Heograpiya ng Timog Silangang Asya Quarter 1 Week 1 Matatag Curriculum
Summary
TLDRThe script delves into the geography of Southeast Asia, the world's largest continent, highlighting its physical features, climate, and biodiversity. It discusses the region's division into mainland and insular Southeast Asia, emphasizing the importance of rivers and the 'Ring of Fire'. The video also touches on the rich natural resources, such as oil and gas, and the challenges faced by the region, including environmental issues like deforestation, land conversion, and ecological imbalances. It concludes by underscoring the significance of understanding and addressing these complex socio-economic and environmental interconnections for sustainable development.
Takeaways
- 🌍 Geography is the study of the physical features of the Earth's surface, including landforms, bodies of water, climate, natural resources, flora, fauna, and human interaction with the environment.
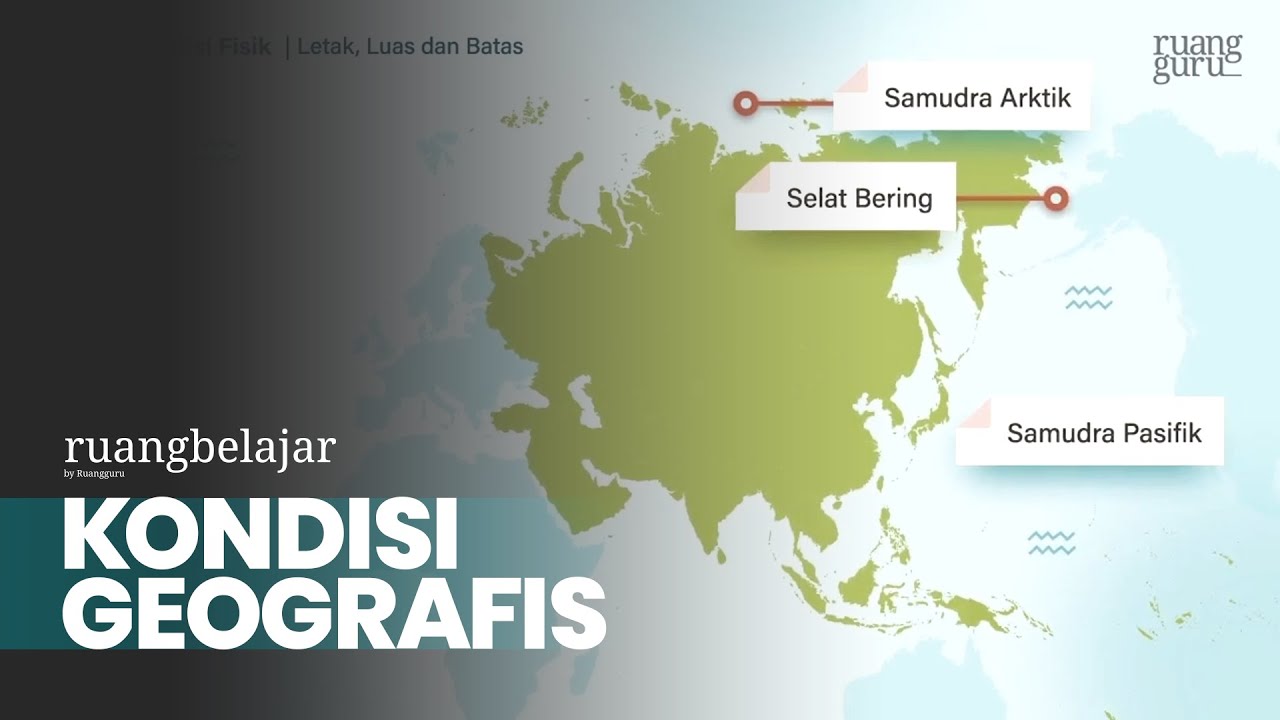
- 🌏 Southeast Asia is a region located between the South China Sea and the Indian Ocean, characterized by mountain ranges and large rivers such as the Mekong and Chao Phraya.
- 🏞️ The mainland Southeast Asia is known for its rugged terrain and mountainous regions, while Insular Southeast Asia consists of numerous islands including the Philippines, Indonesia, and Timor Leste.
