The Inductive and Capacitive Sensor | Different types and applications
Summary
TLDRThe video explains the working principles of capacitive and inductive sensors used in industrial automation. Inductive sensors detect metallic objects by generating electromagnetic fields, while capacitive sensors detect various materials by altering electrostatic fields. The video covers the components of each sensor, their configurations (shielded/unshielded, normally open/closed, PNP/NPN), and their applications, such as detecting liquid levels or container lids. It also compares the strengths and limitations of both sensor types in different environments, making it ideal for automation and control systems.
Takeaways
- 🔧 Sensors like capacitive and inductive sensors are widely used in industrial processes.
- 🧪 Capacitive sensors detect liquid levels, while inductive sensors detect if containers are covered.
- ⚙️ Inductive proximity sensors detect ferrous metal objects without physical contact, and they can also detect non-ferrous metals but at reduced distances.
- 🔄 The sensing range of inductive sensors varies by material and can be found in the sensor's datasheet, typically no more than 80mm.
- 📏 Hysteresis, the difference between activation and deactivation points, helps prevent bouncing between sensor states.
- 🛠️ Inductive sensors can be shielded (detect only at the front) or unshielded (wider detection area) and have various mounting options like flush or non-flush.
- ⚡ Capacitive sensors can detect a wide range of materials beyond metals, including plastic, glass, and liquid, and are used for level sensing.
- 📡 Capacitive sensors rely on changes in electrostatic fields and capacitance to detect objects, while inductive sensors use electromagnetic fields.
- 🔌 Both sensor types can be configured as normally open or closed, with PNP or NPN wiring options, typically powered by DC voltage.
- 🔍 Capacitive sensors are adjustable via a bolt to fine-tune detection distance, making them versatile for different applications.
Q & A
What are the main functions of capacitive and inductive sensors in industrial processes?
-Capacitive sensors detect the filling level of liquids, while inductive sensors detect if containers are covered by detecting the presence of metal lids.
How does an inductive proximity sensor detect metal objects?
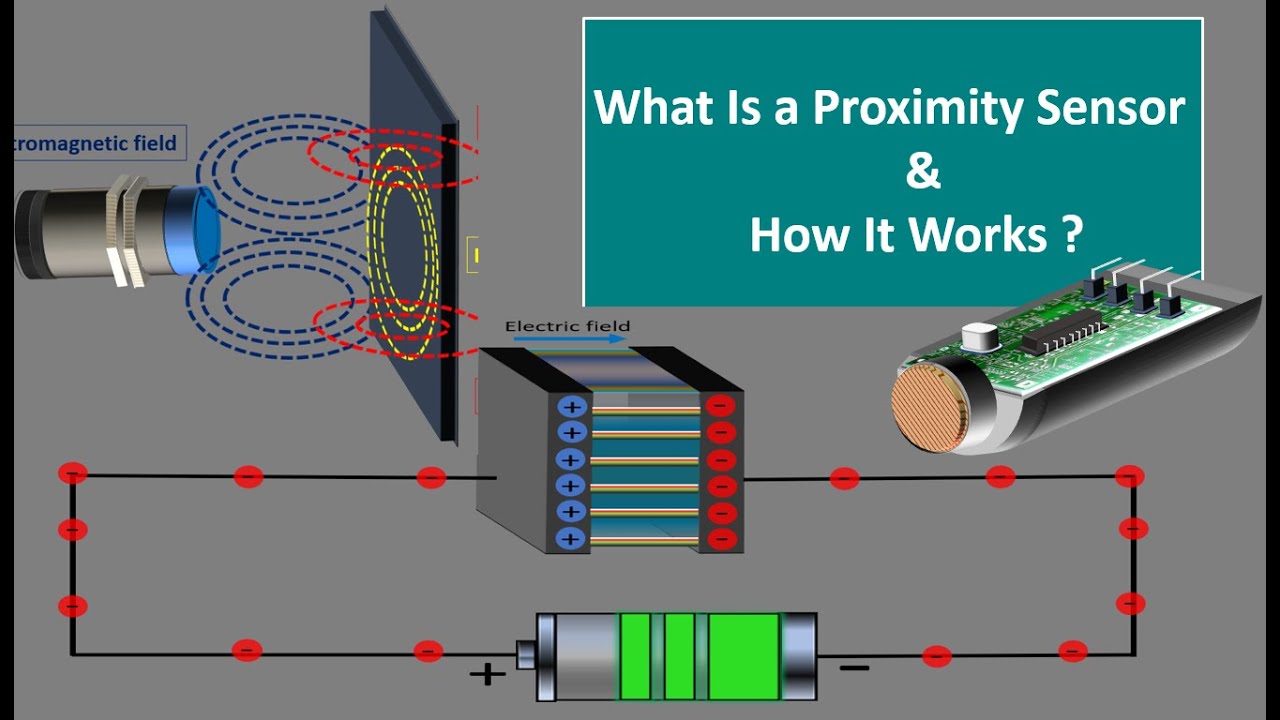
-An inductive proximity sensor detects metal objects by generating an electromagnetic field through an internal coil. When a metal object enters this field, an induction current flows in the metal, which the sensor detects as a change in oscillation, triggering a detection signal.
Can inductive sensors detect non-ferrous metals? If so, how does this affect the sensing range?
-Yes, inductive sensors can detect non-ferrous metals like brass, aluminum, and copper, but the detection range is reduced when compared to ferrous metals.
What is hysteresis in the context of inductive sensors, and why is it important?
-Hysteresis refers to the distance between the activation point and the deactivation point of the sensor. It is important because it prevents the sensor from 'bouncing' between states, ensuring stable detection.
What is the difference between shielded and unshielded inductive sensors?
-A shielded inductive sensor has a metal shield around the coil, limiting detection to the front of the sensor, while an unshielded sensor has a larger detection area, as the coil is not shielded, allowing detection from the sides.
What are the wiring configurations for inductive sensors, and how do they work?
-Inductive sensors typically have three wires: brown (positive power), blue (negative power), and black (signal output). The sensors can be NPN or PNP, referring to the type of transistor used in the sensor's output stage.
What types of objects can capacitive sensors detect?
-Capacitive sensors can detect various materials, including ferrous and non-ferrous metals, plastics, glass, wood, paper, and liquids. They are not limited to detecting metallic objects like inductive sensors.
How do capacitive sensors detect objects?
-Capacitive sensors detect objects by emitting an electrostatic field from dielectric plates. When an object approaches, it alters the capacitance in the field, triggering the sensor to send a detection signal.
What factors affect the detection range of capacitive sensors?
-The detection range of capacitive sensors is influenced by the material of the object, the environmental conditions, and the distance. Many sensors include an adjustment feature to fine-tune the detection distance.
What are the key differences between inductive and capacitive sensors in terms of detection and application?
-Inductive sensors only detect metallic objects and are robust in harsh environments, while capacitive sensors can detect a wider range of materials, including non-metallic objects, but are more sensitive to environmental factors like humidity.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Proximity Sensor working. Inductive proximity sensor, capacitive proximity sensor. proximity switch

Inductive Sensor Explained | Different Types and Applications

Belajar Proximity Sensor & Mengkoneksikannya Ke PLC Omron

Sensor dan Aktuator

Capacitive Sensor Explained | Different Types and Applications

Prototipe Tempat Sampah Cerdas - Tugas Akhir
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)