Heat and Temperature
Summary
TLDRIn this tutorial, Professor Dave explores the concepts of heat and temperature, providing a molecular-level understanding. Temperature is a measure of the heat energy available for work in a system, directly related to the kinetic energy of particles. He explains how heat flows from hotter to cooler objects, reaching thermal equilibrium. The video covers how temperature affects the movement of molecules, causing thermal expansion, and the role of energy transfer in processes like friction. By the end, viewers gain a clearer understanding of heat as energy in transit, setting the stage for deeper study in thermodynamics.
Takeaways
- 😀 Heat and temperature are related to the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules in a system.
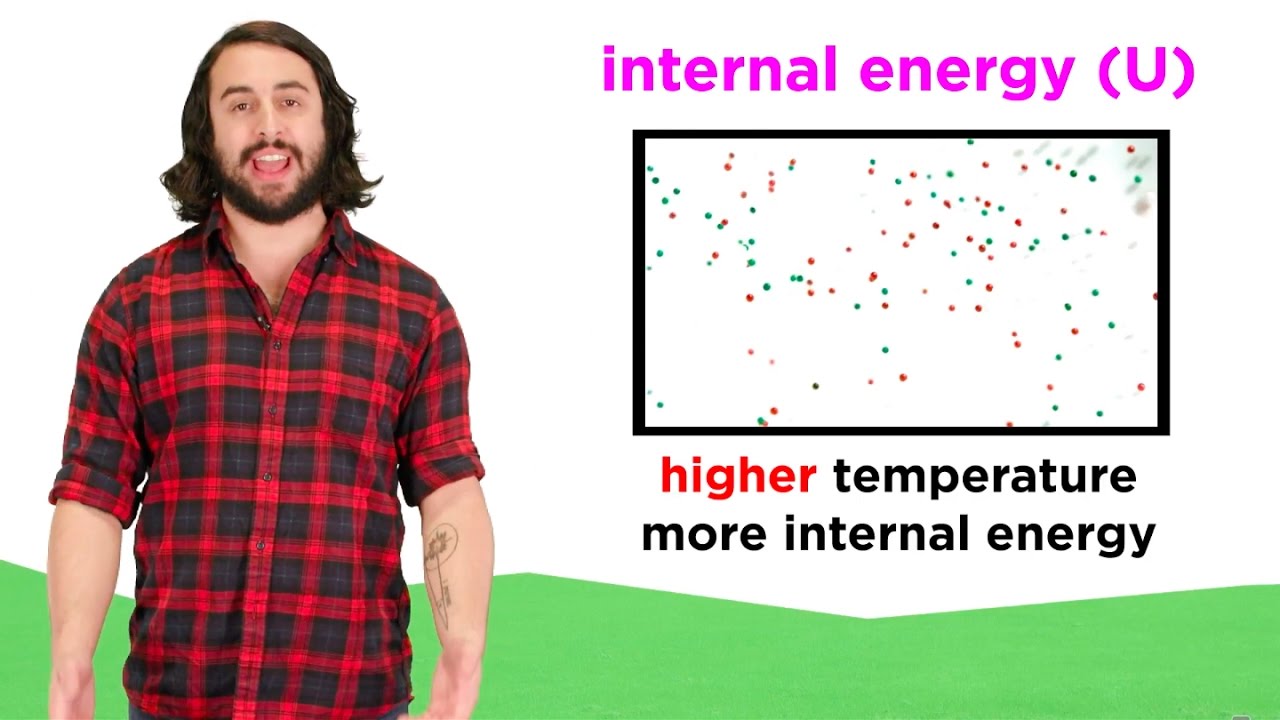
- 😀 Temperature measures the amount of heat energy available for work in a system.
- 😀 Higher temperatures mean faster-moving particles in the system.
- 😀 The kinetic energy of molecules is distributed among translational, rotational, and vibrational motions.
- 😀 Heat always flows from hot objects to cooler ones until thermal equilibrium is reached.
- 😀 Thermometers measure temperature by reaching thermal equilibrium with the environment.
- 😀 Thermal expansion occurs as temperature increases, causing all phases of matter (solid, liquid, gas) to expand.
- 😀 Heat energy is transferred during collisions or through friction, such as when rubbing your hands together.
- 😀 Heat transfer always changes the temperature of an object.
- 😀 Heat is measured in joules, like any other form of energy.
- 😀 Hot objects feel hot and cold objects feel cold because they transfer heat to or from your body, respectively.
Q & A
What is the fundamental concept that we need to understand before learning about thermodynamics?
-The fundamental concept to understand is heat and temperature at the molecular level, as they are key to learning about thermodynamics.
Why is simply saying something is 'hot' or 'cold' not enough in scientific terms?
-In science, we need to quantify temperature with numbers to precisely describe how hot or cold something is, rather than using subjective terms like 'hot' or 'cold'.
What does temperature physically measure?
-Temperature measures the amount of heat energy available for work in a system, which is related to the average kinetic energy of the atoms and molecules within that system.
How is the kinetic energy of molecules related to temperature?
-Higher temperatures mean that molecules are moving faster, which corresponds to greater kinetic energy. This kinetic energy manifests in different forms, including translational, rotational, and vibrational motion.
What happens when heat flows from a hotter object to a cooler one?
-When heat flows from a hotter object to a cooler one, the molecules of the hotter object transfer some of their kinetic energy to the cooler object's molecules, which continues until thermal equilibrium is reached.
What is thermal equilibrium?
-Thermal equilibrium is the state in which two objects or systems are at the same temperature, meaning no net heat flows between them.
How do thermometers work to measure temperature?
-Thermometers measure temperature by allowing heat from the environment to flow into the thermometer fluid. This increases the kinetic energy of the atoms in the fluid, causing the fluid to expand until it reaches thermal equilibrium with the environment.
What is thermal expansion?
-Thermal expansion is the phenomenon where all phases of matter—solid, liquid, or gas—expand when heated, due to the increased kinetic energy of their molecules.
What causes heat to be generated during a collision?
-Heat is generated during a collision because the kinetic energy of the particles is transferred to other particles, causing them to move faster, which results in the generation of heat.
How does friction generate heat?
-Friction generates heat by causing the kinetic energy of the particles in contact to increase, which results in the production of heat energy.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

DIFERENÇA ENTRE CALOR E TEMPERATURA | Prof. Vinicius Pessanha
Internal Energy

Heat Capacity, Specific Heat, and Calorimetry

Termologia - Conceitos Iniciais - Aula 01

Calor sensível e calor latente conceitos para entender definitivamente

Regulation of Gene Expression: Operons, Epigenetics, and Transcription Factors
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
