วิชาโลกดาราศาสตร์อวกาศ - ทฤษฎีการแปรสัณฐาน
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the theory of plate tectonics, exploring the movement of Earth's lithospheric plates and their impact on geological features. It covers key theories, such as continental drift and seafloor spreading, providing evidence for tectonic shifts, including fossil records, rock formations, and oceanic ridges. The video outlines three main types of plate movements: divergent, convergent, and transform, explaining how each results in various natural formations like mountain ranges, ocean trenches, and faults. By the end, viewers gain a comprehensive understanding of the forces shaping Earth's surface.
Takeaways
- 😀 Frank Taylor's theory of continental drift proposes that continents were once joined together and have since drifted apart.
- 😀 Evidence supporting the theory of continental drift includes similarities in rock groups, glacial sediment, and fossils across continents.
- 😀 Harry H's Seafloor Spreading theory suggests that the seafloor expands as tectonic plates move apart.
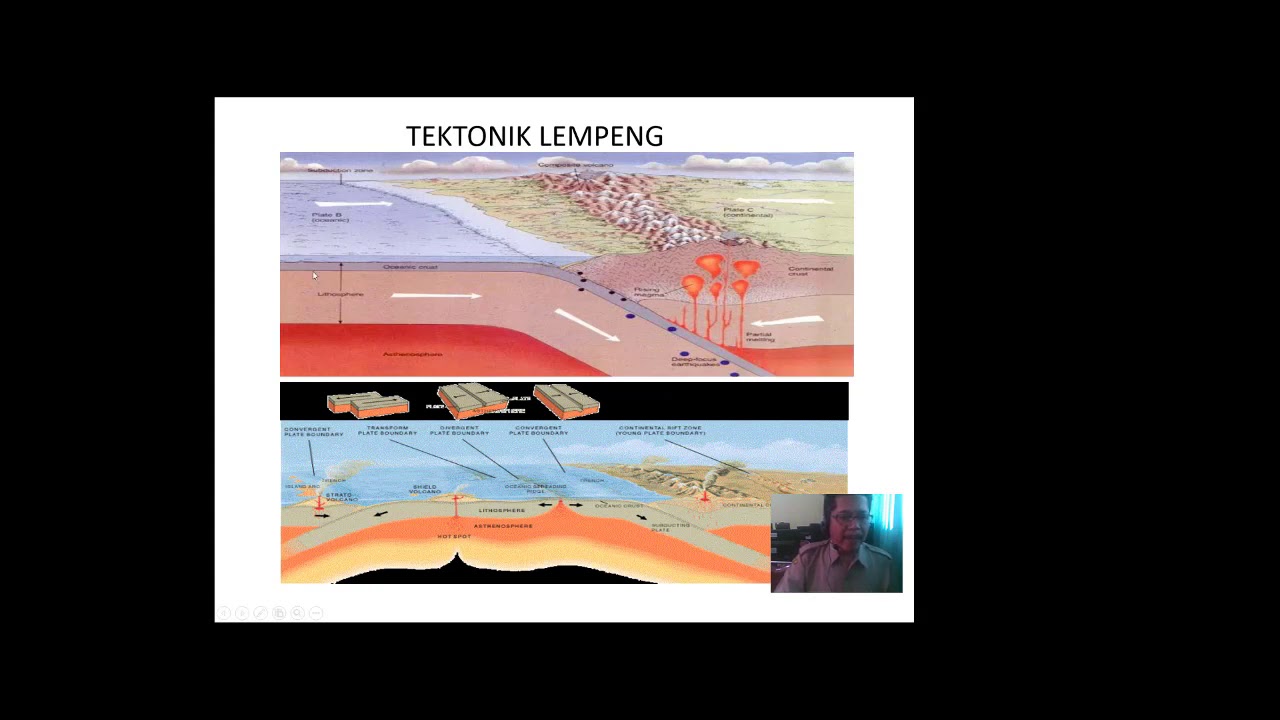
- 😀 The theory of plate tectonics explains the movement of tectonic plates, which is driven by convection currents in the lithosphere.
- 😀 Tectonic plate movement can be classified into three types: plates moving apart, towards each other, and sideways past each other.
- 😀 Seafloor spreading occurs when oceanic plates move apart, forming new oceanic crust and mid-ocean ridges.
- 😀 When oceanic plates collide with each other, volcanic island arcs can form, such as Japan's volcanic belt.
- 😀 Oceanic plates colliding with continental plates can create deep ocean trenches and volcanic arcs, as seen in the Andes mountains.
- 😀 When continental plates collide, they create high mountain ranges, such as the Himalayas, through a process called orogeny.
- 😀 Tectonic plates also move sideways, causing transform faults and earthquakes, like the San Andreas Fault in North America.
Q & A
What is the main focus of Frank Taylor's theory of continental drift?
-Frank Taylor's theory of continental drift suggests that continents have shifted over time, with evidence supporting this idea found in the junctions of the main continents, the similarity of rock groups, glacier sediment bases, and fossils.
How does the theory of seafloor spreading support the concept of continental drift?
-The theory of seafloor spreading supports continental drift by showing how tectonic plates move apart at mid-ocean ridges, creating new oceanic crust. This process also helps explain the age distribution of rocks and the formation of oceanic ridges and trenches.
What is the relationship between convection currents and tectonic plate movement?
-Convection currents in the Earth's lithosphere drive the movement of tectonic plates. These currents carry the lithosphere, causing the plates to move up and down or in different directions, which leads to the formation of different landforms.
What are the three main types of tectonic plate movement described in the transformation theory?
-The three main types of tectonic plate movement are: 1) plates moving apart, 2) plates moving towards each other, and 3) plates sliding past each other.
How does seafloor spreading create new landscapes?
-Seafloor spreading occurs when tectonic plates move apart at mid-ocean ridges, creating new oceanic crust. This process results in the formation of features like ocean ridges and the expansion of the seafloor.
What happens when oceanic plates collide with other oceanic plates?
-When oceanic plates collide with other oceanic plates, one plate may subduct beneath the other, forming deep ocean trenches. This can lead to the formation of volcanic island arcs, like the volcanic belt of Japan.
What occurs when oceanic plates collide with continental plates?
-When oceanic plates collide with continental plates, the oceanic plate subducts beneath the continental plate, forming deep oceanic trenches and sometimes creating volcanic arcs on the continental plate, such as the Andes Mountains in South America.
How do continental plates interact when they collide?
-When continental plates collide, they do not subduct but instead push up against each other, causing the formation of long, high mountain ranges like the Himalayas.
What geological features are associated with tectonic plate collisions?
-Tectonic plate collisions lead to geological features such as mountain ranges, deep ocean trenches, volcanic arcs, and faults, including low-angle reverse or thrust faults.
What is a transform fault, and where is it commonly found?
-A transform fault is a crack in the Earth's lithosphere where tectonic plates slide past each other horizontally. One of the most famous examples is the San Andreas Fault in California.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Tectónica de Placas - Parte II

GRADE 10 SCIENCE QUARTER 1, MODULE 4 : EARTH'S MECHANISM, MANTLE CONVECTION - EINSTEINATICS TV
IPS KELAS 9 MATERI TEORI TERBENTUKNYA BENUA

Introduction to plate tectonics | Middle school Earth and space science | Khan Academy

Teori pembentukan benua

5.a - Plate Tectonics.mp4
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)