Materi Matematika Kelas 9: Kekongruenan dan Kesebangunan
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explains the concepts of congruence and similarity in geometry, aimed at 9th-grade students. It defines congruence as objects having identical shapes and sizes, illustrated through examples like identical squares and shapes. The video also explores similarity, where objects maintain proportional relationships but may differ in size, comparing them to zooming in and out of an image. Key examples include congruent trapezoids and similar figures with proportional side lengths. The video offers step-by-step problem-solving guidance and concludes with a reminder to subscribe for more educational content.
Takeaways
- 📘 Congruence in mathematics means two shapes are exactly the same in both side lengths and angle measures.
- 🚗 Objects with identical shapes and sizes, like two identical cars, are considered congruent, while objects with different sizes are not.
- ⬜ Two squares with equal side lengths (e.g., both 3 cm) are congruent because all corresponding sides and angles are equal.
- 🥫 Two cylinders with the same shape but different dimensions are not congruent since their sizes differ.
- 📏 In congruent shapes, corresponding sides have equal lengths, allowing unknown sides to be determined by matching them with their pairs.
- 📐 In congruent triangles, corresponding angles are equal, which helps in calculating unknown angle measures.
- ➗ The sum of interior angles in a triangle is 180°, and this property is used to find missing angles.
- 🔁 Matching marks on sides or angles indicate corresponding parts in congruent figures.
- 🔍 Similarity differs from congruence because similar shapes have proportional sides and equal angles, but not necessarily the same size.
- 📱 Similarity is compared to zooming in or out on a camera—objects remain the same shape but change in size.
- ⚖️ In similar figures, the ratio between corresponding sides must be consistent throughout the shapes.
- ✅ If all corresponding side ratios are equal (e.g., 2:1 consistently), the figures are proven to be similar.
Q & A
What does congruence mean in mathematics?
-Congruence in mathematics means that two shapes or figures are exactly the same in both size and shape, with corresponding sides and angles being identical.
Can you provide an example of congruence in everyday objects?
-Yes! For example, two cars that have identical shapes and sizes would be congruent. If both cars have the same dimensions and angles, they are congruent to each other.
What makes two squares congruent to each other?
-Two squares are congruent if they have the same side lengths. For instance, if both squares have a side length of 3 cm, they are congruent.
What does it mean when two objects are not congruent?
-When two objects are not congruent, it means they do not have the same size or shape. For example, two cylinders with different heights or diameters are not congruent, even though they are both cylindrical.
How do you determine the side lengths of congruent shapes?
-To determine the side lengths of congruent shapes, you compare the corresponding sides of the figures. For example, in a congruent trapezoid, if one side is given, the corresponding side in the other shape will have the same length.
What is similarity in mathematics, and how does it differ from congruence?
-Similarity refers to figures that have the same shape but may differ in size. The corresponding angles are equal, and the sides are proportional. In contrast, congruence requires both the shape and size to be identical.
Can you give an example of two similar objects?
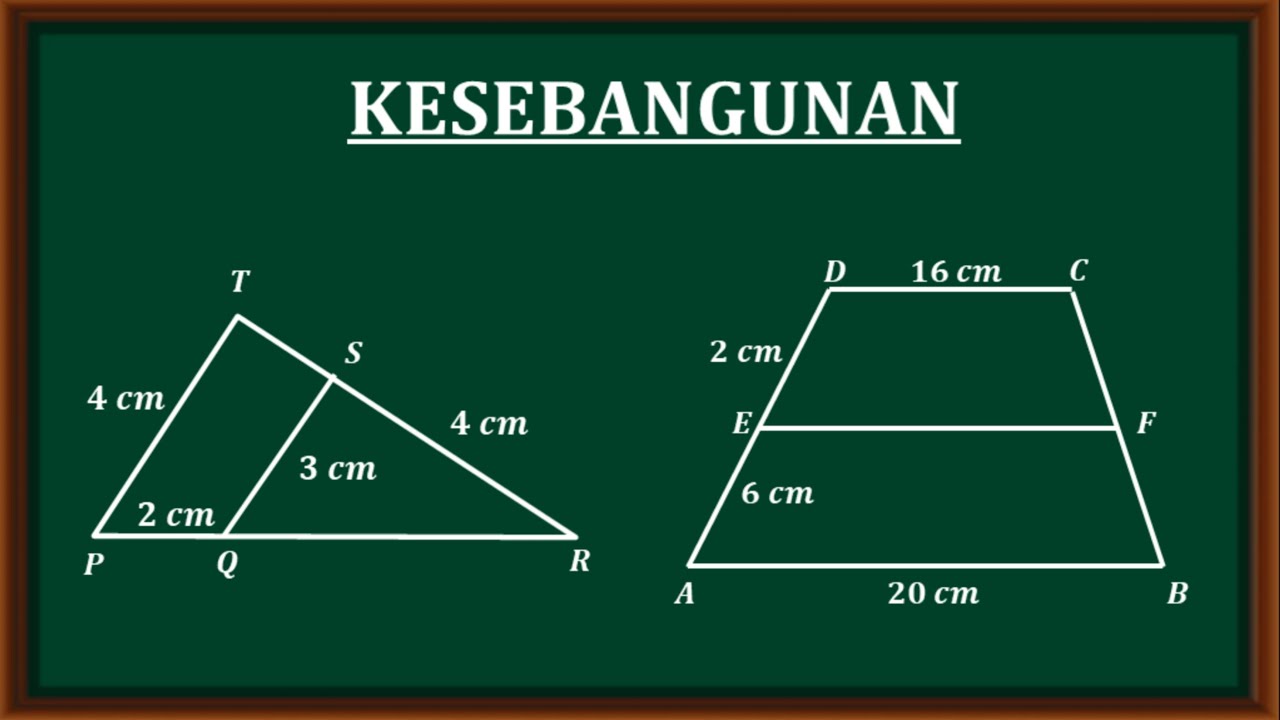
-Two similar objects can be two trapezoids that are proportional in size. For example, one trapezoid is twice as large as the other, but their corresponding angles and side ratios remain the same.
How do you verify that two shapes are similar?
-To verify that two shapes are similar, you check that the corresponding angles are equal and the corresponding sides are proportional. If these conditions hold, the figures are similar.
In the example of two similar trapezoids, how do you simplify the side ratios?
-In the example, the ratio of the sides is given as 16:8. Simplifying this ratio by dividing both numbers by 8 gives 2:1, indicating that one trapezoid is twice the size of the other.
How are the concepts of congruence and similarity used in problem-solving?
-These concepts are used to solve problems by helping identify relationships between shapes. For example, in congruence, you can calculate unknown side lengths based on matching sides, while in similarity, you use proportional relationships to find missing measurements.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

KEKONGRUENAN (Materi Kelas 9 SMP)

segitiga-segitiga yang kongruen 1

Soal soal TKA Matematika Jenjang SMP 2026 Materi Geometri dan Pengukuran | Part 3

MATEMATIKA KELAS 9 HALAMAN 137-143 KURIKULUM MERDEKA EDISI 2022

Kurikulum Merdeka Materi Matematika Kelas 7 Bab 5 Kesebangunan
Kesebangunan - soal dan pembahasan materi kesebangunan matematika tingkat SMP kelas ix
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)