Psychology's Roots
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into the intriguing history of psychology, tracing its philosophical roots from ancient Greece to its emergence as a scientific discipline in the 19th century. It highlights key figures like Aristotle, Plato, and John Locke, who pondered the nature of knowledge. The script also discusses the birth of psychology with Wilhelm Wundt's laboratory experiments and the contrasting schools of thought, including structuralism and functionalism. Influential psychologists such as Freud, Watson, Maslow, and Skinner are mentioned, each contributing unique perspectives that have shaped modern psychology, now a popular academic field.
Takeaways
- 📚 Psychology has a rich history, with roots in philosophy and ancient civilizations, but as a scientific discipline, it is relatively new.
- 🧐 Ancient Greek philosophers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle were among the first to ponder the workings of the human mind and the nature of knowledge.
- 🌐 Psychology's transition from philosophy to science was influenced by the empiricism of John Locke, who proposed the 'tabula rasa' theory of the mind.
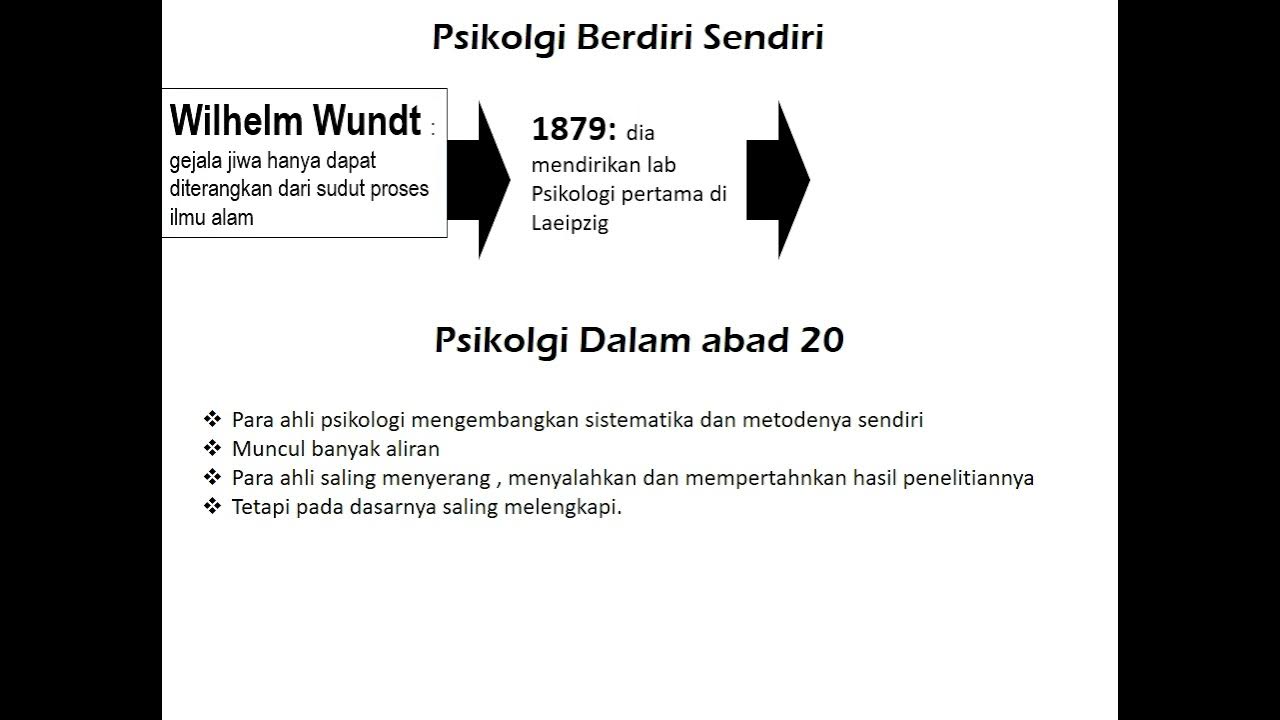
- 🔬 The formal emergence of psychology as a scientific discipline is attributed to Wilhelm Wundt, who conducted the first psychological experiment in Leipzig, Germany.
- 🤔 Early psychological schools like structuralism and functionalism emerged, focusing on different aspects of the mind: its structures and their functions, respectively.
- 🔍 Structuralism, advocated by Edward Titchenor, studied the basic cognitive structures, while functionalism, led by William James, examined the purpose and evolutionary function of these structures.
- 📱 An analogy to illustrate the difference: a structuralist would study the individual components of an iPhone, whereas a functionalist would study why each part was designed and its purpose.
- 🌟 The field of psychology has been shaped by numerous influential figures, including Sigmund Freud, G. Stanley Hall, Margaret Washburn, Mary Calkins, Max Wertheimer, John B. Watson, Abraham Maslow, and B.F. Skinner.
- 🧠 Freud's psychoanalytic theory emphasized the importance of the unconscious mind, while Watson's behaviorism focused on observable behavior, rejecting the study of the mind.
- 💡 Maslow's humanistic perspective countered the determinism of psychoanalysis and behaviorism, advocating for the study of positive aspects of human behavior and potential.
- 📈 Today, psychology is recognized as both an academic discipline and an applied science, with general psychology being the second most popular college major in the US.
Q & A
Who made the statement 'psychology has a long past but a short history'?
-Renowned German psychologist Herbie.
What does the statement 'psychology has a long past but a short history' mean?
-It means that while philosophers have been studying the human mind for thousands of years, psychology as a scientific discipline is relatively new.
What are the pre-scientific origins of psychology?
-The pre-scientific origins of psychology can be traced back to ancient philosophers who studied the human mind, such as those in India, China, the Middle East, and Europe.
