Locations of Volcanoes
Summary
TLDRThis lesson explores the locations of active volcanoes, focusing on their association with tectonic plate movements. Volcanoes typically form along subduction zones, divergent boundaries, and hotspots. The Circum-Pacific Belt, also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire, hosts many active volcanoes, such as Mount Etna and Mount Merapi. Volcanic activity also occurs at divergent boundaries like the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Additionally, hotspot volcanoes like those in Hawaii are formed by mantle plumes. As plates move, these volcanoes age and eventually become extinct. The lesson emphasizes the different plate interactions that give rise to volcanic activity and how volcanoes evolve over time.
Takeaways
- 😀 Volcanoes are formed through the subduction of oceanic plates beneath other plates, often along convergent plate boundaries.
- 😀 Volcanic arcs are found at oceanic-continental convergent plate boundaries, and volcanic island arcs at oceanic-oceanic convergent boundaries.
- 😀 Mount Etna in Sicily is an example of a volcano formed due to a convergent plate margin, located between the Eurasian and African plates.
- 😀 The Circum-Pacific Belt, or the Pacific Ring of Fire, is a major area of active volcanism due to convergent plate boundaries, hosting notable volcanoes like Mount Merapi and Mount Mayon.
- 😀 A significant number of volcanoes also occur along divergent plate boundaries, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, where oceanic plates pull apart and create new crust.
- 😀 The Mid-Atlantic Ridge separates the North American and Eurasian plates, as well as the South American and African plates, and causes volcanic activity.
- 😀 Volcanic activity also occurs along continental-continental divergent boundaries, such as the East African Rift, where volcanoes like Erta Ale are located.
- 😀 Hot spots are volcanic regions not located on plate boundaries, formed by abnormally hot areas in the mantle called mantle plumes.
- 😀 The Hawaiian hot spot is an example of a volcanic hot spot, where volcanic islands are formed as the Pacific Plate moves over the mantle plume.
- 😀 As volcanic islands move away from a hot spot, they become progressively older and eventually become extinct, such as the case with Mauna Loa, the world's largest subaerial volcano.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of this video lesson?
-The main purpose of the video lesson is to discuss the locations of volcanoes and help viewers identify and describe the areas where active volcanism occurs.
What are volcanoes and what typically accompanies volcanic eruptions?
-Volcanoes are areas on the Earth's crust where lava emerges. Volcanic eruptions are often accompanied by pyroclastic flows and tephras.
What geological process leads to the formation of volcanoes?
-Volcanoes are primarily formed due to the subduction of an oceanic plate beneath another plate, which leads to the formation of volcanic arcs and island arcs at convergent plate boundaries.
Can you explain the difference between oceanic-continental and oceanic-oceanic convergent plate boundaries in terms of volcanism?
-At oceanic-continental convergent plate boundaries, volcanic arcs are formed, while at oceanic-oceanic convergent plate boundaries, volcanic island arcs are created.
What is an example of a volcano formed by subduction zones?
-An example of a volcano formed by subduction zones is Mount Etna, located on the east coast of Sicily, Italy.
What is the Circum-Pacific Belt, and why is it significant in terms of volcanism?
-The Circum-Pacific Belt, also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire, is a region around the Pacific Ocean that is surrounded by convergent plate boundaries, leading to a nearly continuous series of volcanic arcs, oceanic trenches, and volcanic belts.
What is the most common type of volcanism at divergent plate boundaries?
-The most common type of volcanism at divergent plate boundaries occurs due to the formation of new crust, typically seen at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, where lava erupts as the plates move apart.
How does volcanic activity manifest in Iceland due to divergence?
-In Iceland, volcanic activity is evident through geysers, which periodically eject hot water and steam as a result of volcanic processes occurring along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
What are hot spots, and how do they lead to volcanic formation?
-Hot spots are volcanic regions fed by anomalously hot mantle material. These areas are not located at plate boundaries but are formed by underlying hot rock, which causes magma to rise to the surface.
Why do hotspot volcanoes become progressively older as they move away from their source?
-Hotspot volcanoes become older as they move away from their source because the tectonic plates shift, carrying the volcanoes away from the mantle plume that provides magma, eventually causing the volcanoes to become extinct.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

DISTRIBUTION OF VOLCANOES, EARTHQUAKES AND MOUNTAIN BELTS IN THE WORLD | SCIENCE 10 - Week 3

Science 10. Q1. Distribution of Active Volcanoes, Earthquake Epicenters and Major Mountain Belts

Ring of Fire : Keuntungan dan Kerugian untuk Indonesia

Tectonic Plates

Natural Hazards
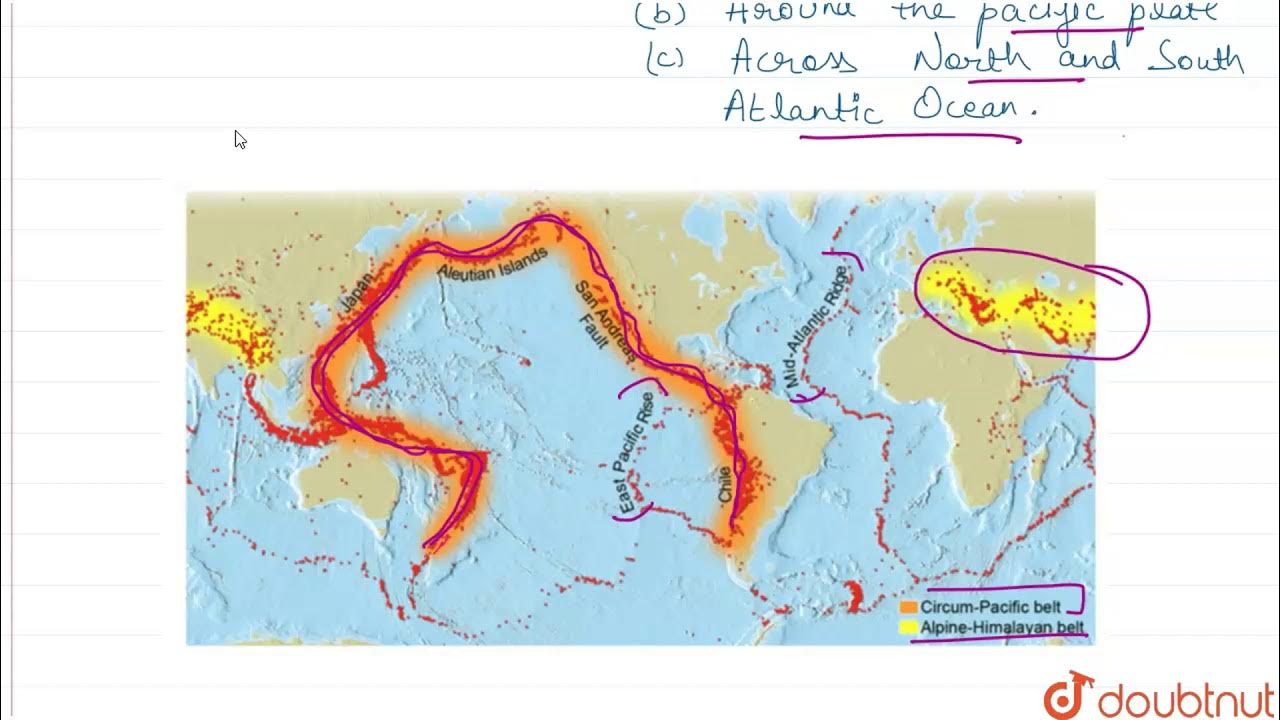
DISTRIBUTION OF EARTHQUAKE AND VOLCANOES
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)