Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Explained
Summary
TLDRThis video dives into the concept of Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), a JavaScript injection vulnerability that can compromise web security. Starting with an engaging story about 'Bobby Tables,' it explains the foundational Same Origin Policy (SOP) and demonstrates how malicious scripts can exploit web inputs. The video explores various XSS types, including reflected, stored, DOM-based, and mutation XSS, and highlights real-world implications such as cookie theft and CSRF token exposure. It also discusses challenges in mitigating XSS and introduces solutions like DOM Purifier. Finally, it promotes an educational website, xss.ponefunction.com, offering hands-on XSS challenges and explanations to help viewers learn effectively.
Takeaways
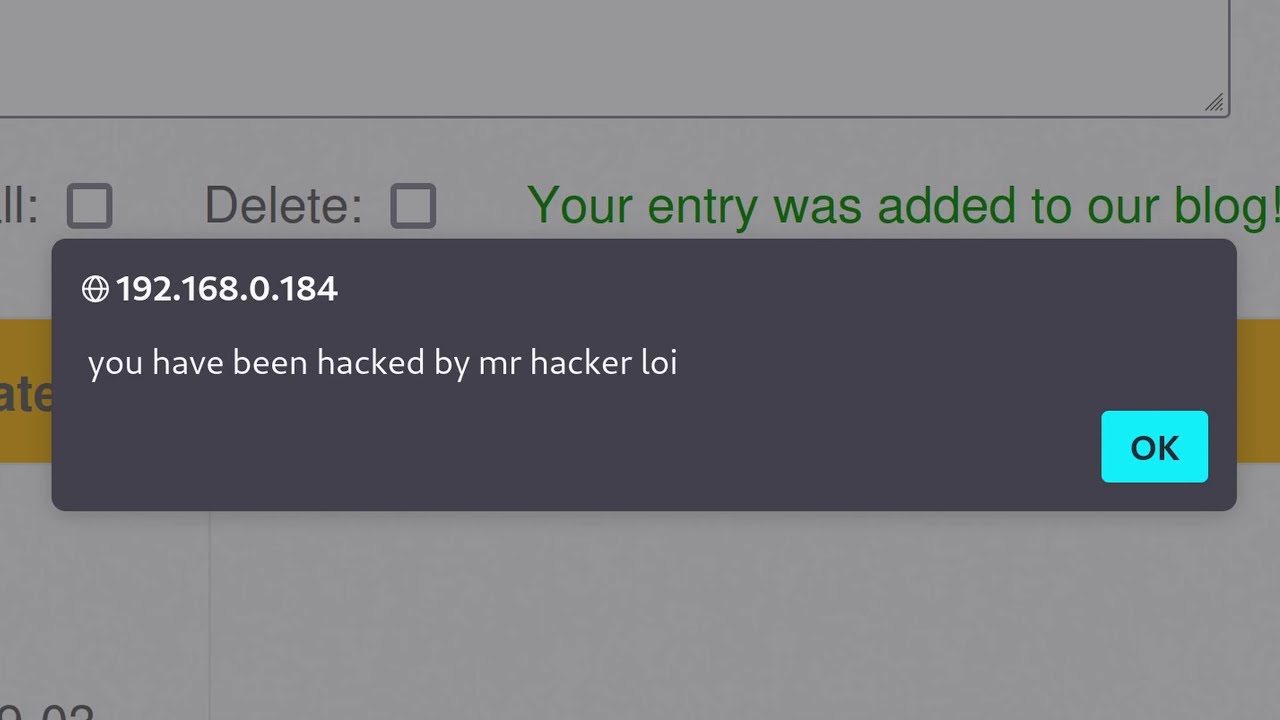
- 😀 XSS (Cross-Site Scripting) is a JavaScript injection technique that allows attackers to run code in another user's browser context.
- 😀 The Same Origin Policy (SOP) is a core web security feature that prevents one website from reading or writing data on another unless protocol, host, and port match.
- 😀 JavaScript has access to the DOM (Document Object Model), allowing manipulation of HTML, stealing cookies, CSRF tokens, or other sensitive information.
- 😀 Reflected XSS occurs when user input is immediately reflected in a web page response and executed as JavaScript.
- 😀 Stored XSS happens when malicious input is saved in a database and served to users later, potentially affecting everyone who views it.
- 😀 DOM-based XSS occurs when user input directly lands in dangerous parts of the client-side JavaScript code and is executed by the browser.
- 😀 Mutation XSS (mXSS) arises when the browser modifies user input before inserting it into the DOM, sometimes leading to unintended code execution.
- 😀 Simply blocking `<script>` tags or HTML symbols is not enough to prevent XSS due to event handlers and other HTML/JavaScript execution vectors.
- 😀 Libraries like DOMPurify can help sanitize HTML and prevent XSS by filtering out unsafe JavaScript while preserving safe content.
- 😀 Understanding and practicing XSS is important for web security, and challenges or exercises can help the community learn about different types of XSS attacks.
Q & A
What does XSS stand for and who coined the term?
-XSS stands for Cross-Site Scripting, and the term was coined by Microsoft.
What is the purpose of the Same Origin Policy (SOP)?
-SOP is a web security feature that prevents one website from reading or writing data to another website unless the protocol, host, and port match. It ensures basic web security by restricting cross-origin access.
How does JavaScript access and manipulate HTML documents?
-JavaScript can interact with the DOM (Document Object Model) APIs provided by browsers, allowing it to read, modify, or manipulate HTML elements, attributes, and content on a web page.
What is reflected XSS and how does it work?
-Reflected XSS occurs when user input is immediately reflected back in a website’s response and executed as JavaScript. For example, submitting `<script>alert(1)</script>` in a form that echoes input directly to the page can trigger an alert.
What is stored XSS and why is it more dangerous than reflected XSS?
-Stored XSS happens when user input is stored in a database and later rendered to other users’ browsers. It is more dangerous because malicious scripts can affect multiple users automatically whenever the stored content is viewed.
What is DOM-based XSS?
-DOM-based XSS occurs entirely on the client side when user input directly modifies the DOM, such as setting `innerHTML` of an element, which can then execute JavaScript without server-side involvement.
What is mutation XSS (mXSS)?
-Mutation XSS happens when the browser alters or mutates user input before inserting it into the DOM, which can sometimes result in cross-site scripting vulnerabilities.
Why is simply blocking `<script>` tags not enough to prevent XSS?
-Blocking `<script>` tags alone is insufficient because JavaScript can also execute via event handlers on HTML elements (like `onclick` or `onload`) or other HTML constructs, bypassing simple tag-based filters.
What is DOMPurify and how does it help with XSS?
-DOMPurify is a library that sanitizes HTML and user input, removing malicious JavaScript while preserving safe HTML, helping to prevent XSS attacks in web applications.
How can developers practice and learn about XSS effectively?
-Developers can practice XSS through dedicated challenge websites, like `xss.ponefunction.com`, which provide exercises with explanations and solutions to understand different types and contexts of XSS attacks.
What is the key takeaway about XSS from the video?
-The key takeaway is that XSS is essentially JavaScript injection, which can take many forms and appear in multiple contexts on a website, making understanding and mitigating it critical for web security.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)