BAB 1 Sistem Bilangan | Matematika Dasar | Alternatifa
Summary
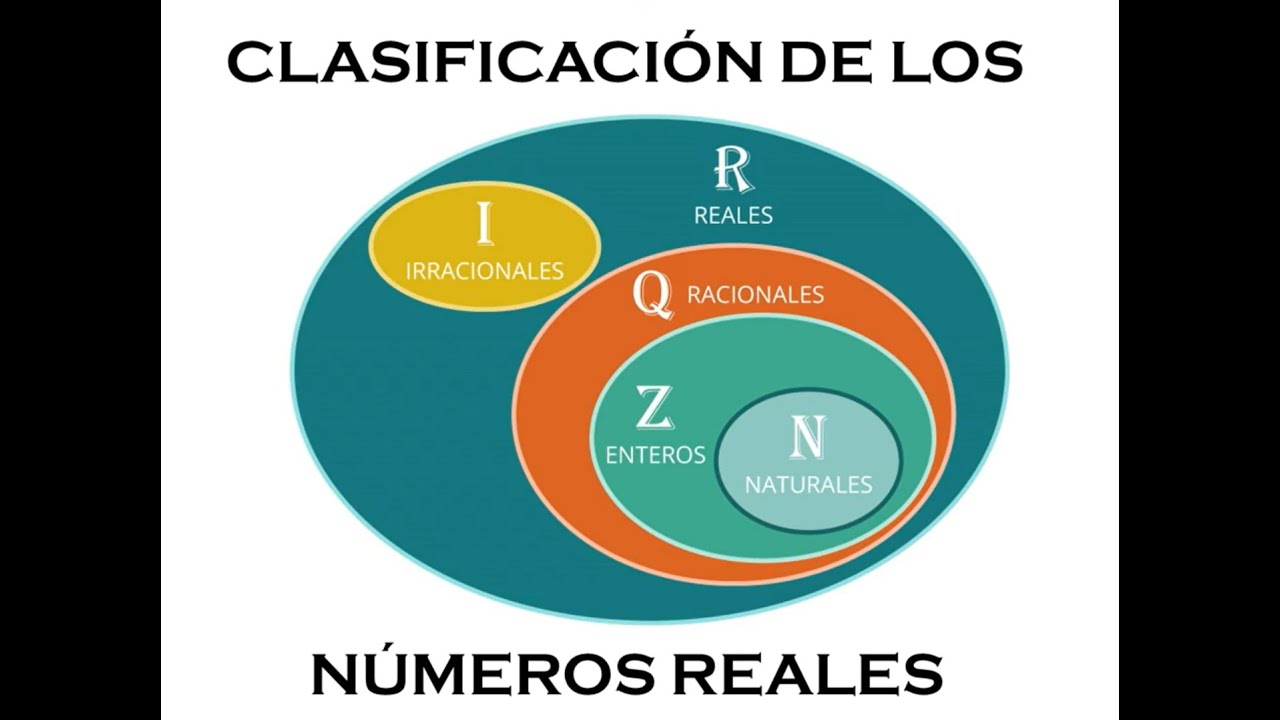
TLDRThe script discusses various number systems, focusing on natural numbers, integers, rational numbers, and real numbers. It explains that natural numbers are limited to addition and multiplication, integers include zero and negatives, rational numbers are expressed as fractions, and real numbers encompass all numbers on the number line. The concept of imaginary numbers and complex numbers is also briefly touched upon.
Takeaways
- 🔢 The number system is the foundation of mathematics.
- 🔢 There are various types of numbers, such as integers, natural numbers, real numbers, and rational numbers.
- 1️⃣ Natural numbers, also known as counting numbers, start from 1 and continue sequentially (1, 2, 3, etc.).
- ➕ Natural numbers can only be added or multiplied to remain natural numbers. Subtracting or dividing them can result in non-natural numbers.
- 0️⃣ Integers include natural numbers, zero, and negative numbers. Operations like addition, subtraction, and multiplication between integers result in integers.
- ➗ Dividing integers can result in fractions or decimal numbers, which are not integers.
- 🔢 Rational numbers can be expressed as fractions, with a numerator and a denominator.
- ✔️ Rational numbers can be operated on using basic arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) except for taking roots.
- 📐 Real numbers include all numbers on the number line, encompassing both rational and irrational numbers.
- 🔢 Imaginary numbers are defined when the square root of a negative number is taken, and combining real and imaginary numbers forms complex numbers.
- 🔢 Prime numbers are integers greater than 1 that are only divisible by 1 and themselves.
Q & A
What are the types of numbers discussed in the script?
-The script discusses various types of numbers including natural numbers, integers, rational numbers, real numbers, complex numbers, and prime numbers.
What is the definition of natural numbers?
-Natural numbers are the numbers used for counting, starting from 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and so on. They are also referred to as counting numbers.
What operations can be performed on natural numbers to still result in natural numbers?
-Natural numbers can be added and multiplied to each other to still result in natural numbers. Subtraction and division are not included as they can result in non-natural numbers like negatives or fractions.
What is the term used for the set of numbers that includes natural numbers, zero, and negative numbers?
-The set of numbers that includes natural numbers, zero, and negative numbers is called integers.
How are integers different from natural numbers?
-Integers include all natural numbers, zero, and negative numbers, whereas natural numbers only include the positive counting numbers starting from one.
What is a rational number?
-A rational number is a number that can be expressed as a fraction where both the numerator and the denominator are integers, and the denominator is not zero.
What happens when you divide integers?
-When you divide integers, the result is not necessarily an integer. It can be a fraction, a decimal, or an irrational number.
What is the definition of a real number?
-A real number is any number that can be found on the number line, including integers, fractions, decimals, and irrational numbers.
What is a complex number?
-A complex number is a number of the form a + bi, where a and b are real numbers, and i is the imaginary unit, which is defined as the square root of -1.
What are prime numbers?
-Prime numbers are natural numbers greater than 1 that have no positive divisors other than 1 and themselves. Examples include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, and so on.
What is the difference between rational and irrational numbers?
-Rational numbers can be expressed as a fraction of two integers, while irrational numbers cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and have non-repeating, non-terminating decimal expansions.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)