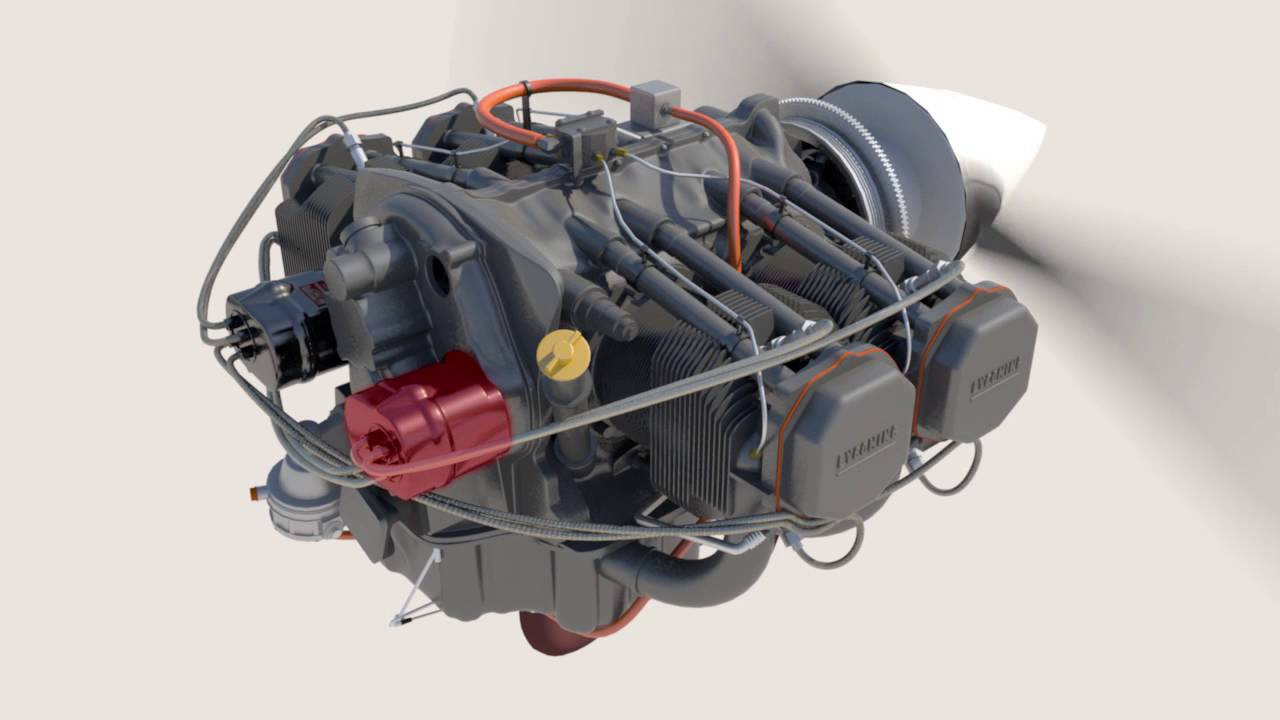
How a Reciprocating Engine Works
Summary
TLDRThe transcript explains the components and operation of an airplane's power plant, focusing on the reciprocating engine's four-stroke cycle: intake, compression, power stroke, and exhaust. It details how the engine converts fuel into thrust, powers aircraft systems, and manages temperature to avoid damage from excessive heat. Key concepts include the roles of the intake and exhaust valves, the significance of air cooling in aircraft engines, and the effects of detonation and pre-ignition. Overall, it highlights the engineering principles that enable safe and efficient flight.
Takeaways
- ✈️ An airplane's powerplant includes the engine, propeller, and accessories that provide thrust and power various aircraft systems.
- 🔧 The heart of the powerplant is the reciprocating engine, which burns gasoline to create power through a series of movements.
