GCSE Physics Revision "Convex Lenses" (Triple)
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of convex lenses and how they form images through refraction. It covers the behavior of light as it passes through different mediums, bending towards or away from the normal. The video demonstrates how ray diagrams show the formation of real, inverted images and highlights key properties like image size and magnification based on the object's distance from the lens. The focus is on understanding focal length, principal focus, and the various image characteristics that arise from different object-lens distances.
Takeaways
- 🔍 Convex lenses are thicker at the center than at the edges and have a distinct symbol students must learn.
- 💡 Lenses refract light: rays bend toward the normal when entering the lens and away from the normal when leaving it.
- 📏 Parallel rays of light passing through a convex lens converge at a point called the principal focus (F).
- 🎯 The focal length is the distance from the center of the lens to the principal focus, and different lenses have different focal lengths.
- ➡️ The central ray passing through the lens along the principal axis does not refract because it travels along the normal.
- 📐 Ray diagrams help show how images form when objects are placed at various distances from a convex lens.
- 🖼️ If the object is more than two focal lengths from the lens, the image formed is diminished, inverted, and real.
- 🔎 If the object is between one and two focal lengths from the lens, the image formed is magnified, inverted, and real.
- 📌 A real image is produced when refracted rays actually meet at a point, meaning the image can be projected onto a screen.
- 📝 The properties of the image (size, orientation, reality) depend on the distance between the object and the lens.
Q & A
What is a convex lens?
-A convex lens is thicker at the center than at the edges. It refracts light, bending it towards the normal when light enters the lens and away from the normal when it exits.
How does light behave when passing through a convex lens?
-When light passes through a convex lens, parallel rays bend towards the normal upon entering, and away from the normal upon exiting. The central ray passes through the lens without refracting.
What is the principal focus of a convex lens?
-The principal focus is the point where rays of light that are parallel to the principal axis meet after passing through the convex lens. The distance from the lens to the principal focus is called the focal length.
How does the focal length vary in different convex lenses?
-Different convex lenses have different focal lengths depending on the strength of the lens. The stronger the lens, the shorter the focal length.
What happens when an object is placed more than two focal lengths away from the lens?
-When the object is more than two focal lengths away, the image produced is smaller than the object (diminished), inverted, and real. The rays actually meet at a point.
What occurs when the object is between one and two focal lengths from the lens?
-When the object is between one and two focal lengths from the lens, the image is magnified, inverted, and real. Like the first case, the rays meet at a point.
What does the term 'real image' mean?
-A real image is one where the rays of light actually meet at a point. It can be displayed on a screen, as the image is formed by real light rays converging.
What are the key properties of an image formed when the object is more than two focal lengths away from the lens?
-The image will be diminished (smaller than the object), inverted (upside down), and real, meaning the light rays meet at a point.
How do you construct a ray diagram for a convex lens when the object is more than two focal lengths away?
-To construct the ray diagram, first draw a line from the top of the object passing through the center of the lens without changing direction. Then, draw another line from the top of the object parallel to the principal axis. This refracts through the principal focus, and where the lines meet shows the top of the image.
What is the significance of the symbol 'F' in relation to a convex lens?
-The symbol 'F' represents the principal focus of the lens. It is used to indicate the point where light rays meet after being refracted by the convex lens.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
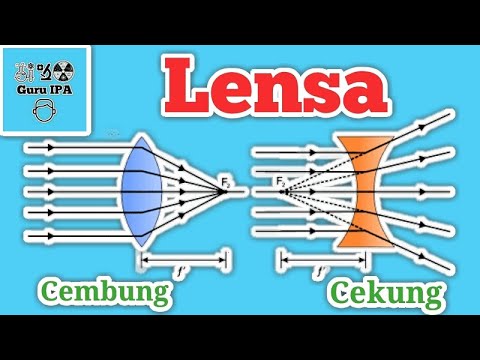
Lensa Cekung dan Lensa Cembung

Qualitative Characteristics (Orientation, Types, and Magnification) of Images Formed by Lenses

Lesson 7: Types of Lenses (Convex and Concave)

Grade 10 SCIENCE | Quarter 2 Module 7 | Refraction in Lenses • Ray Diagrams • Lens Equation

Pembiasan dan Lensa (4) - Lensa Cembung, Sifat Bayangan Lensa Cembung - Fisika SMP

GCSE Physics - How Lenses Work #69
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)