Stone Age | Prehistoric age | Paleolithic | Mesolithic | Neolithic | Stone Age Humans
Summary
TLDRThe Stone Age, spanning nearly three million years, is divided into Paleolithic, Mesolithic, and Neolithic periods. It saw the evolution from Homo Habilis to Homo Sapiens, the use of stone tools, and a nomadic lifestyle. The Paleolithic marked the discovery of fire and cave art, while the Mesolithic introduced refined tools and the domestication of dogs. The Neolithic Revolution brought farming, permanent settlements, and the advent of crafts and the wheel, culminating in the end of the Stone Age with the Bronze Age.
Takeaways
- 🗺️ The Stone Age is the earliest period of human culture, beginning almost three million years ago with the use of stone tools.
- 🕰️ It is divided into three periods: the Paleolithic, Mesolithic, and Neolithic, each representing different stages of human development.
- 🦴 The Paleolithic, or 'Old Stone Age,' saw the evolution of Homo Sapiens from early Homo species and the use of basic stone tools.
- 🔥 Fire was discovered around 500,000 years ago, providing warmth, protection, and a means to cook food.
- 🏞️ Paleolithic people were nomadic, moving in search of food and using caves as temporary shelters.
- 🛠️ Early stone tools were rudimentary, made by striking stones together, and later improved with handles for better utility.
- 🎨 Cave paintings and decorations were part of the spiritual and cultural life of Paleolithic people.
- 🏡 The Mesolithic, or 'Middle Stone Age,' saw the construction of permanent dwellings and the development of finer stone tools.
- 🎣 Fishing and the domestication of dogs were significant advancements during the Mesolithic period.
- 🌾 The Neolithic, or 'New Stone Age,' marked the beginning of agriculture and the domestication of animals, leading to more permanent settlements.
- 🏺 Pottery, weaving, and the invention of the wheel were key crafts and technologies of the Neolithic period.
- 🛑 The Stone Age concluded with the advent of metalworking, transitioning humanity into the Bronze Age.
Q & A
What is the Stone Age and why is it called so?
-The Stone Age is the earliest period of human culture, beginning almost three million years ago with the first evidence of humans using stone tools. It is called the Stone Age because the primary material for making tools during this period was stone.
How is the Stone Age divided into different periods?
-The Stone Age is divided into three distinct periods: the Paleolithic Period, the Mesolithic Period, and the Neolithic Period, each characterized by different stages of human development and tool-making techniques.
What does the term 'Paleolithic' mean and when did it start?
-The term 'Paleolithic' means 'Old Stone Age' and it started about 2.5 million years ago when early humans appeared in Africa, lasting until roughly 12,000 years ago.
Which human species are mentioned in the Paleolithic Period and what was their significance?
-Homo Habilis, Homo Erectus, and Neanderthals are mentioned in the Paleolithic Period. Homo Habilis was the first true human species to evolve from apes, Homo Erectus was likely the first to control fire and cook food, and Neanderthals were a commonly found extinct human species.
How did the lifestyle of Paleolithic people differ from modern humans?
-Paleolithic people were nomadic, moving from place to place in search of food, and spent their time on direct subsistence activities such as gathering edible plants, fruits, berries, nuts, and scavenging meat from dead animals. They also used caves as temporary shelters.
What was the significance of fire in the Paleolithic Period?
-Fire was significant in the Paleolithic Period as it reduced mortality rates, provided protection against predators, and allowed for cooking food, which improved nutrition and health.
What types of tools did Stone Age people use and how did they make them?
-Stone Age people initially used basic stone tools made by striking one stone with another to create sharp edges. Over time, they began attaching handles to stones, creating primitive hand axes, and developed more sophisticated tools like awls for joining pieces together.
What is the Mesolithic Period and how did it differ from the Paleolithic?
-The Mesolithic Period, or 'Middle Stone Age,' saw some humans giving up the nomadic lifestyle and starting to build permanent dwellings near bodies of water. They developed finer, smaller stone tools, and hunting and fishing became more efficient with the creation of bows, arrows, hooks, harpoons, and fishing nets.
What advancements in tool-making and lifestyle occurred during the Neolithic Period?
-The Neolithic Period, or 'New Stone Age,' marked the transition from a nomadic, hunter-gatherer lifestyle to farming and animal domestication. People developed tools for farming, such as plows, and domesticated animals like sheep, goats, and pigs, leading to more permanent settlements and the development of organized communities.
How did the domestication of animals and the beginning of farming impact human society during the Neolithic Period?
-The domestication of animals and the beginning of farming led to humans settling in one place for longer periods, forming permanent villages and organized communities. This allowed for the storage of food and trade of material goods, and the development of crafts such as pottery, basketry, and weaving.
What is considered the most remarkable invention of the Neolithic Period and why?
-The invention of the wheel is considered the most remarkable of the Neolithic Period because it greatly improved transportation and facilitated trade, agriculture, and the movement of people and goods.
How did the Stone Age come to an end?
-The Stone Age ended with the advent of the Bronze Age, which began when humans started working with metal, specifically bronze, to make tools and weapons, marking a significant advancement in technology and culture.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

