86.Overviu PMK 212/2019 tentang Jurnal Akuntansi Pemerintah Pusat
Summary
TLDRThe Indonesian government's financial accounting is guided by PMK 212/2016, which sets general accounting principles for recording transactions, financial events, and reporting. It introduces various types of journals, including transactional, adjustment, and Bogor journals. The 2017 Pemkab 212 replaces the 2013 PMK 215, updating accounting practices in Sakti applications. The government accounting cycle involves identification, recording, summarizing, and financial reporting. It uses single and double-entry systems, standard account charts, and integrated applications to ensure proper financial management and accountability, reflecting the separation of administrative and financial powers as per the 2004 State Treasury Law.
Takeaways
- 📚 The script discusses the accounting practices of the government, specifically focusing on the PMK 212 of 2016, which regulates the general principles of government accounting.
- 📋 PMK 212 of 2016 outlines the procedures for recording transactions and financial events, as well as the submission of financial reports, in accordance with government accounting standards and systems.
- 🔍 The script mentions that PMK 212 of 2016 includes various types of journals such as transaction journals, adjustment journals, and Bogor journals.
- 📈 PMK 212 of 2016 was replaced by PMK 215 of 2013, which only covers government accounting and has been used in the Sakti application.
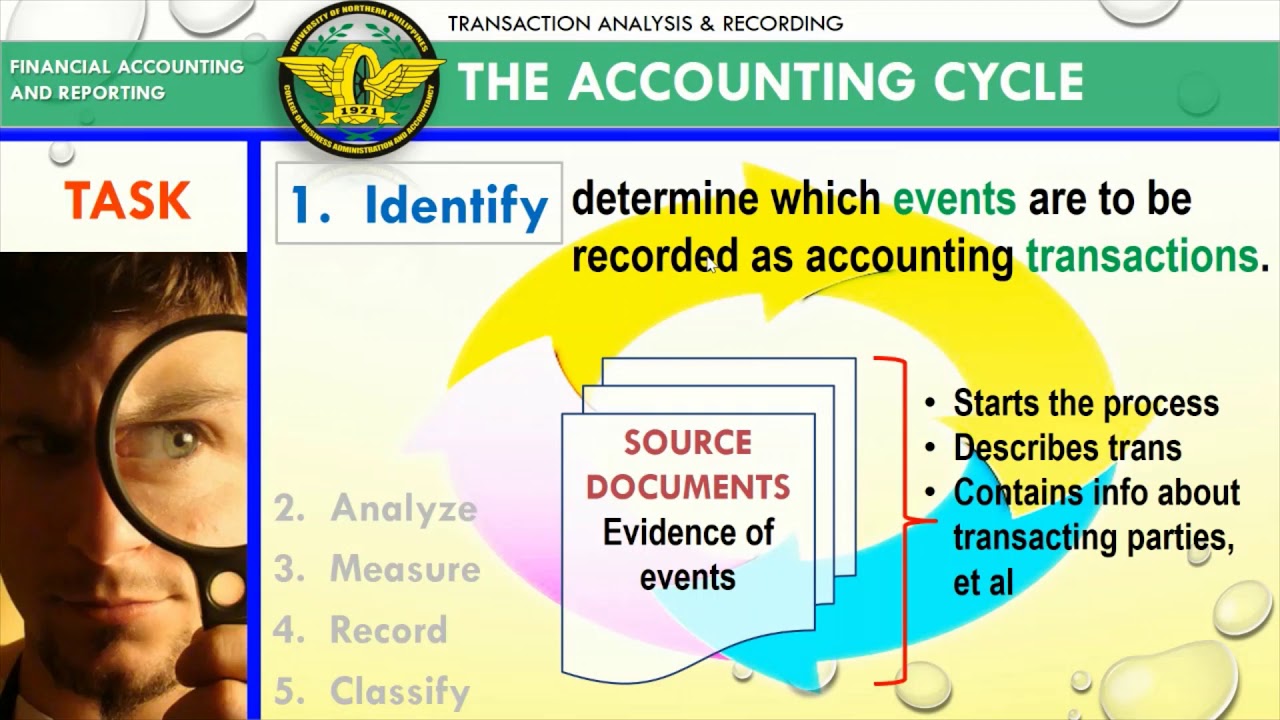
- 🔄 The accounting cycle of the central government is generally divided into four stages: identification, recording and measurement, summarizing financial reports, and preparing financial reports.
- 📊 The script highlights the characteristics of government accounting journals, including the use of a single entry system for budget control and a double entry system for all other journals.
- 🔢 The use of codification or classification of transactions according to PMK is mentioned, which aligns with the standard chart of accounts.
- 📘 The script discusses the use of general ledgers for classifying transactions from journals and special books for transactions from cash journals.
- 💼 The basic equation of government accounting is assets equal to liabilities plus equity, which determines the normal balance of accounts.
- 🏦 The script explains the separation of duties between administrative authority and financial authority, as outlined in Law No. 1 of 2004 on State Treasury.
- 🔗 The connection between accounting records is made through inter-entity accounts, such as receivables from other entities and payables to other entities.
Q & A
What is the main focus of PMK 212/2016?
-PMK 212/2016 focuses on the general principles of accounting for the central government of Indonesia, including the recording of financial transactions and events, and the submission of financial reports in accordance with government accounting standards.
What are the types of journals mentioned in PMK 212/2016?
-The types of journals mentioned include the journal of transactions, journal of financial transactions, journal of transitory transactions, journal of adjustments, and the journal of Bogor.
What replaced PMK 212/2016?
