Types of Information Systems (TPS, MIS, and DSS)
Summary
TLDRThis video script explores the most common types of information systems in organizations: Transaction Processing Systems (TPS), Management Information Systems (MIS), Decision Support Systems (DSS), and Executive Support Systems (ESS). TPS records daily transactions, serving as the primary data source for other systems. MIS consolidates data for routine summary reports, aiding middle management in semi-structured decision-making. DSS and ESS support senior management in unstructured, long-term planning decisions, with DSS focusing on problem-specific solutions and ESS providing strategic forecasting.
Takeaways
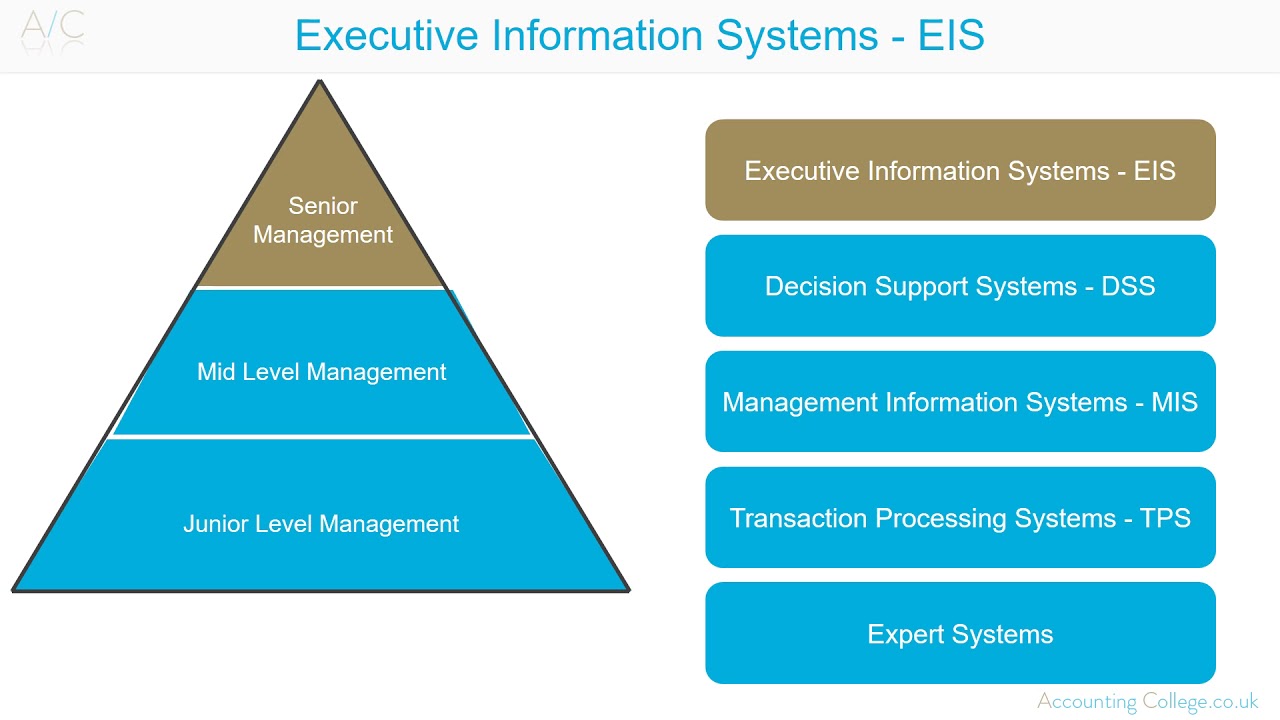
- 💼 **Transaction Processing System (TPS)**: TPS is a system used for recording business transactions and is composed of people, procedures, software, databases, and devices.
- 🛒 **Definition of Transaction**: In TPS, a transaction is any business-related exchange of goods, services, or money, including employee payments, sales, supplier payments, and ATM withdrawals.
- 🏢 **Operational Level**: TPS serves the operational level of an organization, which includes employees at the bottom of the hierarchy, such as cashiers, bank tellers, and nurses.
- 📊 **TPS Functions**: TPS is responsible for data collection, sorting, updating, storing, modifying, and retrieving transaction-related information, as well as generating reports and summaries.
- 👥 **Examples of TPS**: Payroll systems and online reservation systems for airlines are examples of TPS, where the latter allows for real-time booking and transaction recording.
- 🔁 **Batch vs. Real-Time Processing**: TPS can operate in batch mode, processing transactions in groups with a delay, or in real-time, processing each transaction instantly with no delay.
- 📚 **Management Information System (MIS)**: MIS provides routine information to managers and decision-makers, typically used at the tactical level of an organization's management hierarchy.
- 📈 **MIS Importance**: MIS is crucial for operations management and decision-making, as it consolidates data from TPS to generate summary and exception reports.
- 🏛️ **MIS Example**: A university student management information system is an example of MIS, used to generate reports on student registration status for eligibility in exams.
- 🌐 **Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)**: ERP systems integrate various business operations into a unified set of programs, overcoming information silos and enhancing data sharing across organizational units.
- 🛠️ **Decision Support System (DSS)**: DSS aids in problem-specific decision-making, using inputs from both internal (TPS and MIS) and external systems, and is commonly used by senior management for non-routine decisions.
- 🏦 **DSS Example**: A bank loan management system is an example of DSS, used to assess loan applicant creditworthiness and predict loan recovery likelihood.
- 📊 **DSS vs. MIS**: While MIS helps an organization do things right, DSS helps managers do the right thing, focusing on effective decision-making for long-term planning.
- 👨💼 **Executive Support Systems (ESS)**: ESS supports executives at the top management level, such as a sales forecasting system useful for the organization's top decision-makers.
Q & A
What are the three most common types of information systems mentioned in the video?
-The three most common types of information systems mentioned are Transaction Processing Systems (TPS), Management Information Systems (MIS), and Decision Support Systems (DSS).
What is a Transaction Processing System (TPS) and what does it include?
