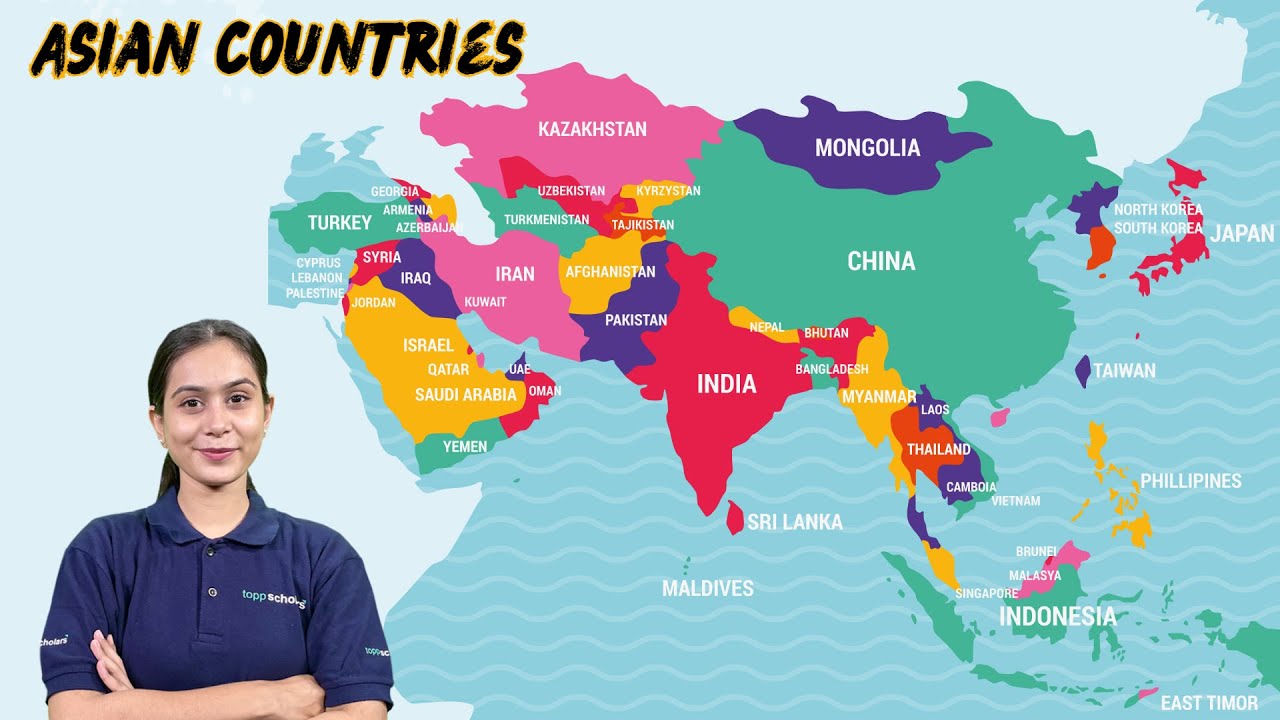
- 🇵🇭 The Philippines is part of Asia, the largest continent, which covers about one-third of the Earth's land area and is divided into five regions: Northern Asia, Western Asia, Southern Asia, Eastern Asia, and Southeast Asia.
- 🌏 Southeast Asia is influenced by the cultures of India and China, earning it the nicknames 'Farther India' and 'Little China'.
- 🌏 Southeast Asia consists of countries like Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, Cambodia, the Philippines, Malaysia, Indonesia, Singapore, Brunei, and Timor Leste.
- 🗺️ Southeast Asia is divided into two parts: Mainland Southeast Asia (or Continental Southeast Asia) and Insular Southeast Asia.
- 🏞️ Mainland Southeast Asia includes Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam, Singapore, and the western part of Malaysia.
- 🏝️ Insular Southeast Asia includes the Philippines, Indonesia, Brunei, Timor Leste, and the eastern part of Malaysia.
- 🇲🇾 Malaysia is unique in that it is part of both Mainland and Insular Southeast Asia.
Q & A
What is the meaning of 'Asya' according to the transcript?
-'Asya' comes from the words 'ajan' and 'asu,' which mean 'place where the sun rises' or 'east.'
How did the current continents form, according to the transcript?
-The current continents formed due to the movement of continental plates, which broke apart the supercontinent Pangea.
What are the five regions of Asia mentioned in the transcript?
-The five regions of Asia are Northern Asia, Western Asia, Southern Asia, Eastern Asia, and Southeast Asia.
Why is Southeast Asia referred to as 'Farther India' and 'Little China'?
-Southeast Asia is referred to as 'Farther India' and 'Little China' due to the influence of India and China on the culture of the region.
Which countries are part of mainland Southeast Asia?
-Mainland Southeast Asia consists of Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam, and the western part of Malaysia.
Which countries belong to Insular Southeast Asia?
-Insular Southeast Asia includes Indonesia, the Philippines, Brunei, Timor-Leste, and the eastern part of Malaysia.
Why is Malaysia categorized as both mainland and insular Southeast Asia?
-Malaysia is categorized as both because its territory is divided between the mainland (western Malaysia) and insular (eastern Malaysia).
What oceans surround mainland Southeast Asia?
-Mainland Southeast Asia is situated between the South China Sea and the Indian Ocean.
What is the difference between mainland and insular Southeast Asia?
-Mainland Southeast Asia refers to the continental part of the region, while insular Southeast Asia refers to the islands scattered in the surrounding oceans.
What is the significance of the South China Sea in Southeast Asia?
-The South China Sea plays a significant role in the geography of Southeast Asia, separating the mainland and insular regions and serving as a crucial area for trade and cultural exchange.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Heograpiya ng Timog Silangang Asya Quarter 1 Week 1 Matatag Curriculum

AP7 Q1 W7 MATATAG MGA SINAUNANG KABIHASNAN SA TIMOG SILANGANG ASYA Part1
Discover the Geography of Asia: Exploring Asian Countries and Their Map #geography #asiancountries

AP7 MATATAG Q1 Week 5 SINAUNANG KASAYSAYAN NG TIMOG SILANGANG ASYA-AUSTRONESIAN MIGRATION WITH PPT

BENUA ASIA - Materi IPS SMP Kelas 9

Topik Benua Asia 6 Wilayah Asia
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
