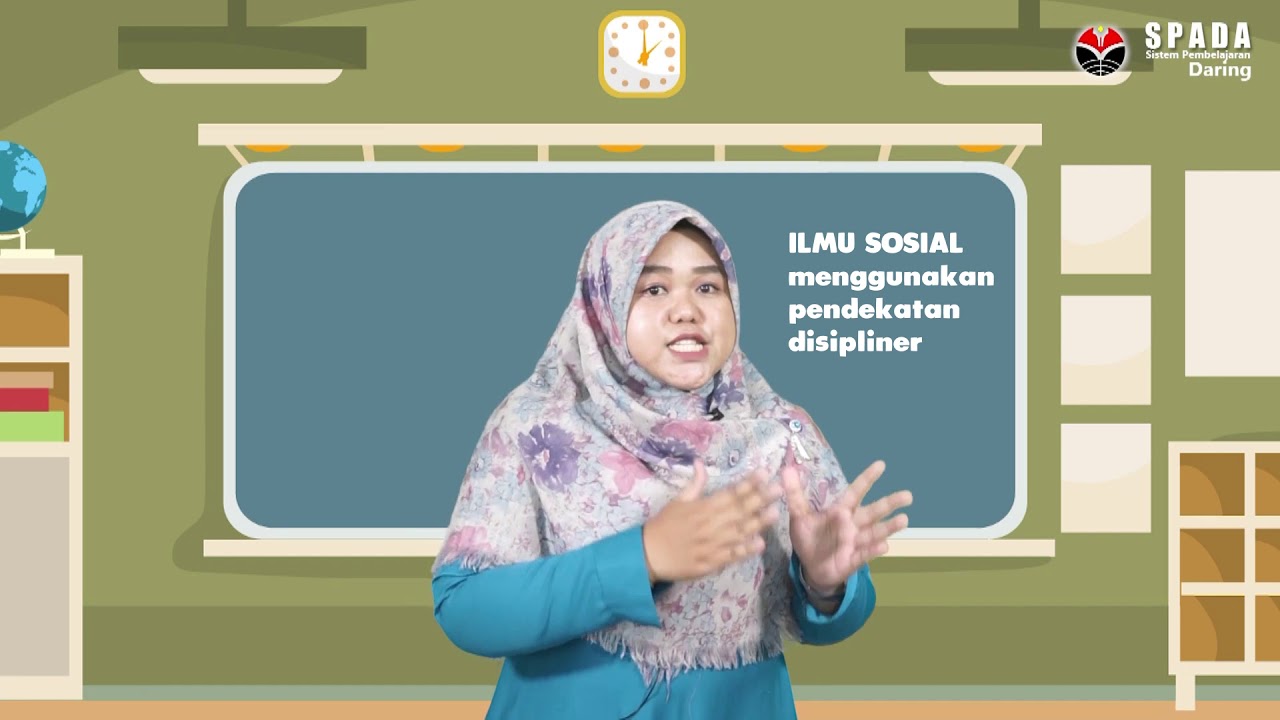
Menjelajah Ilmu Pengetahuan Sosial | IPS SMA
Summary
TLDRThis video script explores the social sciences, covering four major fields: sociology, economics, history, and geography. It delves into the origins and key concepts of each field, explaining how they help us understand human behavior, societal issues, and historical events. The script highlights the impact of the Industrial and French Revolutions on the birth of sociology, introduces the principles of economics, outlines historical methodology, and explores the foundations of geography. The video aims to engage viewers by connecting real-world issues, like climate change and community conflicts, with academic study.
Takeaways
- 😀 Sociology emerged due to societal upheavals, particularly in 18th-century Europe during the Industrial and French Revolutions.
- 😀 Sociology aims to study social interactions, conflicts, norms, social institutions, structures, and welfare.
- 😀 Key figures in sociology include Ibn Khaldun, Auguste Comte (Father of Sociology), Émile Durkheim, Karl Marx, and Max Weber.