-A Transaction Processing System (TPS) is an organized collection of people, procedures, software, databases, and devices used to perform and record business transactions. It includes activities such as payments to employees, sales to customers, payments to suppliers, or cash withdrawals from an ATM.
Who primarily uses Transaction Processing Systems and why?
-Transaction Processing Systems are primarily used at the operational level of an organization by employees such as cashiers, bank tellers, nurses, and others who are involved in performing day-to-day business transactions.
Can you provide an example of a TPS and explain its function?
-An example of a TPS is a payroll system. It collects input data such as the number of employee hours worked and the pay rate, and its primary output consists of paychecks and related reports for the organization's management and required government documents.
What are the two types of transaction processing systems discussed in the video?
-The two types of transaction processing systems discussed are batch processing TPS and real-time processing TPS. Batch processing involves collecting and processing transactions in groups, often with a time delay, while real-time processing handles each transaction immediately.
How does a Management Information System (MIS) differ from a Transaction Processing System (TPS)?
-A Management Information System (MIS) differs from a TPS in that it consolidates data and information from the TPS to generate routine summary and exception reports, which are used by middle management for semi-structured decision making.
What is the purpose of a Decision Support System (DSS) and who typically uses it?
-A Decision Support System (DSS) is used to support problem-specific decision making and is commonly used by senior management to make non-routine decisions and provide solutions to unique and frequently changing problems.
Can you give an example of how a DSS is used in a business context?
-An example of DSS use in business is a bank loan management system, which verifies the credit of loan applicants and predicts the likelihood of loan recovery, aiding in effective decision making regarding loans.
What is the main issue that ERP systems aim to solve in organizations?
-Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems aim to solve the issue of information silos by providing a set of integrated programs that manage vital business operations, making it easier to use and more effective, and allowing for data sharing across all organizational units.
How does a DSS help in making decisions compared to an MIS?
-A DSS helps in making effective decisions by focusing on unstructured decision making that concerns long-term planning, while an MIS helps an organization do things right by providing structured decision support based on defined rules and guidelines.
What is the role of an Executive Support System (ESS) in an organization?
-An Executive Support System (ESS) supports executives, typically at the topmost level of the organization's management hierarchy, by providing tools for tasks such as sales forecasting, aiding in better decision making.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Executive Information Systems - A-Z of business terminology

KELOMPOK 7-SISTEM INFORMASI MANAJEMEN PADA PERUSAHAAN SHOPEE

SISTIM INFORMASI DAN KOMUNIKASI ORGANISASI (PART 1)

Jenis-jenis Sistem Informasi
Management Information Systems - Basics

#1 Sistem Informasi Akutansi dan Keuangan - Pertemuan 1 | Konsep Dasar Sistem Informasi
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)