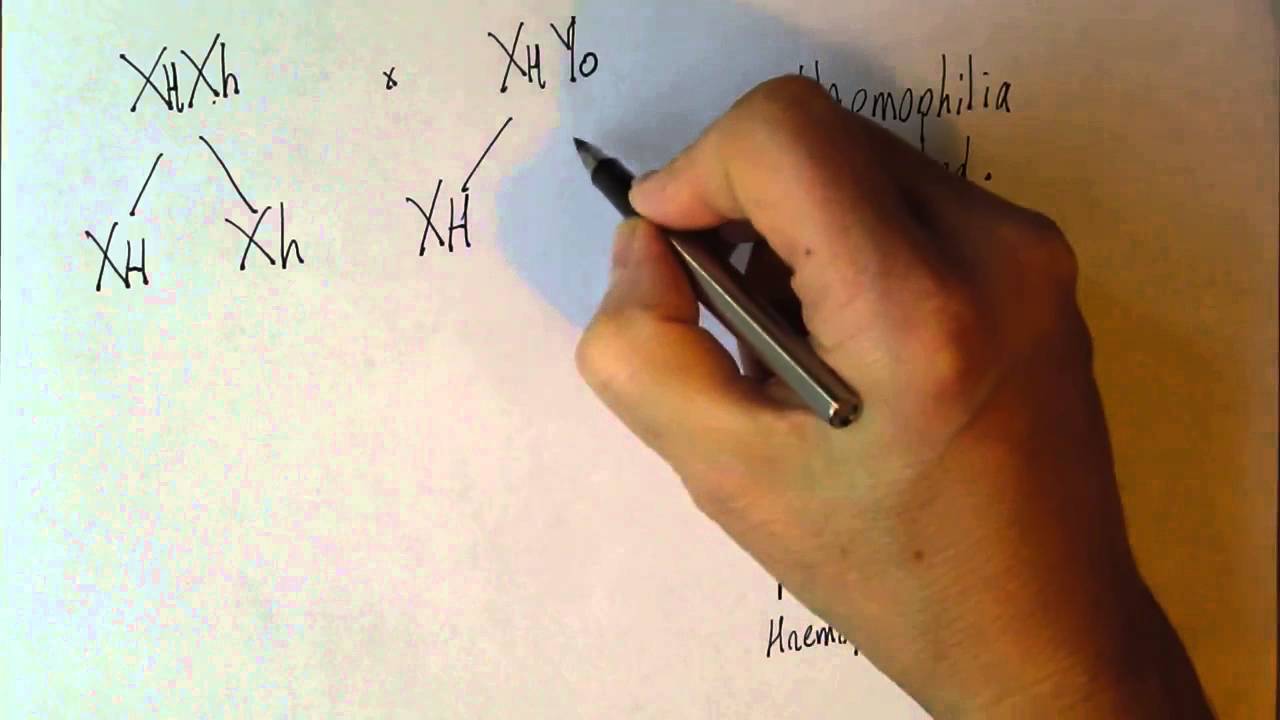NON-MENDELIAN GENETICS: SEX-LINKED TRAITS | SEX INFLUENCED TRAITS | SEX-LIMITED TRAITS | SCIENCE 9
Summary
TLDRThis educational video discusses non-Mendelian genetics, focusing on sex-linked traits like color blindness and hemophilia, which are controlled by the X chromosome and affect males more due to their single X. It explains autosomal traits influenced by sex hormones, such as baldness, and sex-limited traits like lactation. The script uses Punnett squares to illustrate inheritance patterns, emphasizing the impact of sex on trait expression.
Takeaways
- 🧬 Non-Mendelian genetics includes phenomena like incomplete dominance, co-dominance, and multiple alleles, where traits may not follow the simple dominant-recessive patterns described by Mendel.
- 🌟 Incomplete dominance results in an intermediate phenotype, while co-dominance expresses both alleles equally in the phenotype.