- 🌋 The Pacific Ring of Fire, which includes parts of Southeast Asia, is an area with frequent seismic and volcanic activity, posing risks such as earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
- 🐘 The region's biodiversity is rich, with Myanmar and Brunei hosting extensive rainforests that are home to various species of mammals, birds, and reptiles.
- 🌱 The Philippines is known for its production of coconuts, while Indonesia has significant reserves of oil and natural gas, contributing to the region's economic activity.
- 🐄 Agriculture is a key industry in Southeast Asia, with the Philippines leading in the production of coconuts, and countries like Cambodia having fertile lands around the Mekong River.
- 🌿 The region faces environmental challenges such as desertification, salinization, and habitat destruction due to land conversion and deforestation.
- 🌊 Issues like siltation, red tide, and the depletion of the ozone layer are environmental concerns that affect the ecological balance and the well-being of both humans and wildlife.
- 🌡️ Global climate change, influenced by both natural and human activities, is causing shifts in regional climates, which can have significant impacts on the environment and human societies.
Q & A
What is geography and where does the term originate from?
-Geography is the study of the physical features of the Earth's surface, including landforms, bodies of water, climate, and the distribution of plants, animals, and humans. The term originates from the Greek words 'Geo' meaning Earth and 'graphia' meaning description or writing.
How many continents are there in the world and which is the largest?
-There are seven continents in the world: North America, South America, Europe, Africa, Australia, Antarctica, and Asia. Asia is the largest continent.
What are the five regions of Asia and which region does the Philippines belong to?
-The five regions of Asia are North Asia, West Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia, and East Asia. The Philippines belongs to the Southeast Asia region.
What is the geographical feature that connects mainland Southeast Asia and the Insular Southeast Asia?
-The geographical feature that connects mainland Southeast Asia and the Insular Southeast Asia is the South China Sea.
What are the major rivers that flow through mainland Southeast Asia?
-The major rivers that flow through mainland Southeast Asia include the Irrawaddy, Chao Phraya, Mekong, and Salween rivers.
Which countries in Southeast Asia are part of the 'Ring of Fire'?
-The countries in Southeast Asia that are part of the 'Ring of Fire' include the Philippines, Indonesia, and Timor-Leste.
What are the natural resources found in the mainland Southeast Asia region?
-The natural resources found in the mainland Southeast Asia region include significant deposits of oil and natural gas, with Myanmar and Brunei having extensive forests that are home to various species of animals and reptiles.
What are the main agricultural products of the Philippines?
-The main agricultural products of the Philippines include coconuts, abaca, and rice, with the country being a leading producer of coconut oil and copra in the world.
What are the common livestock animals raised in Southeast Asia?
-Common livestock animals raised in Southeast Asia include water buffalo, cattle, horses, goats, sheep, and chickens.
What is the significance of the 'Ring of Fire' in the context of Southeast Asia?
-The 'Ring of Fire' is significant in Southeast Asia as it is an area with a high frequency of volcanic and seismic activities, which can lead to earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. This region includes countries like the Philippines, which has several active volcanoes such as Mount Mayon, Mount Pinatubo, and Taal Volcano.
What is biodiversity and why is Asia considered a major source of it?
-Biodiversity refers to the variety of life in all its forms and interactions, including the different plants, animals, and microorganisms, their genes, and the ecosystems they form. Asia, being the largest continent, is considered a major source of global biodiversity due to its vast range of ecosystems and habitats.
What are some of the environmental issues faced by Southeast Asian countries?
-Some of the environmental issues faced by Southeast Asian countries include desertification, salinization, habitat loss, land conversion, deforestation, siltation, red tides, and depletion of the ozone layer. These issues are often exacerbated by rapid economic development and increasing population pressures.
How does global climate change affect the geography of Southeast Asia?
-Global climate change affects the geography of Southeast Asia by causing shifts in weather patterns, rising sea levels, and increased frequency of extreme weather events, which can lead to flooding, droughts, and other disruptions to ecosystems and human settlements.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)