Who were some of the key ancient Greek philosophers that contributed to the early study of the human mind?
-Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle were key ancient Greek philosophers who asked fundamental questions about the human mind.
What was the difference between Socrates' and Aristotle's views on knowledge?
-Socrates, along with Plato, argued that knowledge is innate, while Aristotle believed that knowledge is learned through observation and experience.
What is John Locke's theory regarding knowledge, and how did it influence modern psychology?
-John Locke argued that the mind at birth is a 'tabula rasa' or blank slate, and that knowledge comes from experience. This idea paved the way for modern empiricism, the theory that all knowledge is derived from our senses.
Who is considered to have conducted the first psychology experiment and what was it about?
-Wilhelm Wundt is considered to have conducted the first psychology experiment, which tested how quickly people reacted to hearing a noise.
What are structuralism and functionalism in psychology?
-Structuralism, led by Edward Titchener, focused on studying the basic cognitive structures of the mind, using introspection. Functionalism, led by William James, focused on the purpose and evolved functions of these structures from an evolutionary perspective.
How did William James' approach to psychology differ from that of Edward Titchener?
-William James cared about the purpose and function of mental structures (functionalism), while Edward Titchener focused on identifying and describing the basic cognitive structures of the mind (structuralism).
Who are some influential figures in the history of psychology mentioned in the script?
-Influential figures mentioned include Sigmund Freud, G. Stanley Hall, Margaret Washburn, Mary Calkins, Max Wertheimer, John B. Watson, Abraham Maslow, and B.F. Skinner.
What were the major early psychological approaches and their main focuses?
-Major early approaches included psychoanalysis by Freud, focusing on the unconscious mind; behaviorism by Watson, focusing on observable behavior; and humanistic psychology by Maslow, focusing on individual choice and human potential.
How has psychology evolved from its pre-scientific roots to its current status?
-Psychology evolved from philosophical questions about the mind in ancient times to a scientific discipline in the 19th century, incorporating various approaches and theories. Today, it is both an academic discipline and an applied science.
What is the popularity of psychology as a college major in the US?
-General psychology is the second most popular college major in the US, according to USA Today, behind Business Administration and Management.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Psicologia da Educação - O que é psicologia: Um pouco da sua história

Ciencias Sociales Historia del pensamiento sociológico

Sejarah Lahirnya Ilmu Psikologi | Seri Sejarah Psikologi
Sejarah Perkembangan Psikologi

Perkembangan Ilmu Geografi - Kurikulum Merdeka Klas X Fase E

O que é "VERDADE"? A Filosofia explica
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)