AP7 Q1 W7 MATATAG MGA SINAUNANG KABIHASNAN SA TIMOG SILANGANG ASYA Part1
Summary
TLDRThe script provides an in-depth overview of ancient civilizations in Southeast Asia, focusing on both Mainland and Insular regions. It discusses key empires such as Funan, Angkor, Pagan, Srivijaya, and Ayutthaya, highlighting their cultural, political, and architectural contributions. The civilizations flourished through agriculture, trade, and religious influences, particularly from Indian and Buddhist cultures. Major landmarks like Angkor Wat and Borobudur are emphasized as symbols of their legacy. The video also examines the development of organized governments, religions, and technological advancements that shaped the history of the region.
Takeaways
- 📜 The lesson covers the ancient civilizations of Southeast Asia, focusing on Mainland and Insular Southeast Asia.
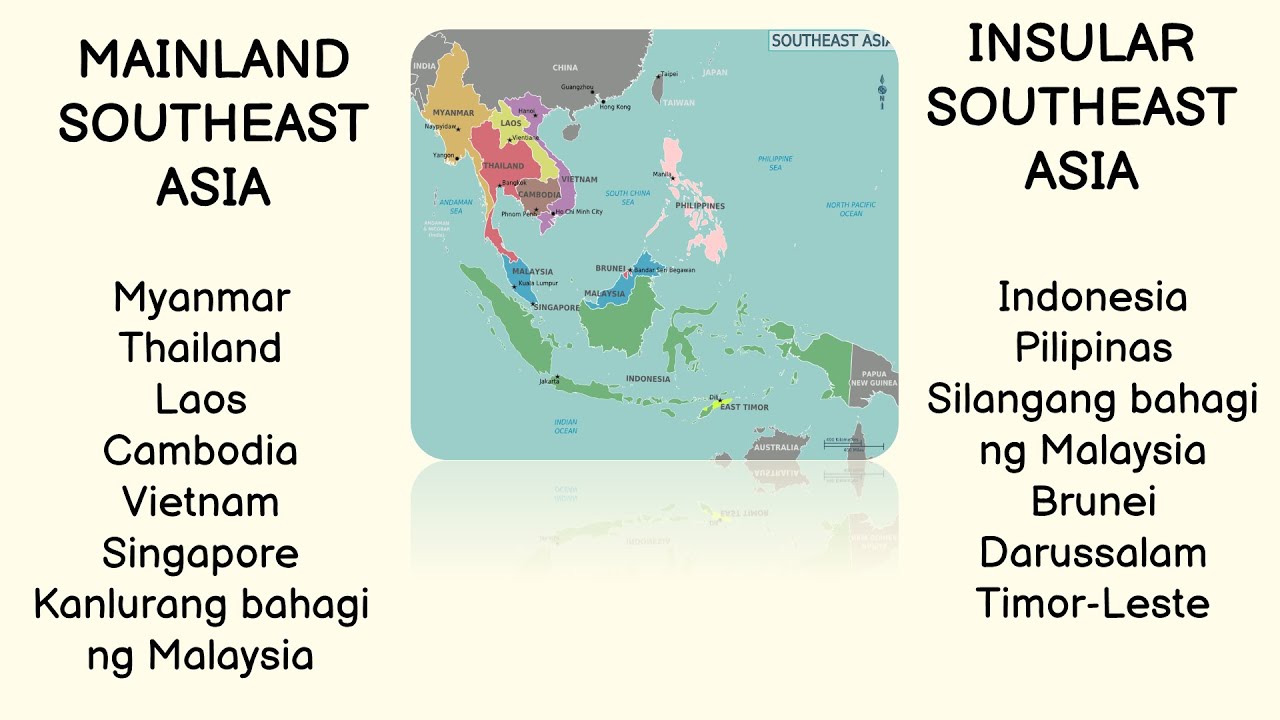
- 🌏 Mainland civilizations include Funan, Angkor, Pagan, and Ayutthaya, while Insular civilizations include Srivijaya, Sailendra, Majapahit, and Malacca.
- 🏛️ These civilizations contributed significantly to the region’s history and societal development, influencing their ways of life.
- 🔎 Key landmarks mentioned include the Shwesandaw Stupa in Myanmar, Angkor Thom in Cambodia, Borobudur in Indonesia, and Wat Phra Si Sanphet in Thailand.
- 🏞️ Early civilizations in the river valleys of Southeast Asia advanced through fishing, agriculture, and adapting to their environments.
- ⚖️ The six main elements of civilization include centralized government, complex religion, economic specialization, social classes, advanced technology, and written language.
- 🌍 Southeast Asia was home to diverse ethnic groups that influenced one another, leading to a mix of languages, cultures, and traditions.
- ⛩️ Indian influences, particularly Buddhism and Hinduism, spread throughout Southeast Asia via trade and cultural exchanges.
- 👑 Notable rulers like Jayavarman II of Angkor and Suryavarman II built grand temples like Angkor Wat, which also served as royal burial sites.
- 📉 The fall of several Southeast Asian empires, like Angkor and Pagan, was due to external conflicts, particularly with the Thai and other emerging powers.
Q & A
What are the main goals of the lesson about ancient civilizations in Southeast Asia?
-The lesson aims to: 1) Analyze ancient civilizations in Mainland and Insular Southeast Asia, 2) Appreciate their contributions to ancient history and society, and 3) Write an essay about the lifestyle of ancient civilizations.
What regions are covered under Mainland and Insular Southeast Asia?
-Mainland Southeast Asia refers to countries on the continental part like Cambodia, Thailand, and Vietnam, while Insular Southeast Asia includes island nations like Indonesia, the Philippines, and Malaysia.