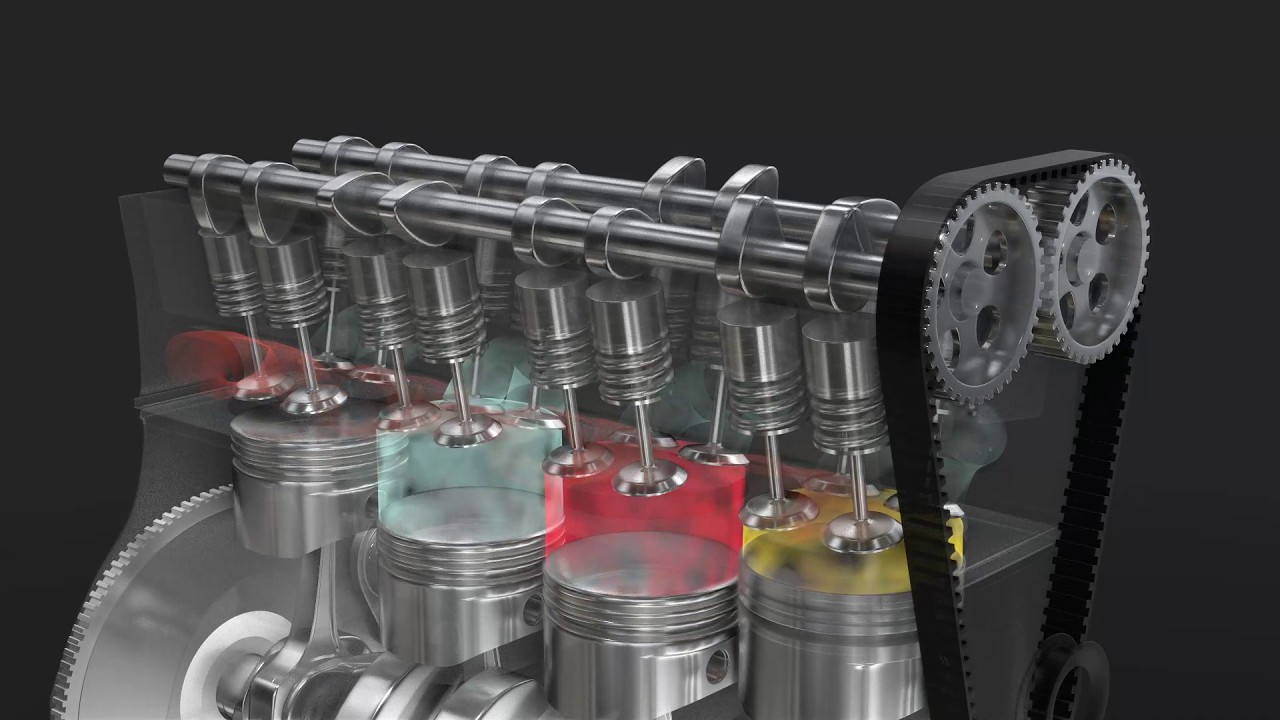
- ⚙️ The engine operates on a four-stroke cycle: intake, compression, ignition (power stroke), and exhaust.
- 🔥 During the ignition stroke, a spark plug ignites the fuel-air mixture, generating heat and pressure that drives the piston down.
- 🔄 The exhaust stroke allows spent gases to escape, completing the cycle and preparing for the next intake.
- 📏 Engine design includes different cylinder arrangements, such as radial, inline, V-type, and opposed, with opposed engines being common in small airplanes.
- ❄️ Airplane engines are typically air-cooled, using outside air to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
- ⚠️ High engine temperatures can lead to loss of power, excessive oil consumption, and potential internal damage.
- 💥 Detonation and pre-ignition are two critical issues that can occur due to improper engine temperature management.
- 🛬 Pilots can reduce engine temperature by lowering the nose to gain speed, thereby improving airflow and cooling.
Q & A
What components are included in an airplane's powerplant?
-An airplane's powerplant includes the engine, propeller, and engine accessories.
What primary function does the powerplant serve for an airplane?
-The powerplant provides thrust, allowing the airplane to accelerate and climb without assistance, while also powering various aircraft systems.
How does a reciprocating engine produce power?
-A reciprocating engine produces power by burning gasoline inside its cylinders, which creates a back-and-forth motion of pistons connected to a crankshaft.
What are the four strokes of the engine cycle?
-The four strokes of the engine cycle are intake, compression, power (ignition), and exhaust.
What role do the intake and exhaust valves play in the engine cycle?
-The intake valve opens to allow the fuel-air mixture into the cylinder, and the exhaust valve opens to let out spent exhaust gases after the power stroke.
What types of cylinder arrangements are common in reciprocating engines?
-Common cylinder arrangements in reciprocating engines include radial, inline, V-type, and opposed configurations.
Why are opposed engines commonly used in small airplanes?
-Opposed engines are favored in small airplanes because they produce good power-to-weight ratios without generating excessive drag.
How does an airplane engine stay cool?
-Airplane engines are air-cooled by routing outside air across the cylinders, aided by fins on each cylinder that enhance cooling efficiency.
What can excessively high engine temperatures lead to?
-Excessively high engine temperatures can cause a loss of power, excessive oil consumption, and potential permanent internal damage.
What are detonation and pre-ignition in engine operation?
-Detonation is when fuel explodes suddenly in the cylinder instead of burning evenly, while pre-ignition occurs when fuel ignites spontaneously before the spark plug fires, both leading to engine knocking.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)