What pros know about APERTURE that beginners often ignore
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the creator explains aperture in photography, breaking down its impact on light, focus, and depth of field. The aperture controls how much light enters the camera, affecting exposure and image sharpness. A wider aperture (lower f-stop) creates a blurry background, ideal for portraits, while a smaller aperture (higher f-stop) is best for landscapes. The video also touches on using aperture for different effects like starburst and highlights the 'sweet spot' for lens sharpness. The creator encourages experimenting with aperture settings to find the best approach for unique photo effects.
Takeaways
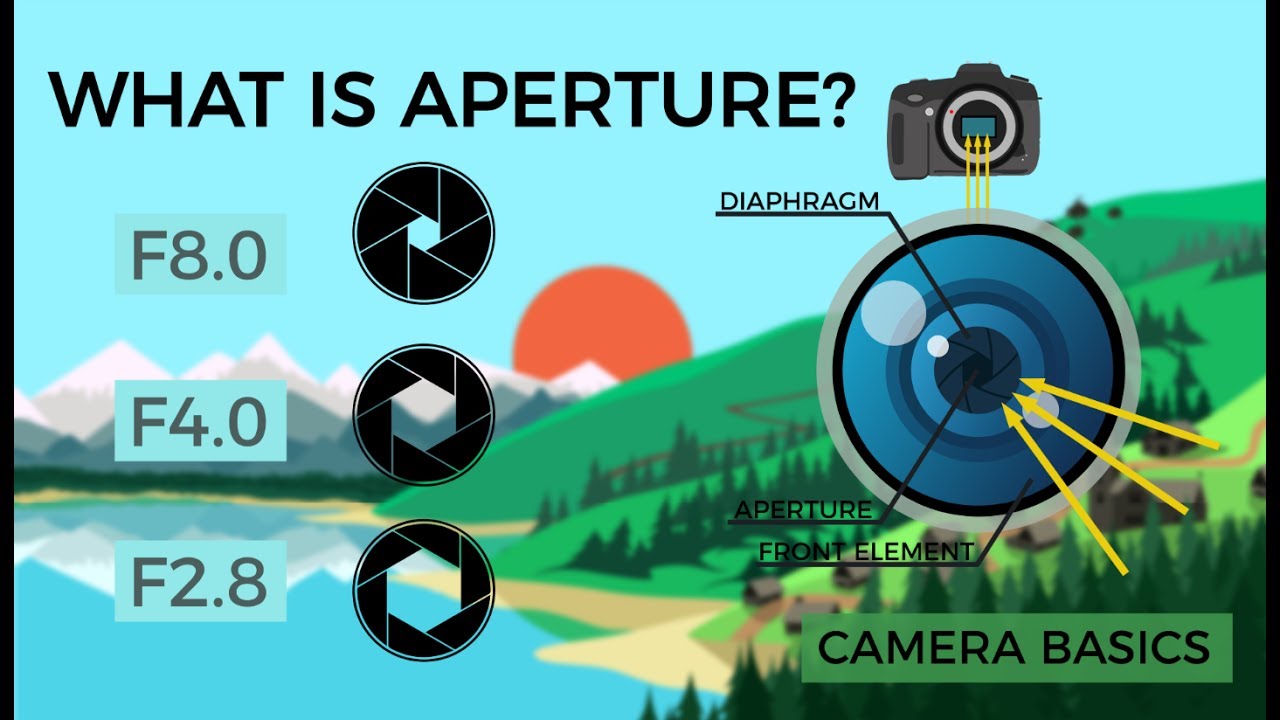
- 😀 Aperture controls the amount of light entering the camera through the lens, like the diameter of a water pipe.
- 😀 The f-stop system is used to measure aperture size, with lower f-stop numbers like f1.4 representing larger openings and higher numbers like f16 indicating smaller ones.
- 😀 Wide apertures (e.g., f1.8 or f2.8) are great for portraits, as they create a blurred background (Bokeh effect) and make the subject stand out.
- 😀 A smaller aperture (e.g., f11 or f16) provides a deeper depth of field, ensuring everything from foreground to background stays in focus, ideal for landscapes.
- 😀 Smaller apertures reduce the amount of light reaching the sensor, which may require a slower shutter speed or a tripod to avoid camera shake.
- 😀 Aperture affects exposure, with wider apertures allowing more light and smaller apertures needing more shutter time to maintain proper exposure.
- 😀 In bright conditions, using a smaller aperture (e.g., f16) helps avoid overexposure by limiting the amount of light entering the lens.
- 😀 Using ND filters allows for shallow depth of field (blurred background) even in bright conditions by physically limiting the light entering the camera.
- 😀 Lens aberrations (imperfections) can make photos less sharp at wide apertures, but sometimes these imperfections can add an artistic effect.
- 😀 The sweet spot for most lenses, in terms of sharpness, is usually between f5.6 and f8, offering the best image quality.
- 😀 Don't be afraid to experiment with different apertures to create unique effects, such as motion blur or miniature effects, by adjusting aperture size and shooting angle.
Q & A
What is aperture in photography?
-Aperture is the opening in a camera lens that allows light to pass through to the camera sensor. It's like the diameter of a pipe; the larger the opening, the more light enters the camera.
How are aperture sizes measured?
-Aperture sizes are measured in f-stops, not in centimeters or inches. A lower f-stop, like f1.4, represents a larger opening, while higher f-stops, like f16, represent smaller openings.
Why does a wider aperture create a blurry background?
-A wider aperture, like f1.8 or f2.8, results in a shallow depth of field, meaning only a small portion of the photo is in focus, which causes the background to blur out.
What is depth of field?
-Depth of field refers to the area in an image that appears in focus. A wide aperture creates a shallow depth of field, focusing only on a small part of the scene, while a smaller aperture increases the depth of field, making more of the scene sharp.
When would you use a small aperture like f11 or f16?
-A small aperture like f11 or f16 is used when you want to capture a scene with a deep depth of field, such as landscapes, where you need everything from the foreground to the background to be in focus.
How does aperture affect exposure?
-Aperture directly affects the amount of light that enters the camera. A wider aperture allows more light, while a smaller aperture allows less. The aperture setting must be balanced with shutter speed to achieve proper exposure.
What is an ND filter and when would you use it?
-An ND (Neutral Density) filter is used to reduce the amount of light entering the camera. It's helpful when using wide apertures in bright conditions or when filming video with a shallow depth of field, preventing overexposure.
Why might photos look less sharp when using a wide aperture?
-Photos can appear less sharp when using a wide aperture due to lens aberrations, such as color fringing or softness around the edges. These imperfections are more noticeable at wider apertures.
How can you create a Starburst effect with the Sun?
-To create a Starburst effect, use a small aperture like f16 or f22 when photographing a bright light source, like the Sun. The smaller the aperture, the more defined the rays of light will be.
What is the 'sweet spot' of a lens?
-The 'sweet spot' of a lens refers to the aperture setting where the lens performs best in terms of sharpness and overall image quality. For most lenses, this is typically around f5.6 to f8.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)