From Elements to Compounds and Mixtures!
Summary
TLDRThis video script explores the concept of elements, molecules, compounds, and mixtures. It begins by explaining that elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down further by chemical processes. The script details the properties of metals, non-metals, and metalloids, and the process of combining atoms to form molecules and compounds. It also highlights how compounds have distinct properties from the elements they’re made of, and the chemical processes of decomposition and electrolysis. Lastly, it covers mixtures, their classification, and separation methods like filtration and distillation.
Takeaways
- 😀 Elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down further by chemical processes.
- 😀 Sugar is not an element because it can be broken down into carbon and water vapor, which are both made up of elements.
- 😀 Hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon are examples of elements that cannot be broken down further.
- 😀 Chemical symbols represent elements, like H for Hydrogen, C for Carbon, and O for Oxygen.
- 😀 Elements can be classified based on their properties, such as metallic, non-metallic, or metalloids.
- 😀 Metals are typically solid at room temperature, are good conductors of heat and electricity, and are malleable and ductile.
- 😀 Metalloids have both metallic and non-metallic properties, and they are moderate conductors of electricity and heat.
- 😀 Non-metals can be solid, liquid, or gas at room temperature and are generally poor conductors of heat and electricity.
- 😀 Atoms are the fundamental units of elements, and molecules are formed when atoms combine chemically.
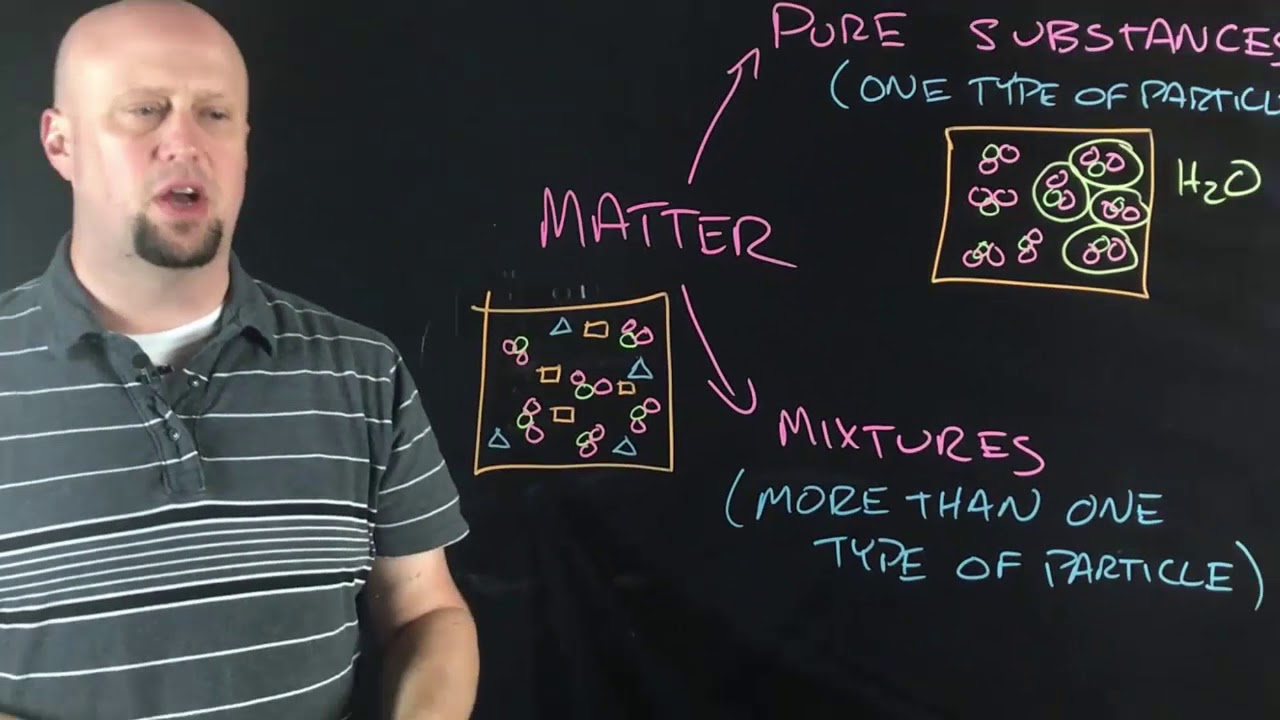
- 😀 Compounds are made by combining different elements, and their properties differ from the individual elements they are made of.
- 😀 Mixtures are combinations of substances where no chemical reaction occurs, and their components can be separated physically.
Q & A
What happens when sugar is heated for too long during caramelization?
-When sugar is heated for too long, it breaks down into carbon and water vapors, turning black and bitter instead of forming the sweet caramel we expect.
Why is sugar not considered an element?
-Sugar is not an element because it can be broken down into simpler substances, specifically carbon and water vapors, through chemical processes.
What is the definition of an element?
-An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into two or more simpler substances by chemical processes.
How are chemical symbols used in chemistry?
-Chemists use chemical symbols, usually consisting of one or two letters, to represent elements. For example, hydrogen is 'H', carbon is 'C', and oxygen is 'O'.
What are the primary properties of metals?
-Metals are typically solid at room temperature (except mercury), have a shiny appearance, high melting points, high heat conductivity, and are malleable, ductile, and sonorous. They are also excellent electrical conductors.
What distinguishes metalloids from metals and non-metals?
-Metalloids have properties of both metals and non-metals. They are solid, have a shiny appearance, are brittle when hammered, and are moderate conductors of heat and electricity. Silicon is a typical example of a metalloid.
What are the characteristics of non-metals?
-Non-metals tend to have a dull appearance, are poor conductors of electricity and heat, and can exist in all three physical states at room temperature—solid, liquid, or gas. They generally have low melting and boiling points.
What is the difference between atoms, molecules, and compounds?
-Atoms are the fundamental units of elements. Molecules are made by combining two or more atoms, and compounds are molecules formed by atoms of different elements. For example, water is a compound made of hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
What is the chemical formula of water and what does it represent?
-The chemical formula of water is H2O, indicating that each molecule consists of two hydrogen atoms (H) and one oxygen atom (O).
How are compounds formed, and how do their properties differ from the elements that make them?
-Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements chemically combine. Their properties can be very different from the elements that form them. For example, magnesium oxide has different properties from both magnesium and oxygen.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

GCSE Chemistry Revision "Elements, Compounds and Mixtures"

Classification of matter | Structure and properties of matter | High school chemistry | Khan Academy

GCSE Science Revision Chemistry "Elements, Compounds and Mixtures"
Classification pt 1 Pure Substances

GCSE Chemistry - Differences Between Compounds, Molecules & Mixtures #3

Pure Substances and Mixtures, Elements & Compounds, Classification of Matter, Chemistry Examples,
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)