Which ancient civilizations are mentioned for Mainland Southeast Asia?
-The ancient civilizations mentioned for Mainland Southeast Asia are Funan, Angkor (Khmer), Pagan, Tungguli, and Ayutthaya.
What ancient civilizations are highlighted for Insular Southeast Asia?
-The civilizations highlighted for Insular Southeast Asia include Sri Vijaya, Sailendra, Majapahit, and Malacca.
What were the main contributions of the Angkor (Khmer) Empire in Cambodia?
-The Angkor Empire built monumental structures like Angkor Wat and Angkor Thom, practiced advanced irrigation for agriculture, and adopted Indian influences in their architecture and religion.
What are the primary elements that define a civilization according to the script?
-A civilization is defined by six elements: 1) Organized and centralized government, 2) Complex religion, 3) Specialization in economic activities, 4) Social hierarchy, 5) Advanced knowledge in technology, arts, and architecture, and 6) A system of writing.
How did the Funan Kingdom rise to power in Southeast Asia?
-The Funan Kingdom, established around 100 CE in present-day Cambodia and Vietnam, expanded its influence through its strategic location along the Mekong River Delta and established strong trade relations with China.
What role did Indian influence play in the development of Southeast Asian civilizations?
-Indian influence, brought through trade, introduced elements like Buddhism, Hinduism, and Indian art and architecture, which significantly shaped the culture, religion, and politics of Southeast Asian civilizations like Funan and Angkor.
What was the significance of Angkor Wat and Angkor Thom in the Khmer Empire?
-Angkor Wat and Angkor Thom were grand temple complexes that reflected the religious and political power of the Khmer kings. Angkor Wat served as both a religious center and a royal tomb, while Angkor Thom was a fortified city with important monuments.
How did the Ayutthaya Kingdom rise to prominence in Southeast Asia?
-The Ayutthaya Kingdom, founded by King U-Thong, became a powerful state in Thailand by uniting various regions, adopting Theravada Buddhism, and codifying Hindu-based laws, maintaining power through trade and military strength.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
AP7 MATATAG Q1 Week 1 LOKASYON AT PISIKAL NA KATANGIAN NG TIMOG SILANGANG ASYA with POWERPOINT

Heograpiya ng Timog Silangang Asya Quarter 1 Week 1 Matatag Curriculum

Music and Arts 7 Quarter 2 Week 2.Matatag.Lesson Exemplar Based
Discover the Geography of Asia: Exploring Asian Countries and Their Map #geography #asiancountries

Rangkuman Materi SKI Kelas 9 Bab 2 Semester 1| Kerajaan Islam di Indonesia

Menuju Kemajuan! Inilah Negara Indonesia
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)