Memorise 15x More - Modified Memory Palace/Method of Loci | STUDY CLINIC
Summary
TLDRThe video script introduces a powerful memorization technique, particularly beneficial for medical students and professionals, known as the method of loci or memory palace technique. The speaker demonstrates a modified version of this method, which involves creating absurd and interactive elements within a familiar environment to enhance recall. The script provides a step-by-step example using causes of abdominal pain, illustrating how to transform a list into a vivid, memorable journey. The technique is emphasized as a high-yield tool for rote learning, with the potential to memorize up to a hundred items effectively.
Takeaways
- 📚 The script introduces a memorization technique particularly useful for medical students and professionals, emphasizing its high efficiency in saving study time.
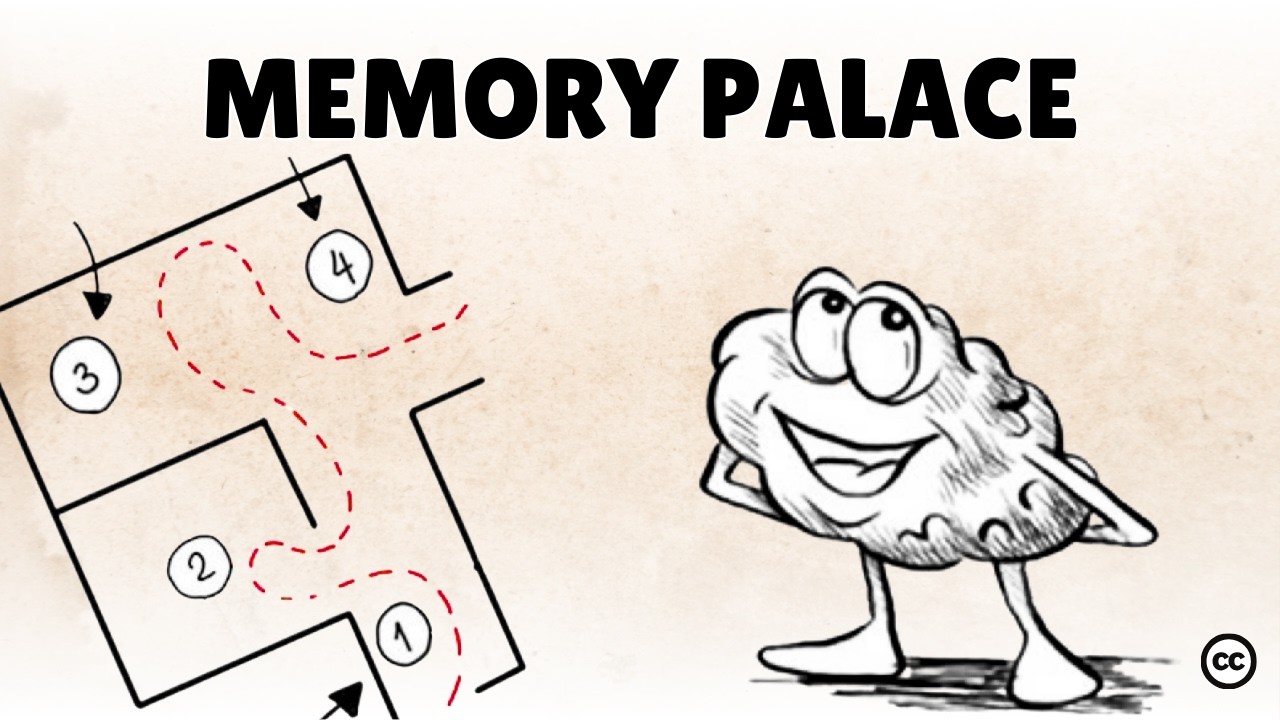
- 🏰 It demonstrates the 'Method of Loci' or 'Memory Palace' technique, a traditional memorization method with some limitations for studying purposes.
- 🔄 The speaker introduces a variation called the 'Modified Method of Loci', which is more effective for studying and overcomes some of the limitations of the traditional method.
- 📝 The speaker uses a list of causes of abdominal pain as an example to illustrate the memorization technique, showing how to create and remember absurd and interactive elements.
- 🎨 The importance of creating vivid, absurd, and interconnected elements in the memory palace is highlighted to facilitate better recall.
- 🧠 The memorization process involves associating these elements with the information to be learned, similar to recalling a detailed TV show episode.
- 🔑 The speaker emphasizes that the elements should interact with each other and be spaced out effectively within the memory palace.
- 📉 The script mentions that while the technique is powerful, it should be used as a last resort, with a preference for understanding and logical learning over rote memorization.
- 🔍 The 'Modified Method of Loci' is explained as a way to adapt the environment to the memorization needs, making it more flexible and avoiding the issue of running out of places in a traditional memory palace.
- 🎭 The modified technique involves creating an environment as part of the absurd event, which can be visualized like a painting, and does not require the memorizer to navigate through it.
- 📈 The speaker shares personal experience with the technique, noting the ability to memorize up to 250 items after investing time, and the low rate of forgetting once memorized.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video script?
-The main topic of the video script is a memorization technique known as the method of loci or memory palace technique, and its modified version for effective learning, particularly useful for medical students and professionals.
What is the method of loci?
-The method of loci is a mnemonic device that involves associating items to be remembered with specific locations in a familiar environment, allowing the person to mentally 'walk' through the environment to recall the items.
What is the modified method of loci that the speaker introduces?
-The modified method of loci involves creating an environment as part of the absurd event instead of navigating through a pre-existing 'palace.' This modification allows for a more flexible and personalized approach to memorization.
Why is the method of loci beneficial for medical students and house officers?
-The method of loci is beneficial for medical students and house officers because it can significantly reduce the time required to memorize large amounts of information, such as causes of abdominal pain or other medical knowledge.
How does the speaker demonstrate the method of loci in the script?
-The speaker demonstrates the method of loci by memorizing a list of causes of abdominal pain using a series of absurd and interactive events within a familiar environment, which helps in associating and recalling the information.
What are the key principles of the method of loci as described in the script?
-The key principles of the method of loci as described in the script are creating absurd and distinct elements, ensuring these elements interact with each other, and spacing them out within the environment to facilitate easy recall.
How does the speaker ensure the elements in the method of loci are memorable?
-The speaker ensures the elements are memorable by making them absurd and interactive, creating a vivid and immersive environment that can be mentally navigated to recall the associated information.
What is the advantage of the modified method of loci over the traditional one?
-The advantage of the modified method of loci is that it allows for a more personalized and flexible approach, where the environment or 'palace' is created as part of the memorization process, adapting to the specific needs of the information being learned.
Why is it important to not rely solely on memorization techniques according to the speaker?
-According to the speaker, it is important not to rely solely on memorization techniques because true understanding comes from making sense of the information logically. Memorization should be a last resort for information that doesn't fit into a logical framework.
How can the modified method of loci be applied to other areas of study or professional development?
-The modified method of loci can be applied to other areas of study or professional development by adapting the environment to the specific content being learned, creating a personalized and immersive experience that facilitates memorization and recall of complex information.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Mind Palace (Simple Guide) - 5 Steps to Remember Things With a Memory Palace
The Memory Palace : Can You Do It?

My system for memorizing everything INSTANTLY.

How to Remember Everything For the Rest Of Your Life

Secrets of The Geometrical Memory Palace Technique For Studying

Cara Menghafal ala Sherlock Holmes dengan Mind Palace
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)