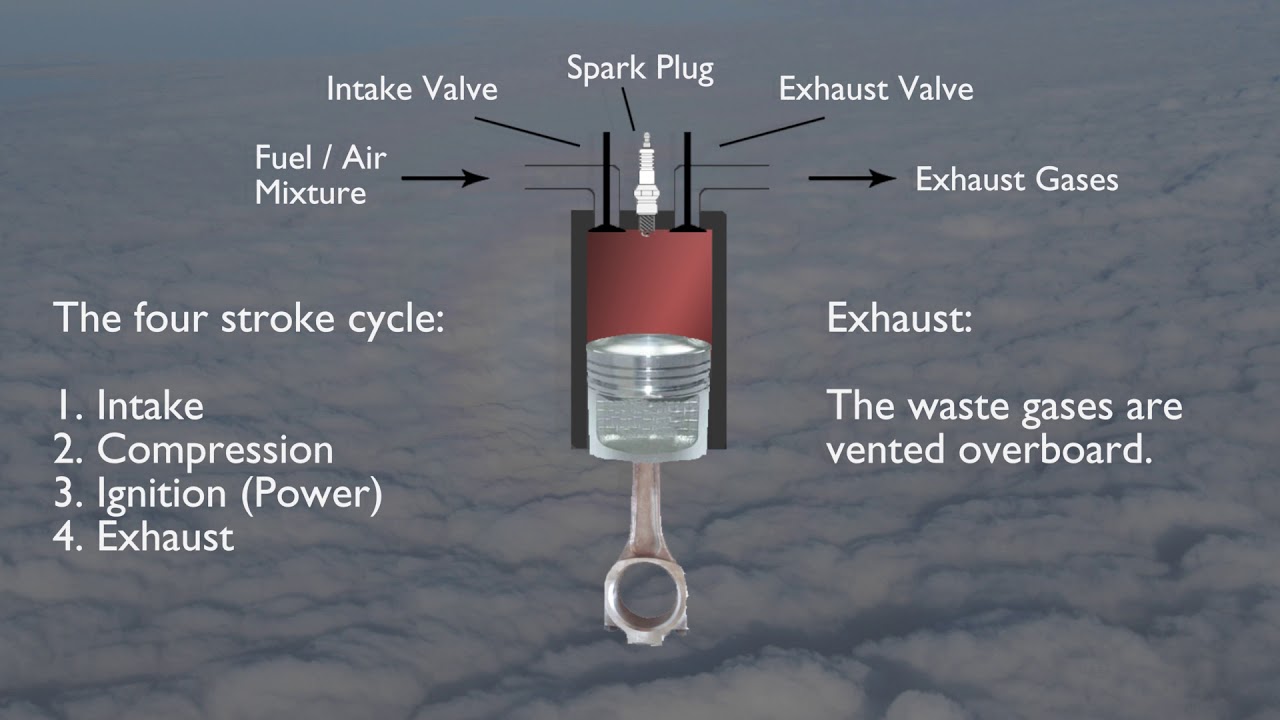
JET ENGINE FUEL SYSTEM
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the critical role of fuel systems in aircraft engines, focusing on the CFM 56-7 engine. It outlines the five key functions of aircraft fuel systems: increasing fuel pressure, heating, adjusting, filtering, and delivery to nozzles. The script explains the intricate process from fuel intake at the engine fuel pump to combustion in the chamber, including the crucial steps of oil-fuel heat exchange and filtration. It also touches on the HMU's role in fuel regulation and the importance of precise fuel planning for engine efficiency and safety.
Takeaways
- 🚀 The fuel systems in aircraft engines are crucial for ensuring safe and efficient operation, especially with fossil fuels which are easily ignited.
- 💧 Aircraft fuel systems serve five main purposes: increasing fuel pressure, heating, adjusting, filtering, and delivering fuel to the nozzles.
- 🛠️ The engine fuel pump is the first component in the CFM 56 engine's fuel system, responsible for pressurizing fuel and supplying it to the HMU and fuel nozzles.
- 🔥 The HMU (Hydromechanical Unit) adjusts fuel to the combustion chamber and servo fuel system based on inputs from the EEC and throttle.
- ♻️ Oil fuel coolers in the system facilitate heat exchange between oil and fuel, ensuring ideal combustion temperatures and preventing ice formation in fuel.
- 🚫 The high-pressure shut off valve in the HMU stops fuel flow to the combustion chamber when the throttle lever is turned off or in emergency situations.
- 📏 The fuel flow transmitter measures the amount of fuel passing through it, providing data for engine management and informing pilots about fuel usage.
- 🔍 The fuel nozzle filter cleans the fuel by filtering out organic and metal particles, ensuring a cleaner supply to the mechanical systems.
- 🔄 The fuel system includes a bypass mechanism that allows fuel to bypass filters if they become clogged, preventing system malfunctions.
- ✈️ Understanding the complex fuel systems in aircraft engines is vital for pilots and technicians to operate, maintain, and troubleshoot engines effectively.
Q & A
What is the primary function of aircraft fuel systems?
-The primary function of aircraft fuel systems is to ensure that the appropriate amount of fuel is delivered to the combustion chamber in a safe and efficient manner.
Why is fuel considered more dangerous than other fluids in engines?
-Fuel is considered more dangerous due to its easily ignitable nature, which poses a higher risk compared to other fluids used in engines.
What are the five general purposes of engine fuel systems in aircraft?
-The five general purposes are increasing the pressure of the fuel, heating, adjusting, filtering, and sending it to the fuel nozzles.
How does adjusting fuel in aircrafts relate to pressing the accelerator pedal in cars?
-Adjusting fuel in aircrafts works similarly to pressing the accelerator pedal in cars, as it controls the amount of fuel sent to the engine to manage acceleration.
What is the role of the engine fuel pump in the CFM 56-7 engine fuel system?
-The engine fuel pump in the CFM 56-7 engine fuel system is responsible for supplying pressurized fuel to the HMU and the fuel nozzles, and its filters clean the fuel going to the HMU.
What is the purpose of oil fuel coolers in the fuel system?
-Oil fuel coolers serve to heat the fuel to reach the ideal combustion temperature and to melt any frozen water particles in the fuel, ensuring efficient combustion and preventing system malfunctions.
What does the HMU (Hydromechanical Unit) do in the fuel system?
-The HMU sends fuel adjusted to the combustion chamber and servo fuel system according to reference information from the EEC and throttle, and it also stops fuel flow to the combustion chamber when the fire extinguisher handle is activated.
What is the function of the fuel flow transmitter in the fuel system?
-The fuel flow transmitter measures the amount of fuel passing through it and sends this information to the EEC, which helps in fuel planning and informs the pilot about fuel usage.
How do fuel nozzles contribute to efficient combustion?
-Fuel nozzles ensure proper and efficient combustion by atomizing the adjusted fuel coming through the manifolds into the combustion chamber.
What happens to the fuel that the HMU does not use?
-The fuel that the HMU does not use returns to the IDG oil cooler outlet, then through the oil/fuel heat exchanger back to the fuel pump.
How does the hydromechanical unit manage fuel for the engine servo system?
-The hydromechanical unit provides fuel flow control to various units such as the fuel metering valve, transient bleed valve, and active clearance control valves for both high and low-pressure turbines, as well as variable bleed valves and variable stator vanes.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)