IPS KELAS 9 MATERI TEORI TERBENTUKNYA BENUA
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explores the formation of continents and oceans, focusing on Alfred Wegener's theory of continental drift, which suggests that all continents were once part of a supercontinent called Pangea. The theory explains how Pangea split into two landmasses, Laurasia and Gondwana, and how they later separated into the continents we know today. The video also covers the theory of plate tectonics, describing the movement of Earth's lithospheric plates and their impact on the planet's surface, including the formation of mountains, oceans, and earthquakes. Evidence for these theories, such as matching coastlines and geological similarities, is discussed to strengthen the concepts.
Takeaways
- 😀 Continents and oceans are not fixed, but have evolved over millions of years.
- 🌍 The five continents are Asia, America, Africa, Europe, and Australia, while Antarctica is uninhabited.
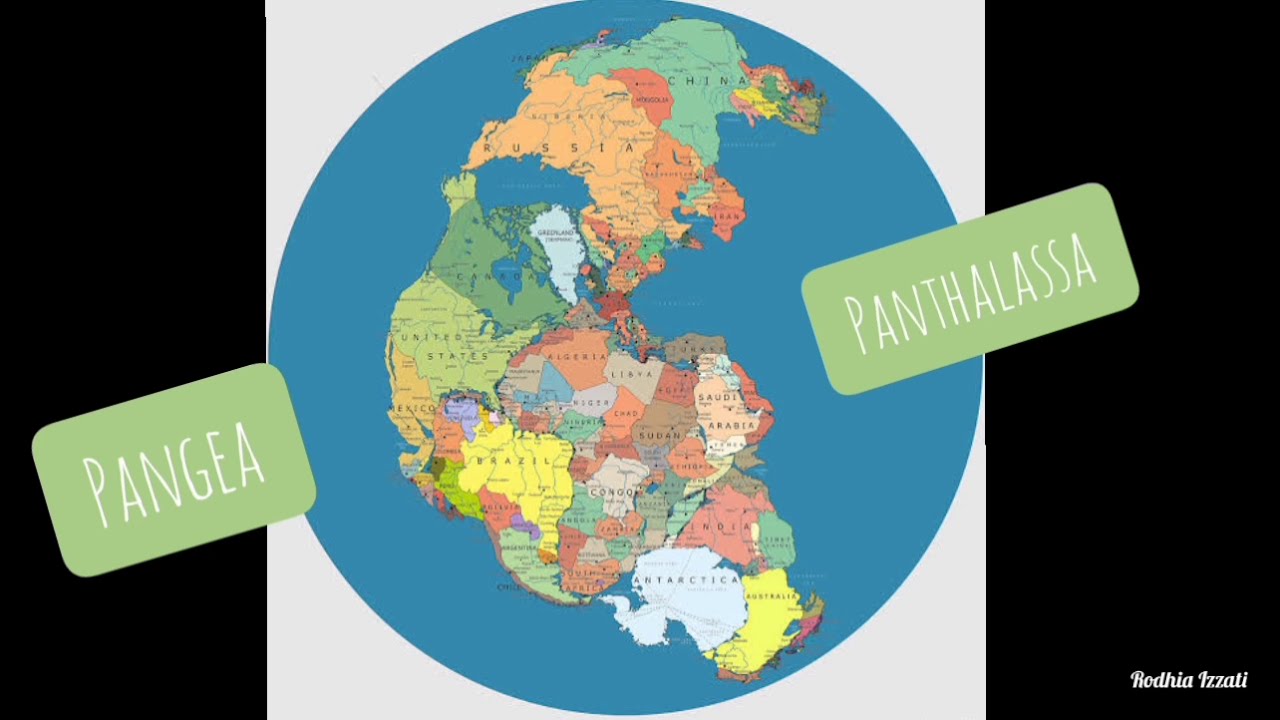
- 📜 Alfred Wegener proposed the theory of continental drift, stating that continents were once part of a single supercontinent called Pangea.
- 🔄 Pangea eventually split into two major landmasses: Laurasia in the north and Gondwana in the south.
- 🌎 Gondwana further split into the Americas and Africa, while Laurasia split into Asia, Europe, and Australia.
- 🧭 Evidence supporting Wegener’s theory includes matching coastlines, similar geological formations, and fossil evidence across continents.
- 🌋 The tectonic plate theory suggests that Earth’s surface is made up of large, moving plates that float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere.
- ⚡ The movement of tectonic plates can cause earthquakes, volcanoes, and the formation of mountains.
- ↗️ Tectonic plate movements are classified into three types: divergent (plates move apart), convergent (plates move toward each other), and transform (plates slide past each other).
- 💡 Divergent movement can create ocean ridges and valleys, while convergent movement can create mountains and ocean trenches.
- 🌊 The breakup of Gondwana resulted in the formation of several modern continents, including South America, Africa, Asia, Europe, and Australia.
Q & A
What is the first topic discussed in the transcript?
-The first topic discussed is the introduction to social science, focusing on continents and oceans.
How many continents are mentioned in the transcript and which one is the largest?
-Five continents are mentioned: Asia, America, Africa, Europe, and Australia. Asia is the largest continent.
What is the significance of Antarctica according to the script?
-Antarctica is notable because it is a continent that is not inhabited by humans.
According to the script, did the continents always exist as they are now?
-No, the continents did not always exist as they are now. The script mentions that there are theories explaining how continents formed.
Who proposed the theory of continental formation discussed in the transcript?
-The theory was proposed by Alfred Wegener, a German scientist.
What is Pangea and how is it related to the formation of today's continents?
-Pangea was a supercontinent that existed around 300 million years ago. According to Wegener, Pangea broke into two major landmasses, Laurasia and Gondwana, which further split to form the continents we know today.
What evidence does Alfred Wegener provide to support his theory of continental drift?
-Wegener's evidence includes the similarity of coastlines, such as the matching shapes of the eastern coast of Africa and the western coast of America, as well as similarities in rock formations across continents.
What is the second theory mentioned in the transcript about continental formation?
-The second theory is the theory of plate tectonics, which explains the movement of Earth's lithospheric plates and how these movements cause the formation and change of continents and oceans.
What are the three types of plate movements described in the transcript?
-The three types of plate movements are: divergent (plates moving apart), convergent (plates moving towards each other), and transform (plates sliding past each other).
What natural phenomena result from the movements of tectonic plates?
-The movements of tectonic plates can lead to the formation of mountains, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and the creation of oceanic features like ocean ridges and trenches.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Evidences Of Plate Tectonics,Continental Drift,Seafloor Spreading,Magnetic Reversal,Grade 10 Science

Araling Panlipunan 8 MATATAG Q1 Week 1-2 Mga Teorya sa Pagkakabuo ng mga Kontinente with PPT and DLL

Evidence of Plate Movement
Teori Perkembangan Bumi

CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY | SCIENCE 10 - Week 8 Part I

TEORI PERGERAKAN LEMPENG TEKTONIK
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)