- 🔬 Multiple alleles occur when there are more than two variants of a gene that control a particular trait.
- 🧬 Humans have 46 chromosomes, with 22 pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes determining the sex of the individual.
- 👦 Males have XY sex chromosomes, and females have XX, with autosomal chromosomes being the same for both sexes.
- 🤔 The probability of having a male or female offspring is 50% due to the random assortment of X or Y chromosome from the father.
- 🧬 Sex-linked traits are controlled by genes on the sex chromosomes and can affect both males and females, but males are more susceptible due to having only one X chromosome.
- 👓 Examples of X-linked traits include color blindness and hemophilia, which are recessive and can be more prevalent in males.
- 📊 Punnett Squares are used to predict the genotypes and phenotypes of offspring based on the genotypes of the parents.
- 🦲 Sex-influenced traits like baldness are expressed differently in males and females due to hormonal influences, with males requiring only one recessive allele to express the trait.
- 🍼 Sex-limited traits, such as lactation, are expressed exclusively in one sex, despite being carried by the genes of both sexes.
Q & A
What are the three forms of non-Mendelian genetics mentioned in the script?
-The three forms of non-Mendelian genetics mentioned are incomplete dominance, co-dominance, and multiple alleles.
What is the definition of incomplete dominance in genetics?
-Incomplete dominance is a form of inheritance where the dominant trait is not completely dominant over the other allele, resulting in an intermediate phenotype.
How does co-dominance differ from incomplete dominance in terms of phenotype expression?
-In co-dominance, both alleles are expressed equally in the phenotype, meaning both traits are observed or expressed, unlike incomplete dominance where the phenotype is intermediate.
What is the typical chromosome composition for humans in terms of autosomes and sex chromosomes?
-Most humans have 46 chromosomes, consisting of 22 pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes. Males have XY sex chromosomes, while females have XX.
How does the sex chromosome composition affect the probability of having male or female offspring?
-The composition of sex chromosomes determines the sex of the offspring. A male offspring is produced when an egg is fertilized by a sperm carrying a Y chromosome, while a female offspring results from a fertilized egg by a sperm carrying an X chromosome, leading to a 50% probability for each.
What are sex-linked traits and how do they differ from autosomal traits?
-Sex-linked traits are those controlled by genes on the sex chromosomes and can affect both males and females, but may manifest more prominently in one sex. They differ from autosomal traits, which are not influenced by sex chromosomes.
Why are males more susceptible to X-linked traits than females?
-Males are more susceptible to X-linked traits because they have only one X chromosome, so if it carries a recessive gene for a disorder, they will express the trait since there is no second X chromosome to potentially mask it.
What is color blindness, and how is it inherited according to the script?
-Color blindness is the inability to distinguish certain colors, particularly green. It is an X-linked recessive trait, meaning a person will be colorblind if they inherit the recessive gene from both parents for females or from the mother for males.
How does the Punnett Square help in determining the genotypes and phenotypes of offspring in the context of sex-linked traits?
-The Punnett Square is a diagram used to predict the genotypes and phenotypes of offspring by combining the genotypes of the parents. It helps visualize the possible combinations of alleles that the offspring can inherit, especially for traits like color blindness that are sex-linked.
What is the difference between sex-influenced traits and sex-limited traits, as mentioned in the script?
-Sex-influenced traits are autosomal traits that are affected by sex hormones and may manifest differently in males and females due to hormonal differences. Sex-limited traits, on the other hand, are traits that are expressed exclusively in one sex, such as lactation being limited to females.
How does the hormonal influence affect the expression of sex-influenced traits like baldness?
-The hormonal influence affects the expression of sex-influenced traits by causing a difference in the expression threshold between males and females. For example, baldness is influenced by testosterone levels, which are higher in males, so males with even one recessive allele for baldness may show the trait, whereas females typically need two recessive alleles.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)