Earned Income vs Capital Gains: Why the Rich Pay Less Tax
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the crucial differences between earned income and capital gains, highlighting how taxes are levied differently. While earned income is taxed heavily, capital gains from assets like stocks or real estate are taxed at lower rates, offering wealth-building advantages. The video illustrates how the wealthy often leverage capital gains and tax strategies to accumulate wealth much faster than salaried employees. It emphasizes that ownership and investments, rather than working for a paycheck, are the key to financial freedom and long-term success. Understanding this distinction can lead to smarter financial strategies and better wealth management.
Takeaways
- 😀 Earned income (e.g., wages, salaries) is taxed at a higher rate than capital gains (e.g., profits from selling stocks or real estate).
- 😀 The tax code distinguishes between earned income, portfolio income, and passive income, each taxed differently.
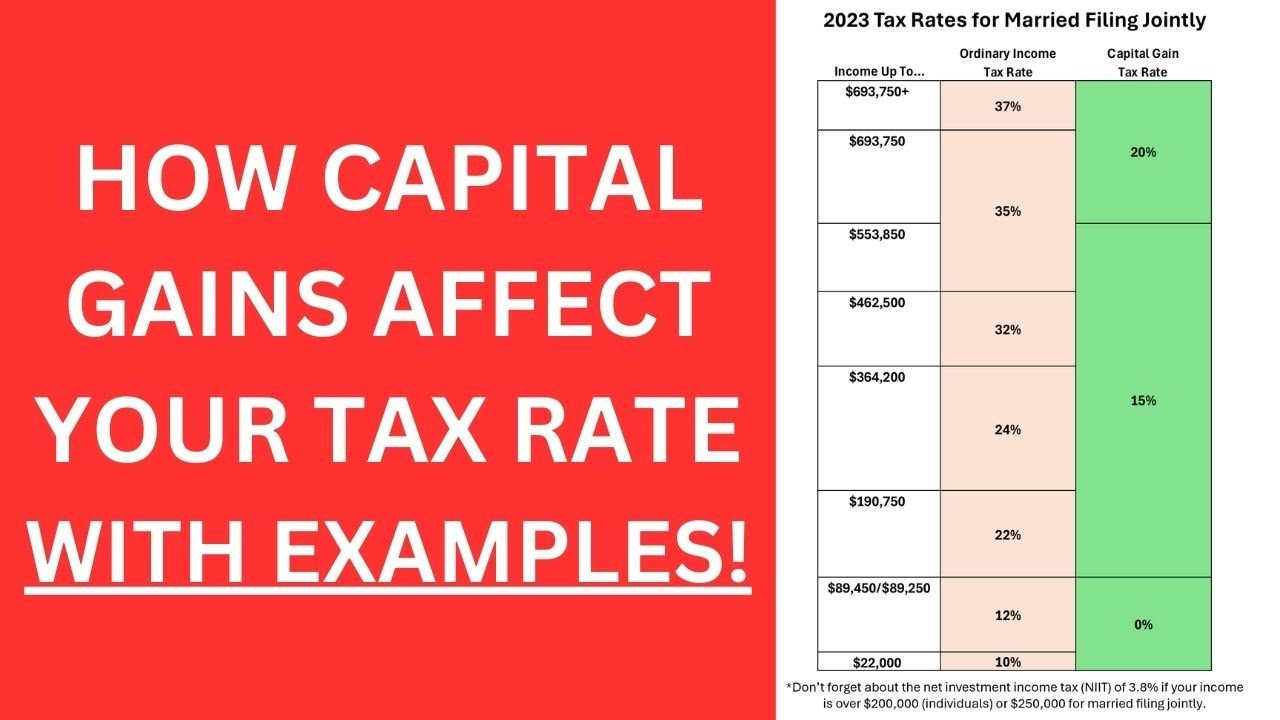
- 😀 The tax rate on earned income in the U.S. can reach up to 37%, whereas long-term capital gains are taxed at a maximum rate of 20%.
- 😀 Wealthy individuals often generate income from capital gains, dividends, and business income, not just from traditional jobs.
- 😀 Capital gains income is usually taxed at 0%, 15%, or 20%, depending on your taxable income, with no payroll taxes applied.
- 😀 A high-paid employee making $200,000 could pay around $60,000 in taxes, while someone making the same amount from capital gains could pay only $30,000.
- 😀 Wealthy people often use strategies to minimize taxes, such as taking founder shares instead of a salary or leveraging tax exemptions on small business stock.
- 😀 The U.S. government created favorable tax treatment for capital gains in the 1920s to encourage investment in businesses, homes, and land.
- 😀 Many countries, including the U.S., treat capital gains more favorably than earned income, creating a tax advantage for asset owners.
- 😀 Over time, the share of wealth going to business owners has increased, while the share going to workers has decreased, contributing to the growing wealth gap.
- 😀 The future of work will likely reward ownership over labor, as assets can generate passive income and grow in value without requiring more time or effort.
Q & A
What is the key difference between earned income and capital gains?
-The key difference is that earned income, such as wages and salaries, is taxed more heavily (up to 37%), whereas capital gains from assets like stocks or real estate are taxed at a lower rate (0%, 15%, or 20%), depending on the income level.
How does the IRS treat different types of income?
-The IRS treats earned income, portfolio income, and passive income differently. Earned income is taxed the most, with rates ranging from 10% to 37%. Portfolio income, like long-term capital gains, is taxed at 0%, 15%, or 20%, and passive income may benefit from depreciation and other tax shelters.
How much can a high-paid employee pay in taxes compared to an investor?
-A high-paid employee can pay 40-50% in taxes, while an investor, such as a private equity investor, might pay under 20% due to the favorable tax treatment of capital gains and dividends.
What tax strategies do wealthy people use to reduce their tax burden?
-Wealthy individuals often structure their income to fall under capital gains, such as taking founder shares or equity instead of a salary. They also use strategies like the 'buy borrow die' approach or leverage Qualified Small Business Stock (QSBS) exemptions to minimize taxes.
What is the impact of capital gains on the tax bills of investors?
-Capital gains are taxed at preferential rates, making them a more tax-efficient form of income. Additionally, investors can use tax loss harvesting, which allows them to offset gains with losses, reducing their overall tax bill.
How does capital gains tax differ from earned income tax?
-Capital gains tax is much lower than earned income tax. While earned income can be taxed up to 37%, long-term capital gains are taxed at rates of 0%, 15%, or 20%. This provides a significant advantage for those who invest in assets.
What historical reason explains the lower taxation on capital gains?
-The government wanted to encourage investment in businesses, homes, and land. By offering lower tax rates on capital gains, it incentivized people to invest in assets that would grow in value over time, which in turn helped boost the economy.
How do other countries treat capital gains compared to the US?
-Many developed countries also offer favorable treatment for capital gains. For example, the UK taxes capital gains at 10-20%, Germany imposes no tax after one year, and Singapore doesn't tax capital gains at all, while regular income tax rates can exceed 40% in these countries.
How does the future of work relate to ownership versus effort?
-The future of work will increasingly reward ownership over effort. As technology, AI, and automation reduce the need for human labor, those who own income-generating assets will have more security and freedom than those relying solely on a paycheck.
How have income distribution trends changed over time in the US?
-Over time, the share of income going to workers has decreased, while the share going to business owners and investors has increased. In 1970, workers received 64% of the economy's income, but by 2023, that dropped to less than 59%, highlighting the growing wealth gap between labor and ownership.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)