Pedigree for determining probability of exhibiting sex linked recessive trait | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRThe video script explains the inheritance of color blindness through a pedigree chart, using symbols to represent gender and the trait. It details how to deduce the genotypes of Tom and Barbara, a couple with a colorblind son. By analyzing the family's genetic makeup, the instructor calculates the probability of their next child being colorblind as 50%, using a Punnett square to illustrate the possible genetic outcomes.
Takeaways
- 🔍 The video discusses a pedigree chart representing the inheritance of color blindness through three generations.
- 👦 The standard convention in the chart is that a square represents a male, and a circle represents a female.
- 🌈 If a symbol is colored in, it indicates that the individual exhibits the trait, specifically color blindness in this context.
- 🌟 Color blindness is identified as an X-linked recessive trait, meaning it is more likely to affect males due to the way it is inherited.
- 🤔 The probability of Barbara's next child being colorblind is the main question posed in the video.
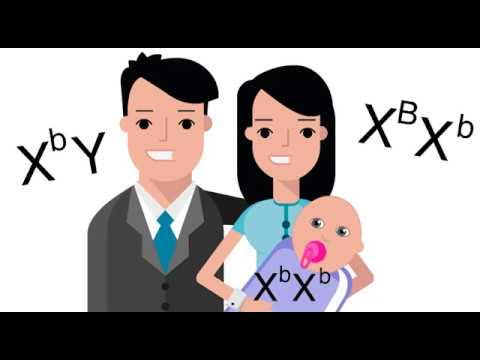
- 👨 Tom, being male and colorblind, has the genotype XcY, where 'c' represents the colorblind allele.
- 👩 Barbara, being female, has two X chromosomes, and her genotype can be deduced from her parents' genotypes.
- 👴 Bill, Barbara's father, must have passed on an X chromosome with the colorblind allele, as he is colorblind.
- 👵 Bonnie, Barbara's mother, could either be a carrier (XcX) or not a carrier (XX), but she does not exhibit color blindness.
- 👶 Barbara's genotype is XcX+, indicating she is a carrier of the colorblind allele but does not exhibit the trait.
- 📊 Using a Punnett square, the possible outcomes for Barbara and Tom's offspring are calculated, showing a 50% chance of their child being colorblind.
Q & A
What is the purpose of the pedigree chart in the script?
-The pedigree chart in the script is used to represent the inheritance of color blindness through three generations.
What are the symbols used in the chart to represent males and females?
-In the chart, a square symbol represents a male, and a circle represents a female.
How is color blindness indicated on the chart?
-Color blindness is indicated by coloring in the symbol for an individual, showing that they exhibit the trait.
What is the significance of Tom's genotype in the script?
-Tom's genotype is significant because he is colorblind, which means his single X chromosome must carry the recessive allele for color blindness.
Why can't both of Barbara's X chromosomes have the recessive allele for color blindness?
-If both of Barbara's X chromosomes had the recessive allele for color blindness, she would exhibit the trait, but she does not, indicating she is a carrier with at least one dominant allele.
How did Barbara inherit her X chromosomes?
-Barbara inherited one X chromosome from her father, which must have the colorblind allele, and one from her mother, which does not have the colorblind allele.
What is the probability that Barbara and Tom's next child will be colorblind, according to the script?
-The probability that Barbara and Tom's next child will be colorblind is 50%, as two out of the four possible genetic outcomes result in color blindness.
What is the Punnett square used for in the script?
-The Punnett square is used to visualize the possible genetic outcomes for their offspring, showing the combinations of alleles they can inherit from each parent.
What does the lowercase 'c' represent in the script?
-In the script, the lowercase 'c' represents the recessive allele for color blindness.
How many scenarios result in a colorblind offspring in the script's Punnett square?
-Two out of the four scenarios in the Punnett square result in a colorblind offspring.
What are the four possible outcomes for the offspring of Barbara and Tom, as described in the script?
-The four possible outcomes are: a colorblind female with two recessive alleles, a female carrier with one recessive and one dominant allele, a colorblind male with the recessive allele on his only X chromosome, and a non-colorblind male with a dominant allele on his only X chromosome.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

What are Pedigree Charts

Pedigrees | Classical genetics | High school biology | Khan Academy
17. Inheritance (Part 2) (Cambridge IGCSE Biology 0610 for exams in 2023, 2024 and 2025)

KELAINAN TERPAUT GONOSOM || PENYAKIT MENURUN TERPAUT GONOSOM

NON-MENDELIAN GENETICS: SEX-LINKED TRAITS | SEX INFLUENCED TRAITS | SEX-LIMITED TRAITS | SCIENCE 9
Sex linked Inheritance
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)