- 😀 Sociology is empirical (research-based), theoretical (logically explained), cumulative (developing), and non-ethical (describes rather than judges social phenomena).
- 😀 Economics focuses on human efforts to satisfy their needs and deals with scarcity, prioritizing primary needs over secondary and tertiary ones.
- 😀 Adam Smith's contributions to economics marked the start of systematic economic studies, earning him the title of the Father of Economics.
- 😀 Economics is categorized into descriptive (describes reality), theoretical (explains causal relationships), and applied economics (addresses issues through policies).
- 😀 Financial literacy is crucial for managing money, including budgeting for expenses, bills, savings, and investments.
- 😀 History is the study of past events, with Herodotus, known as the Father of History, being an important figure in the field.
- 😀 Historical science is concerned with understanding human events in relation to space, time, and causes, using chronology and periodization to structure knowledge.
- 😀 Geography studies the Earth's surface, material objects (geospheres), and human aspects (socio-cultural, economic, political), with key figures like Eratosthenes and Marco Polo contributing to its development.
Q & A
What is sociology and how did it originate?
-Sociology is a branch of social science that studies individuals and society. It originated during the 18th century, particularly due to social changes brought about by the Industrial and French Revolutions. These revolutions disrupted traditional societal structures, creating new social problems, which led to the development of sociology.
Who are some notable sociologists and their contributions?
-Notable sociologists include Ibn Khaldun, considered the founder of sociology, and Auguste Comte, known as the 'Father of Sociology'. Other significant figures include Emil Durkheim, Karl Marx, and Max Weber, who all contributed extensively to the development of sociological theories and concepts.
What are the main characteristics of sociology as a science?
-Sociology has several key characteristics: it is empirical (based on scientific research), theoretical (explains phenomena logically), cumulative (constantly developing), and dynamic (it adapts to changing social contexts). Sociology does not focus on determining right or wrong but rather explains various social phenomena.
What are the three categories of economics?
-Economics is divided into three categories: descriptive economics, which describes real economic conditions and problems; theoretical economics, which explains causal relationships and how economic systems function; and applied economics, which addresses economic issues through policy measures.
Why was economics developed and what is its primary focus?
-Economics emerged due to the problem of scarcity, where human needs exceed the available resources. It primarily focuses on how individuals and societies manage their resources to meet needs and desires. The development of economics was also influenced by Adam Smith, who is known as the Father of Economics.
What is the meaning of historical science, and who is considered its father?
-Historical science studies past events and human activities. The term 'history' comes from the Arabic word 'syajarotun', meaning tree. Herodotus, often called the 'Father of History', was the first to use sources such as inscriptions and oral stories to document history, especially the Persian War.
What are the key concepts of historical science?
-Key concepts in historical science include human actors, space and time, chronology (arranging events in time sequence), periodization (grouping history based on certain criteria), and analyzing causes and effects of events. These help to understand historical changes and continuity over time.
What is the difference between diachronic and synchronic perspectives in history?
-The diachronic perspective studies events dynamically over time, observing how they change or evolve. The synchronic perspective, on the other hand, focuses on a specific moment in time, analyzing events in-depth at a particular point without considering their historical progression.
How did geography evolve and what does it focus on?
-Geography emerged as a discipline in the 3rd century BC with Eratosthenes, who introduced the concept of mapping the Earth's surface. Geography evolved further with figures like Ibn Batuta and Marco Polo, who documented travels and landscapes. It focuses on the relationship between humans and the Earth, including physical aspects (abiotic and biotic phenomena) and non-physical aspects (social, economic, and political aspects).
What are the fundamental principles of geography?
-Geography is grounded in several principles: the principle of distribution (examines the spatial distribution of phenomena), the principle of interaction (explores the relationships between different phenomena), the principle of description (describes phenomena using maps or diagrams), and the principle of chorology (analyzes the spatial and interactional aspects of phenomena).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)