Introduction to plate tectonics | Middle school Earth and space science | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRThis script explores the concept of plate tectonics, explaining how Earth's lithosphere is divided into tectonics plates that move over the asthenosphere. It describes the slow movement of these plates, which has reshaped Earth's continents from a single supercontinent, Pangea, to their current configuration. Evidence such as matching coastlines and shared fossils supports this theory. The script also details the three types of plate boundaries—convergent, divergent, and transform—and illustrates how these interactions shape geological features and cause earthquakes. The driving force behind plate movement is attributed to gravity acting on the denser plates over the more pliable asthenosphere.
Takeaways
- 🌏 The Earth's lithosphere, which includes the crust and upper mantle, is divided into tectonic plates that move over the asthenosphere.
- 🏁 Tectonic plates move at a very slow pace, only a few centimeters per year, similar to the growth rate of human fingernails.
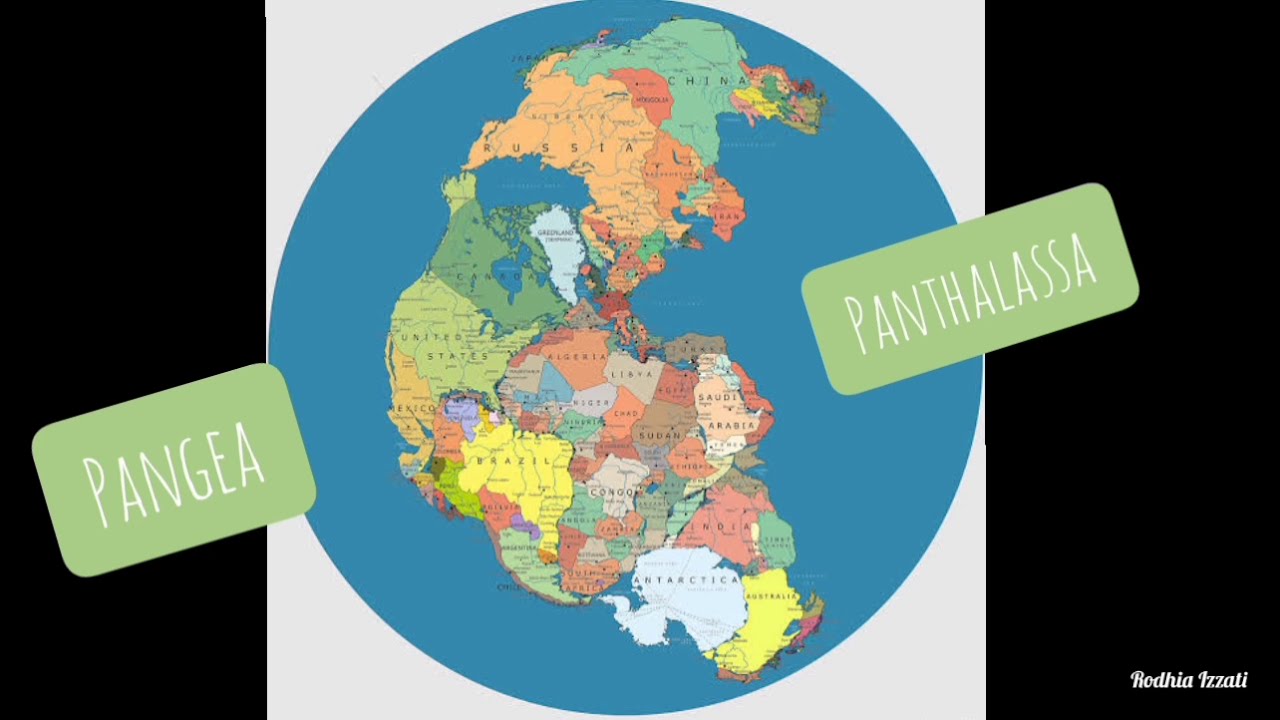
- 🌌 The continents were once part of a supercontinent called Pangea, which broke apart over 200 million years ago to form the continents we know today.
- 🧩 Evidence for plate tectonics includes the jigsaw puzzle-like fit of continents' coastlines, such as the east coast of South America and the west coast of Africa.
- 🦕 Fossils of the same species found on different continents suggest that these land organisms lived when the continents were connected.
- 🚫 Tectonic plates move in various directions and interact at their edges in three main ways: convergent, divergent, or transform boundaries.
- 🏞️ Convergent boundaries, like the collision of the Indian and Eurasian plates, can create mountain ranges, such as the Himalayas.
- 🌋 Divergent boundaries occur where two plates move apart, potentially forming rift valleys and mid-ocean ridges.
- 🌀 Transform boundaries involve plates sliding past each other, leading to friction, pressure buildup, and earthquakes.
- 🌡️ The movement of tectonic plates is influenced by gravity, with the denser plates sinking into the asthenosphere at convergent boundaries.
- 🏔️ The Himalayan mountains continue to grow due to the ongoing collision of the Indian and Eurasian plates, adding over a centimeter each year.
Q & A
What is the Earth's lithosphere and what is its composition?
-The Earth's lithosphere is the rigid outermost layer of the Earth, composed of the crust and the upper part of the mantle. It is broken up into tectonic plates that move on the asthenosphere.
How fast do tectonic plates move relative to each other?
-Tectonic plates typically move only a few centimeters per year, which is comparable to the rate at which human fingernails grow.
What was the supercontinent that existed before the continents drifted apart to form the current layout of Earth?
-The supercontinent that existed before the continents drifted apart is called Pangea.
What evidence supports the idea that continents were once connected as part of a supercontinent?
-Evidence such as matching coastlines, fossils of the same species found on different continents, and the fit of the continents on a map like a jigsaw puzzle support the idea of continental drift and the existence of Pangea.
How do scientists categorize the interactions between tectonic plates at their edges?
-Scientists categorize the interactions between tectonic plates as convergent, divergent, or transform boundaries based on how the plates move relative to each other.
What is a convergent boundary and how does it affect the Earth's surface?
-A convergent boundary is where two plates come together, often resulting in the formation of mountain ranges, such as the Himalayas, due to the compression and uplift of the crust.
What is the significance of the Himalayan mountains in the context of plate tectonics?
-The Himalayan mountains are significant because they are formed by the collision of the Indian tectonic plate with the Eurasian plate, demonstrating the ongoing process of plate tectonics.
What are divergent boundaries and what landforms can they create?
-Divergent boundaries occur where two tectonic plates move apart, and they can create landforms such as rift valleys and mid-ocean ridges.
What is a transform boundary and how does it relate to earthquakes?
-A transform boundary is where two plates slide past each other, causing friction and pressure buildup that, when released, can result in earthquakes.
What role does gravity play in the movement of tectonic plates?
-Gravity plays a key role in the movement of tectonic plates, particularly at convergent boundaries where the edges of the plates can sink into the asthenosphere due to gravity.
How do the interactions of tectonic plates contribute to the changing landscape of Earth over millions of years?
-The interactions of tectonic plates, through convergent, divergent, and transform boundaries, contribute to the formation and shifting of landforms, mountain ranges, and oceanic features, shaping the Earth's landscape over geological time.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)