The Three Stone Age Eras

A Pré-História - Paleolítico, Neolítico, Mesolítico e Idade dos Metais

MASA PRAAKSARA || |Periodisasi Secara Arkeologis
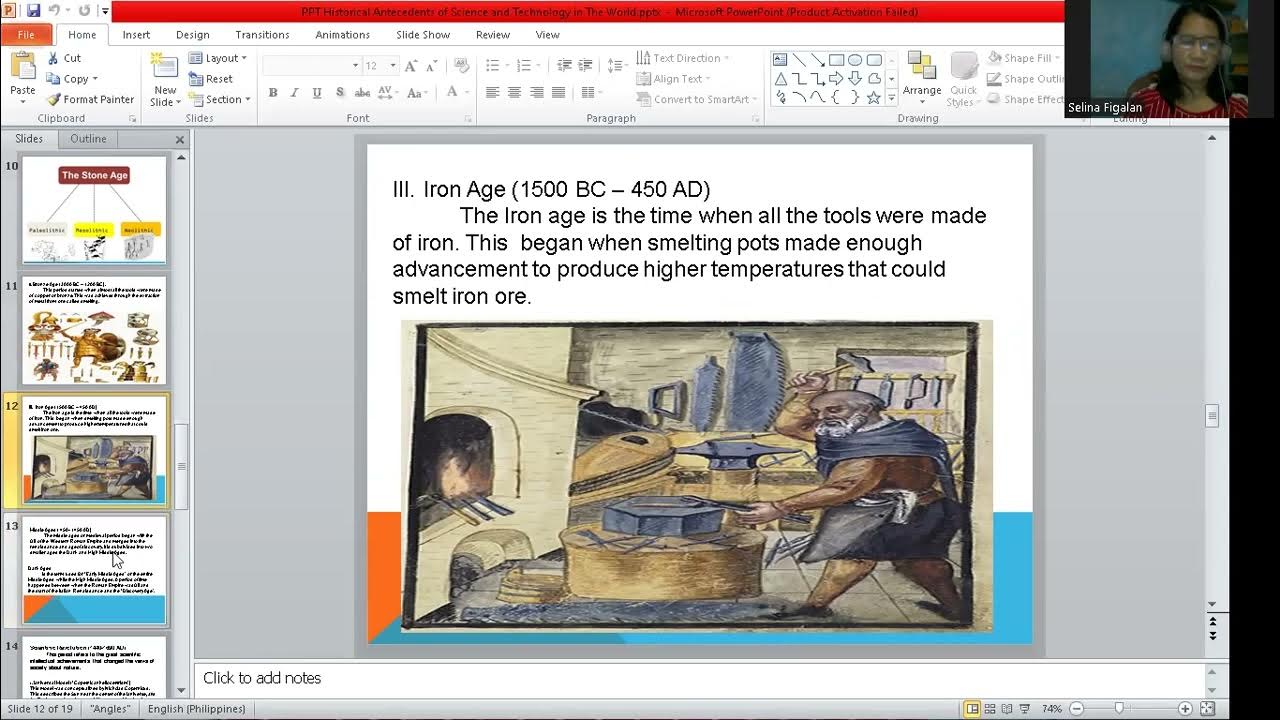
Historical Antecedents of Science and Technology in the World

Manusia Prasejarah | Pembagian Zaman Batu dan Logam (Arkeologi & Geologi) | IPS Kelas 8

How to Create Trending Historical Documentaries Using Kling AI 3D Animation (A-Z Guide)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)