Gradient Descent Explained
Summary
TLDRGradient descent is a popular optimization algorithm used to train machine learning models, including neural networks. It helps minimize a cost function by gradually adjusting weights and biases to improve predictions. The process involves taking small steps downhill to reduce errors, with learning rate controlling step size. There are three types of gradient descent: batch, stochastic, and mini-batch, each balancing computational efficiency and speed differently. While powerful, gradient descent can struggle with challenges like saddle points or vanishing/exploding gradients. Despite this, it's a fundamental tool for training models and refining predictions.
Takeaways
- 😀 Gradient descent is an optimization algorithm used to train machine learning models by adjusting weights and biases based on data.
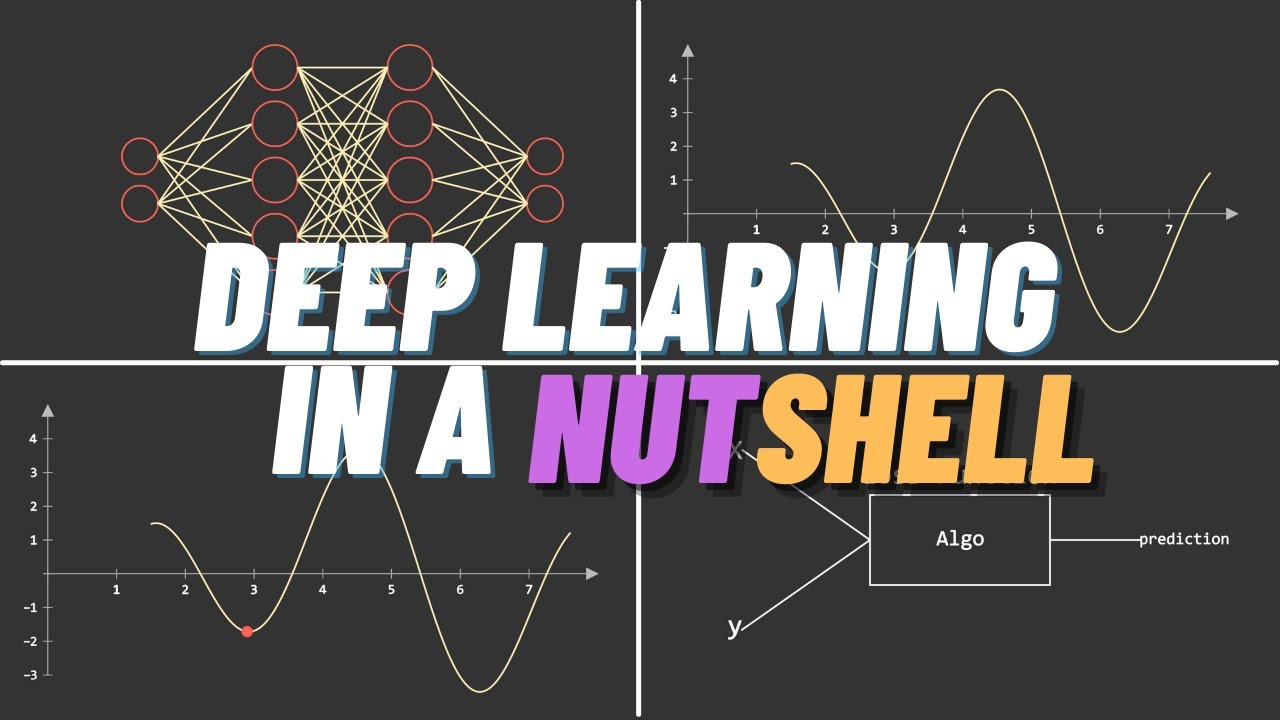
- 😀 Neural networks consist of layers of neurons with weights and biases that help the model learn patterns in data.
- 😀 A cost function measures how far the model's predictions are from actual values, and gradient descent aims to minimize this cost.
- 😀 Gradient descent works by taking small steps in the direction that reduces the cost function, moving downhill on a graph.
- 😀 The learning rate controls the size of the steps taken during gradient descent. A high learning rate might miss the optimal point, while a low rate might take too long to converge.
- 😀 An example of gradient descent in action is using it to predict house prices by training a model on labeled data like location, size, and sale price.
- 😀 If predictions are inaccurate, the weights and biases are adjusted, and the model retrains, with gradient descent helping to find the optimal weights.
- 😀 There are three types of gradient descent: batch gradient descent, stochastic gradient descent (SGD), and mini-batch gradient descent.
- 😀 Batch gradient descent processes the entire dataset at once but can be slow due to large datasets requiring more memory and time.
- 😀 Stochastic gradient descent (SGD) processes one training example at a time, which is faster but less computationally efficient.
- 😀 Mini-batch gradient descent strikes a balance by splitting the dataset into small batches, offering both speed and efficiency.
- 😀 Challenges in gradient descent include difficulty finding the global minimum in non-convex problems, especially near saddle points, and issues like vanishing or exploding gradients in deep neural networks.
- 😀 Despite its challenges, gradient descent remains a widely used and powerful optimization tool for training machine learning models.
Q & A
What is gradient descent?
-Gradient descent is an optimization algorithm used to train machine learning models, where small steps are taken in the direction that reduces the error (or cost) most efficiently. It's like trying to find your way down a dark mountain by feeling your way around.
How does gradient descent work in machine learning?
-In machine learning, gradient descent helps adjust the weights and biases of a neural network by reducing the difference between predicted and actual values, minimizing the cost function over time, and improving the accuracy of predictions.
What is a neural network?
-A neural network consists of layers of interconnected neurons. These neurons process input data and adjust weights and biases to make predictions. The learning process helps the network make better predictions over time.
What is the cost function in gradient descent?
-The cost function measures the difference between the network's predictions and the actual values. Gradient descent aims to minimize this function by adjusting the model's parameters (weights and biases) to reduce errors.
What are weights and biases in a neural network?
-Weights are the parameters that determine the strength of connections between neurons in the network, while biases help shift the activation of a neuron. Together, they are adjusted during training to improve the network's predictions.
Can you explain the learning rate in gradient descent?
-The learning rate controls the size of the steps taken during the gradient descent process. A smaller learning rate means smaller, more precise adjustments, while a larger learning rate may lead to faster but less precise updates.
How does gradient descent apply to real-world problems like predicting house prices?
-In predicting house prices, a neural network is trained using data such as the location and size of the house. The model then predicts the sale price, and gradient descent adjusts the weights and biases based on the difference between the predicted and actual prices.
What are the three types of gradient descent?
-The three types of gradient descent are: (1) Batch gradient descent, which updates the model after evaluating all training examples; (2) Stochastic gradient descent, which updates the model after each training example; and (3) Mini-batch gradient descent, which updates the model after processing small batches of training data.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of batch gradient descent?
-Batch gradient descent is computationally efficient but can have long processing times, especially with large datasets. It processes the entire dataset at once, which can be slow and requires significant memory.
What are some challenges of gradient descent?
-Some challenges include struggling to find the global minimum in non-convex problems, dealing with saddle points, and issues like vanishing or exploding gradients, which can make training deep neural networks more difficult.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)