Paired Sample t-Test for Before and After Data
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the process of conducting a paired sample T-test using before and after data, demonstrated through a classroom example. The instructor compares pre-test and post-test scores to determine if there was any significant improvement in student performance. The video covers how to input data into Excel, calculate descriptive and inferential statistics, and interpret the results. Emphasis is placed on the importance of hypothesis testing, the significance of p-values, and critical values in decision-making, with practical tips on data formatting and result interpretation.
Takeaways
- 😀 The script explains the concept of a paired sample t-test, often used to compare 'before and after' data from the same group of subjects.
- 😀 In the context of teaching, a pre-test is given to measure students' knowledge before a lesson, and a post-test is given afterward to assess improvement.
- 😀 The independent variable in this case is the lesson (or treatment) intended to change the students' behavior or knowledge.
- 😀 The paired sample t-test compares the same subjects' scores on two related variables (pre-test vs post-test).
- 😀 Hypothesis testing involves the null hypothesis (no difference) and the alternative hypothesis (there is a difference between pre-test and post-test).
- 😀 The script explains how to use Excel's Data Analysis Toolpak to conduct a paired sample t-test, including entering data ranges and checking for labels.
- 😀 The p-value, when less than the alpha level (usually 0.05), allows you to reject the null hypothesis, indicating that there is a statistically significant difference.
- 😀 The t-test results also depend on the degrees of freedom (n-1), with 23 participants yielding 22 degrees of freedom in the example.
- 😀 The script highlights the importance of formatting the results, particularly the p-value, for easier interpretation and reporting.
- 😀 The paired sample t-test can also be conducted by reversing the order of the data (post-test before pre-test) and still yields the same result.
- 😀 The critical t-value is used to assess whether the test statistic falls in the rejection region, which helps in rejecting or accepting the null hypothesis.
Q & A
What is the purpose of the paired sample T-test in the video?
-The paired sample T-test is used to compare the pre-test and post-test data for the same group of students to determine if there is a statistically significant difference in their performance.
What is the independent variable in the classroom example provided?
-The independent variable in the example is the lesson or treatment given to the students to potentially change their behavior or knowledge.
What is the dependent variable in the classroom example?
-The dependent variable is the students' performance as measured by their pre-test and post-test scores.
What does the null hypothesis state in a paired sample T-test?
-The null hypothesis states that there is no difference between the pre-test and post-test results; that is, the observations of the two samples are the same.
How is the alpha level (α) typically set in a paired sample T-test?
-The alpha level is usually set to 0.05, which is the threshold for determining whether the results are statistically significant.
What happens if the p-value is less than the alpha level?
-If the p-value is less than the alpha level (0.05), the null hypothesis is rejected, indicating that there is a statistically significant difference between the pre-test and post-test results.
What does the T-value represent in a paired sample T-test?
-The T-value represents the calculated statistic used to determine whether the observed differences between the pre-test and post-test are statistically significant.
What is the degree of freedom (df) in a paired sample T-test?
-The degree of freedom is calculated as the number of participants minus one (n - 1). In the example, with 23 participants, the degree of freedom is 22.
Why is it important to check the 'Labels' option when performing a paired sample T-test in Excel?
-Checking the 'Labels' option ensures that the first row of data, which contains the variable names, is not included in the analysis. It helps avoid errors in the calculation of the T-test.
What should you do if the P-value is extremely small, as indicated by an 'E' notation (e.g., 0.00000008)?
-You should format the cell to show the P-value in a more readable format, such as with two decimal places, to better interpret the result.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Cara Uji Beda Dua Kelompok dengan Jamovi | Independent Sample t-test dan Paired Sample t-test
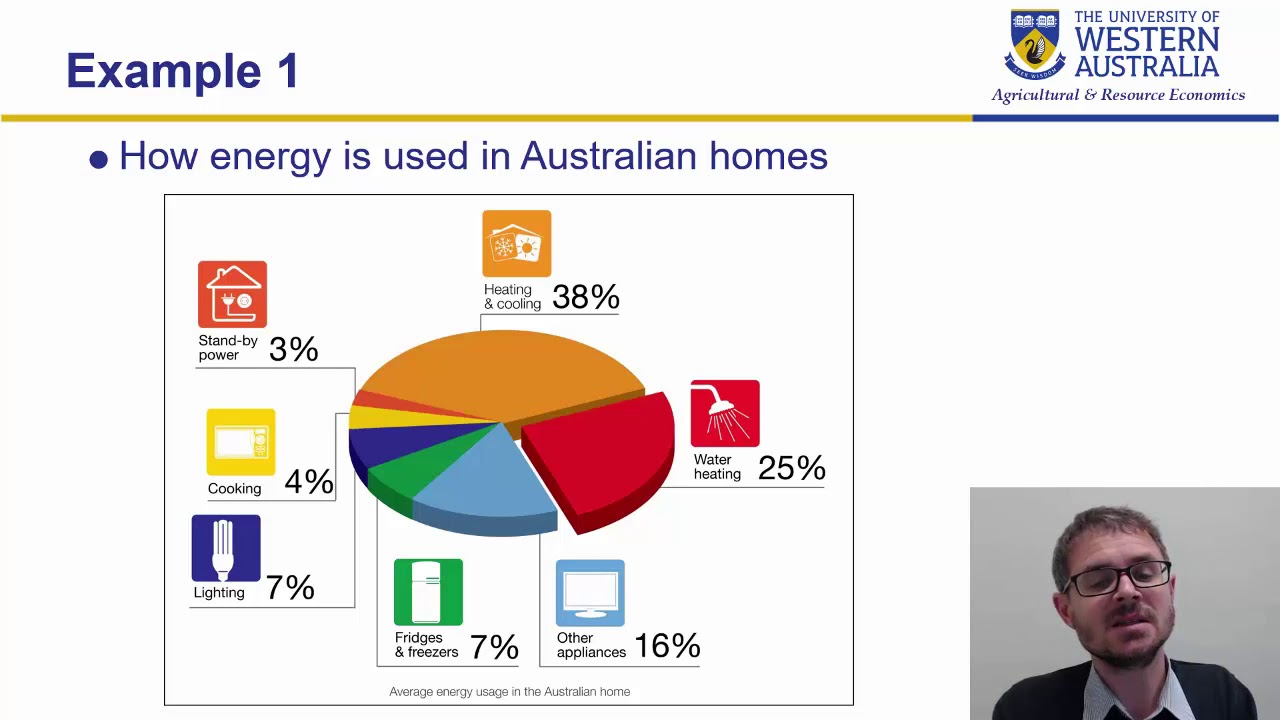
Wk 4 part5

KULIAH STATISTIK - ANALISIS T-TEST

SIMULASI UJI T EFEKTIF DAN CEPAT MELALUI SPSS_BELAJAR STATISTIKA

Modul 6 - Uji Beda Rata rata Dua Sampel Berpasangan (Dependen) (Paired Sample t-test)
Hypothesis Testing: Calculations and Interpretations| Statistics Tutorial #13 | MarinStatsLectures
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)