Teorías sobre la toma de decisiones - Adopción de decisiones entre alternativas
Summary
TLDRThis video discusses various decision-making theories, including rationality, bounded rationality, and intuition. It explores how decisions are made in organizations, highlighting structured and unstructured problems, and the types of decisions required for each. The video also examines certainty, risk, and uncertainty in decision-making, along with the influence of different managerial styles, such as directive, analytical, conceptual, and behavioral. Common biases and errors in decision-making are also discussed, with practical advice on improving the decision-making process, emphasizing logic, consistency, and the balance of analytical and intuitive thinking for better organizational outcomes.
Takeaways
- 😀 Rational decision-making involves logical and consistent choices aimed at maximizing value within specific constraints.
- 😀 Bounded rationality refers to decision-making that is limited by an individual's ability to process information, leading to satisfactory rather than optimal solutions.
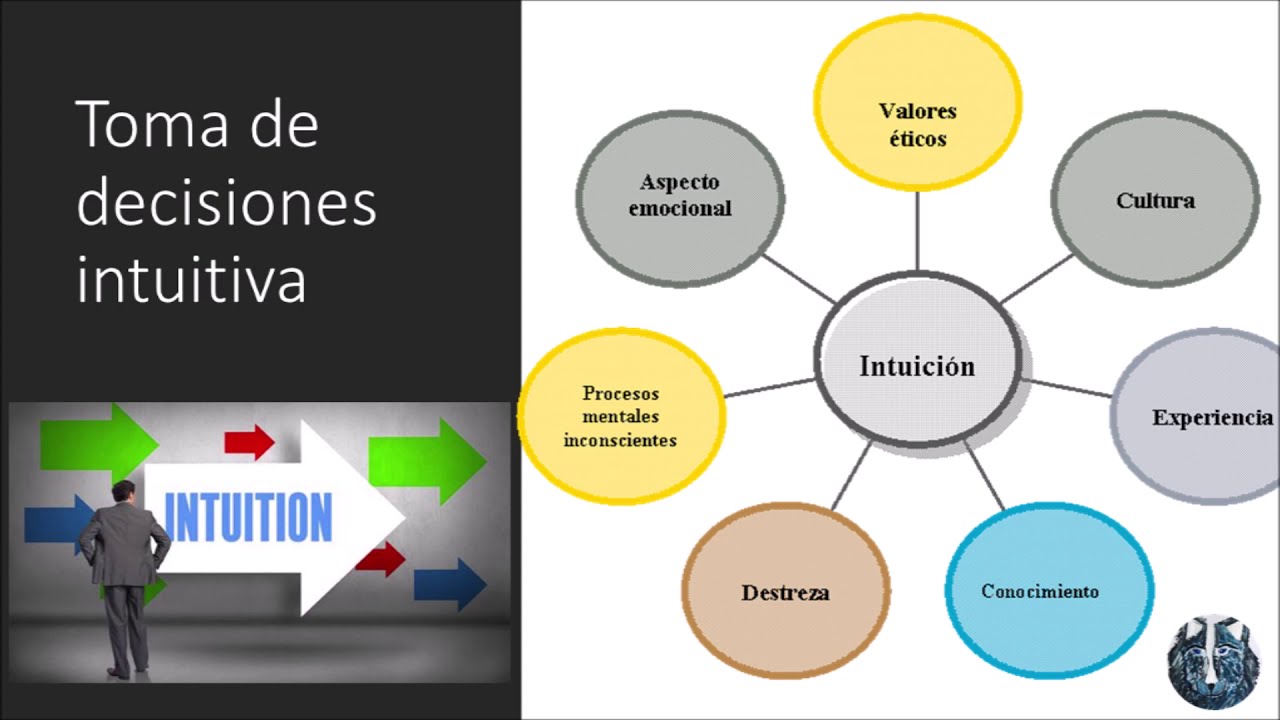
- 😀 Intuitive decision-making relies on experience, judgment, emotions, and unconscious processes to make decisions, often without fully analyzing all information.
- 😀 Structured problems are simple, easy to define, and solved through repetitive, programmed decisions such as customer complaints or inventory issues.
- 😀 Unstructured problems are complex, novel, and require unique, non-programmed decisions, such as opening a new plant in a foreign country.
- 😀 As you move up in an organization, problems become less structured, and decisions become more unprogrammed and complex.
- 😀 Decision-making occurs under conditions of certainty, risk, or uncertainty. Certainty allows for confident decision-making, while risk involves estimating probabilities, and uncertainty means decisions are made without knowing outcomes or probabilities.
- 😀 In uncertain scenarios, different strategies lead to varying results, where optimistic managers may focus on maximizing potential, while pessimistic ones prioritize minimizing risk.
- 😀 Decision-making styles vary based on tolerance for ambiguity and thinking style: directive (rational and quick), analytical (rational with more information), conceptual (intuitive and creative), and behavioral (intuitive, team-focused).
- 😀 Common decision-making biases include overconfidence, immediate gratification, anchoring, selective perception, and confirmation bias, which can distort judgment and decision outcomes.
- 😀 To improve decision-making, focus on what is important, be logical and consistent, gather necessary information, combine objective and subjective thinking, and make decisions confidently when required.
Q & A
What is the rational decision-making model and its assumptions?
-The rational decision-making model assumes decisions are logical, consistent, and made to maximize value under specific constraints. It assumes the problem is clearly defined, there is a single goal, all alternatives are known, preferences are clear, and there are no time or cost constraints.
How does bounded rationality differ from rational decision-making?
-Bounded rationality suggests that while decisions are rational, they are limited by the individual's ability to process information. Instead of aiming for an optimal solution, a satisfactory one is chosen due to limited resources or incomplete information.
What factors influence intuitive decision-making?
-Intuitive decision-making is influenced by experience, knowledge, skill, unconscious mental processes, emotions, ethical values, and cultural factors.
What is the difference between structured and unstructured problems?
-Structured problems are simple, easy to define, and have clear solutions, often solved with programmed decisions. Unstructured problems are complex, new, or ambiguous, requiring tailored, non-programmed decisions.
What types of problems require programmed decisions?
-Programmed decisions are needed for structured problems, such as customer complaints or inventory management, where solutions are predefined and repetitive.
What decision-making approach is suitable for problems with high uncertainty?
-For problems with high uncertainty, intuitive decision-making or non-programmed decisions are more suitable because they rely on experience and judgment rather than clear data.
How do certainty, risk, and uncertainty affect decision-making?
-In a certainty situation, outcomes are known. In a risk situation, probabilities of outcomes are estimated but not guaranteed. In uncertainty, neither the outcomes nor probabilities can be reasonably predicted.
How do decision-makers choose strategies under uncertainty?
-Decision-makers may choose strategies based on their risk tolerance. For example, an optimistic manager may choose a strategy that maximizes the potential outcome, while a pessimistic manager may choose one that minimizes potential loss.
What are the four decision-making styles described in the script?
-The four decision-making styles are: Directorial (quick and logical decisions), Analytical (gathers and processes more information), Conceptual (intuitive and creative, looking for long-term solutions), and Behavioral (focuses on teamwork and the impact on others).
What are some common cognitive biases that affect decision-making?
-Common cognitive biases include overconfidence, immediate gratification, anchoring bias, selective perception, confirmation bias, and sunk cost fallacy. These biases can lead to faulty decisions if not recognized and addressed.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)