8. Pemilihan Proses
Summary
TLDRThis video discusses the third stage of chemical plant design: process selection. It covers key steps such as defining process conditions, conducting initial economic analysis, and choosing processes based on technical, economic, and environmental factors. The video highlights the importance of clarity in process description, the use of flow diagrams, and optimization methods. The process selection is carried out using a grading system to evaluate alternative processes. Finally, the video touches on creating detailed engineering flow diagrams and the importance of accurately describing the entire process from raw material to finished product.
Takeaways
- 😀 Process selection is a critical stage in chemical plant design, focusing on selecting the safest, most efficient, and profitable process from multiple alternatives.
- 😀 The process description must be clear, detailing the reactions, operating conditions, and whether the system is batch or continuous.
- 😀 Initial economic analysis, comparing raw material prices to product prices, is essential for determining process sustainability and profitability.
- 😀 A flow diagram, typically in the form of a block diagram or process flow diagram (PFD), is needed to visually describe the process.
- 😀 Tool selection in process design must balance safety standards with economic feasibility, ensuring the tools are neither too expensive nor too cheap.
- 😀 Optimization is key in process design, such as recycling unreacted raw materials or using heat exchangers to minimize energy usage.
- 😀 Three main aspects to consider in process selection: technical, economic, and environmental impact.
- 😀 Technical aspects involve raw material conversion, product quality, and operating conditions (e.g., temperature and pressure).
- 😀 Economic aspects include total investment, rate of return on capital, and the time required to recoup the investment (payback period).
- 😀 Environmental impact considerations include the process's effect on waste generation and pollution levels.
- 😀 The grading or ranking method, like factor-rating, is used to assess different processes based on the technical, economic, and environmental aspects.
- 😀 After selecting a process, a detailed engineering flow diagram (PFD) is created to describe the process using standardized symbols and tool codes.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video discussed in the script?
-The video focuses on process selection in chemical plant design, specifically the third stage of designing a chemical plant. It discusses the criteria for selecting the most effective and efficient process that will generate the highest profit while ensuring safety and economic feasibility.
What are the conditions that must be met before conducting process selection?
-The conditions that must be met include: a clear process description (covering reactions, operating conditions, and systems), an initial economic analysis showing profit potential, a flow diagram (block diagram or process flow diagram), the selection of economically feasible and safe processing tools, and optimization through measures such as recycling and heat exchange.
What are the three key aspects to consider when selecting a process?
-The three key aspects to consider when selecting a process are technical aspects (such as raw material conversion and product quality), economic aspects (including total investment, rate of return, and payback time), and environmental impact (focusing on pollution and waste management).
How can the process selection be evaluated based on the discussed method?
-The process selection can be evaluated using a grading or ranking method, where each alternative process is assessed based on its technical, economic, and environmental aspects. The process with the highest total score is selected for further development and described in a Process Flow Diagram (PFD).
What is the purpose of creating a Process Flow Diagram (PFD)?
-The purpose of creating a PFD is to visually represent the selected process, including key equipment codes, mass balances, process flows, and utilities. It serves as a blueprint for the detailed engineering and design of the chemical plant.
What information is typically included in a Process Flow Diagram (PFD)?
-A PFD includes tool codes, main process flows, recycling processes, utility connections (such as pumps or compressors), mass balances for each flow, and other essential elements like the title, process owner, and designer. It provides a comprehensive depiction of the plant's processes.
What does 'tool code' refer to in the context of process selection?
-In process selection, a tool code is a system used to identify specific equipment in the plant design. It typically consists of a letter representing the tool type (e.g., 'R' for reactor), followed by numbers indicating the area number, serial number, and whether the tool is a main or supporting tool.
What is the difference between a batch process and a continuous process?
-A batch process involves no continuous inflow and outflow during the process, resulting in accumulation of materials. In contrast, a continuous process allows for continuous inflow and outflow of materials, and in a steady-state condition, there is no accumulation.
How does the design of the chemical plant process take into account waste and pollution?
-The design of the chemical plant process considers waste and pollution by evaluating the environmental impact of the process. This includes assessing the potential waste generated and ensuring that waste management measures are in place to minimize environmental harm.
What is the importance of tool code numbering in plant design?
-Tool code numbering helps in identifying and organizing the equipment in a chemical plant design. It provides clarity on the location, type, and role of each tool, which is crucial for efficient construction, operation, and maintenance of the plant.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

