Analisis Jalur (Kelompok 2 PD)
Summary
TLDRPath analysis is a part of multivariate analysis that examines cause-effect relationships between variables. Unlike regression analysis, it assesses both direct and indirect effects, using mediating variables. First introduced by Sewall Wright in 1934, path analysis includes independent, dependent, mediating, exogenous, and endogenous variables. Key assumptions include linearity, normality, and no multicollinearity. The process involves creating a path diagram, calculating path coefficients, and conducting hypothesis tests like the Sobel test and model fit test to evaluate the model's validity and variable relationships.
Takeaways
- 😀 Path analysis is a part of multivariate analysis that explores the cause-effect relationships between variables.
- 😀 Unlike regression analysis, path analysis evaluates both direct and indirect relationships, including those through mediating variables.
- 😀 Path analysis can be seen as an extension of regression analysis, with a focus on more complex models involving mediating variables.
- 😀 Key terms in path analysis include independent variables, dependent variables, mediating variables, exogenous variables, and endogenous variables.
- 😀 Assumptions of path analysis include the use of interval/ratio data, linear relationships, and the assumption of independence between errors.
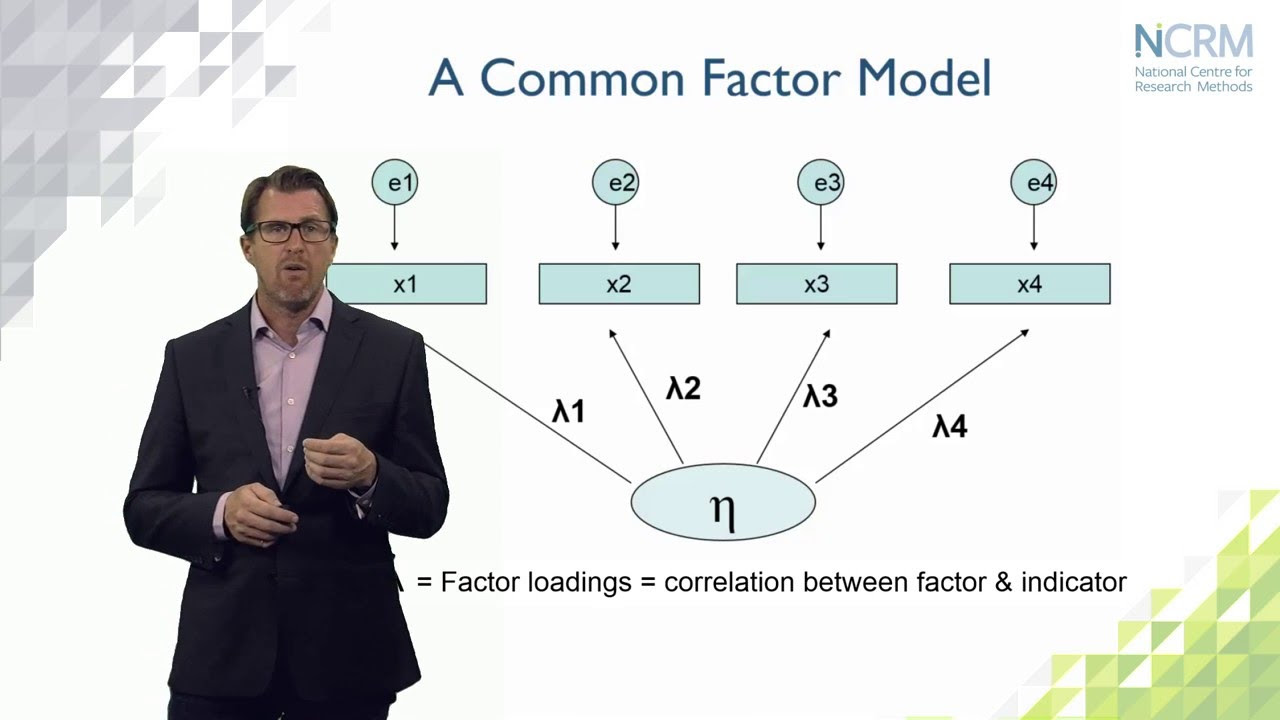
- 😀 Errors in measuring variables can impact the path coefficients, which are used to assess the influence of independent variables on dependent variables.
- 😀 A path diagram is essential in path analysis to visually represent the relationships between variables and the flow of influence.
- 😀 Exogenous variables are independent and not influenced by other variables, while endogenous variables are affected by other variables in the model.
- 😀 Path coefficients quantify the direct influence of variables and help in identifying indirect and total influences on the dependent variable.
- 😀 Hypothesis testing in path analysis involves path coefficient tests, Sobel tests for mediating effects, and model fit tests to evaluate the overall model adequacy.
Q & A
What is path analysis?
-Path analysis is a type of multivariate analysis that studies the relationship between variables and tests hypotheses of causality or cause-effect relationships. It was first introduced by geneticist Sewall Wright in 1934.
How does path analysis differ from regression analysis?
-In regression analysis, only direct relationships between independent and dependent variables are analyzed. Path analysis, however, allows for the analysis of both direct and indirect relationships between variables through mediating variables.
What are the key terms in path analysis?
-Some common terms in path analysis include independent variables, dependent variables, mediating or intervening variables, exogenous variables, and endogenous variables. Error terms are also considered in path analysis.
What are exogenous and endogenous variables?
-Exogenous variables are those whose values are not influenced by other variables in the model, such as independent variables. Endogenous variables, on the other hand, are influenced by other variables in the model, like dependent and mediating variables.
What assumptions are needed for path analysis?
-Path analysis assumes a linear relationship between variables, normal distribution, homoscedasticity (constant error variance), no multicollinearity, and no correlation between errors. The variables should be measured on interval or ratio scales.
Why is a path diagram important in path analysis?
-A path diagram visually represents the relationships between variables in a path analysis, making it easier to understand the causal structure. It helps to show direct and indirect influences among variables.
What is the purpose of path coefficients in path analysis?
-Path coefficients represent the direct influence of one variable on another. They help quantify the magnitude and direction of relationships between variables, indicating the strength and type of the causal effect.
What is the role of error terms in path analysis?
-Error terms represent unaccounted influences that can affect endogenous variables. Every endogenous variable is influenced not only by other variables but also by an error term that accounts for any other unexplained factors.
How is hypothesis testing done in path analysis?
-Hypothesis testing in path analysis includes tests like the path coefficient test to check for direct effects, the Sobel test for indirect effects through mediating variables, and model fit tests such as the chi-square test to assess the overall fit of the model.
What is the Sobel test used for in path analysis?
-The Sobel test is used to determine whether there is a significant mediating effect in a model. It tests the hypothesis that the indirect effect (through a mediating variable) is different from zero.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)