-PMK 212/2016 was replaced by Pemkab 212/2017, which updated the accounting practices for the government, addressing the non-compliance issues that had been used in the Sakti application.
How is the accounting cycle for the central government of Indonesia generally divided?
-The accounting cycle for the central government is generally divided into four stages: identification of transactions, recording and measurement of financial transactions, preparation of financial summaries, and preparation of financial reports.
What are the characteristics of government accounting journals as described in the script?
-The characteristics include the use of a single-entry system for budget control, a double-entry system for all other journals except for the budget journal, the use of codification for transaction identification, and the use of ledger books for classifying transactions.
What is the significance of the single-entry system in government accounting?
-The single-entry system is used for managerial control of transactions and budgeting. It simplifies the accounting process by recording transactions in one account only, which is particularly useful for budgetary control.
How does the double-entry system differ from the single-entry system in government accounting?
-The double-entry system records transactions in at least two accounts, reflecting both the debit and credit aspects of financial events, providing a more comprehensive and balanced view of the government's financial activities.
What role does codification play in the identification of transactions in government accounting?
-Codification is used to classify transactions according to the Standard Chart of Accounts (SCA), ensuring consistency and standardization in the recording and reporting of financial data.
What is the purpose of using ledger books in government accounting?
-Ledger books are used to classify transactions that originate from journals, such as the general ledger for all transactions and specific books for transactions involving cash or specific accounts.
How does the script describe the relationship between accounting and the separation of powers in government finance?
-The script describes the separation of administrative authority and accounting authority, where administrative authority is responsible for budget execution and payment orders, while accounting authority manages cash disbursements and receipts, ensuring transparency and accountability in financial management.
What is the significance of the integration of accounting systems in government finance as mentioned in the script?
-The integration of accounting systems allows for a more efficient and effective management of financial transactions and reporting, facilitating the connection between different entities and ensuring the accuracy and consistency of financial records.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Pengantar Akuntansi 1 - Pengantar Akuntansi dan Perusahaan Part 1

Meaning and Definitions & Attributes of Accounting | Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 1 | CBSE 2024

Akuntansi Sebagai Sistem Informasi | Ekonomi Kelas 12 - EDURAYA MENGAJAR
Transaction & Analysis Recording, Part I

Lesson 008 - Accounting Concepts and Principles

FABM1 Week 2 Grade 11 - Accounting Concepts and Principles
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)