ERP CRM and HCM Business Process Management [How To Do Business Process Improvement]
Multistage Amplifier: Design Example

MO Chapter 6 Product Design

Unit Operations in Chemical Engineering - Course Trailer

10 Common Digital Transformation Mistakes [Tips for a Better Digital Strategy and Roadmap]
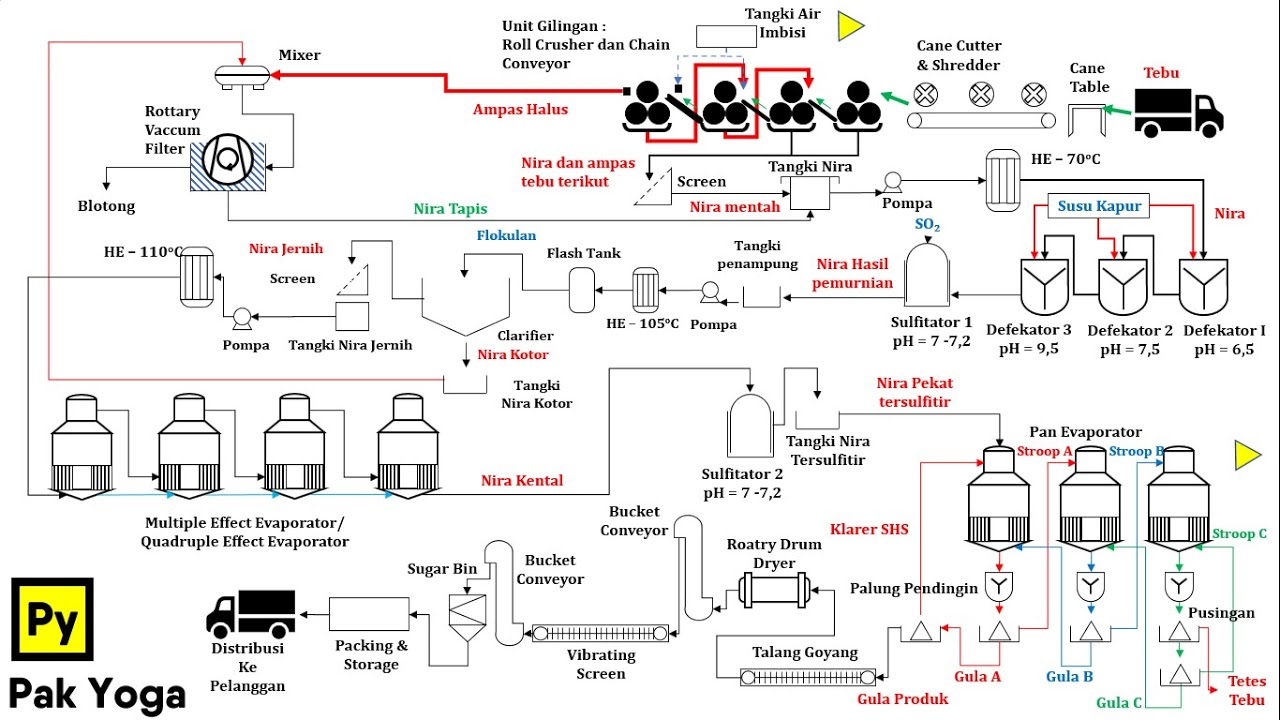
Kimia Industri - Diagram Alir Proses Pembuatan Gula tebu
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)