Penentuan Krom dalam Air Limbah Menggunakan AAS
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial explains the procedure for determining chromium levels in wastewater using Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS). It covers the preparation of standard solutions, including calibration curves and concentration calculations. The video also demonstrates how to handle samples, spike tests, and measures absorbance for accurate results. Key steps include preparing samples with nitric acid, measuring absorbance of standard solutions, and calculating the concentration of chromium in the samples using regression equations. Additionally, the tutorial covers how to determine the limits of detection (LOD) and quantification (LOQ), as well as the accuracy and precision of the results.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video discusses the determination of chromium in wastewater using the AAS (Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy) method.
- 😀 Key equipment used includes an analytical balance, electric heater, spray bottles, atomic absorption spectrophotometer, beakers, pipettes, and porcelain crucibles.
- 😀 The procedure for preparing a standard chromium solution includes dissolving potassium dichromate in concentrated nitric acid and diluting with aquades.
- 😀 A 100 mg/L chromium standard solution is prepared by accurately measuring and diluting potassium dichromate.
- 😀 The standard solution is then used to prepare a series of chromium concentrations (0.2 mg/L, 0.8 mg/L, etc.) for calibration.
- 😀 Six beakers are prepared with 50 mL of water samples, to which nitric acid is added, and the samples are heated for volume reduction.
- 😀 A spike procedure involves adding a known amount of chromium standard to samples to assess recovery rates.
- 😀 Absorbance is measured for both the calibration standards and test samples using the atomic absorption spectrophotometer.
- 😀 A calibration curve is created from the standard solutions, allowing the calculation of chromium concentration in unknown samples.
- 😀 Accuracy is evaluated through recovery calculations, while precision is determined by standard deviation from repeated measurements.
Q & A
What method is used to determine the chromium concentration in wastewater in this video?
-The method used to determine the chromium concentration in wastewater is Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS).
What equipment is used in the analysis process?
-The equipment used includes an analytical balance, electric heater, spray bottle, Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer, stirrer, measuring flask, pipette, and porcelain dishes.
What are the chemicals used in the analysis?
-The chemicals used are concentrated nitric acid, potassium dichromate, and distilled water (aquades).
How is the standard solution of chromium prepared?
-To prepare the standard solution of chromium, 28.2 mg of potassium dichromate is weighed, dissolved in nitric acid, and then diluted with distilled water to reach a final volume of 100 mL, yielding a concentration of 100 mg/L of chromium.
How is the 10 mg/L chromium standard solution prepared?
-To prepare the 10 mg/L standard solution, 10 mL of the 100 mg/L chromium solution is transferred into a 100 mL measuring flask and diluted with aquades to the mark.
What concentrations are created for the calibration curve?
-The concentrations created for the calibration curve are 0.2, 0.8, 1.6, 2.4, 3.2, and 4 mg/L, prepared by mixing various volumes of the 10 mg/L standard solution and diluting with distilled water.
How is the sample preparation done for wastewater analysis?
-For wastewater analysis, 50 mL of the water sample is placed in a beaker, and 5 mL of concentrated nitric acid is added. The mixture is then heated to reduce the volume to 10 mL and transferred into a 50 mL measuring flask, then diluted with aquades.
What is the purpose of spiking the sample in the analysis?
-The purpose of spiking the sample is to add a known amount of chromium to the sample to assess recovery efficiency and to calculate the chromium concentration accurately by comparing the sample and spike.
How is the concentration of chromium in the sample calculated?
-The chromium concentration in the sample is calculated using the regression equation from the calibration curve, specifically using the formula x = (y - c) / m, where y is the absorbance, c is the intercept, and m is the slope.
What are the methods used to assess the accuracy and precision of the analysis?
-Accuracy is assessed by calculating the recovery percentage, which is the difference between the chromium concentrations in the spike and the sample. Precision is evaluated by calculating the standard deviation of the measurements from the sample.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Metode pengujian logam Fe dengan AAS
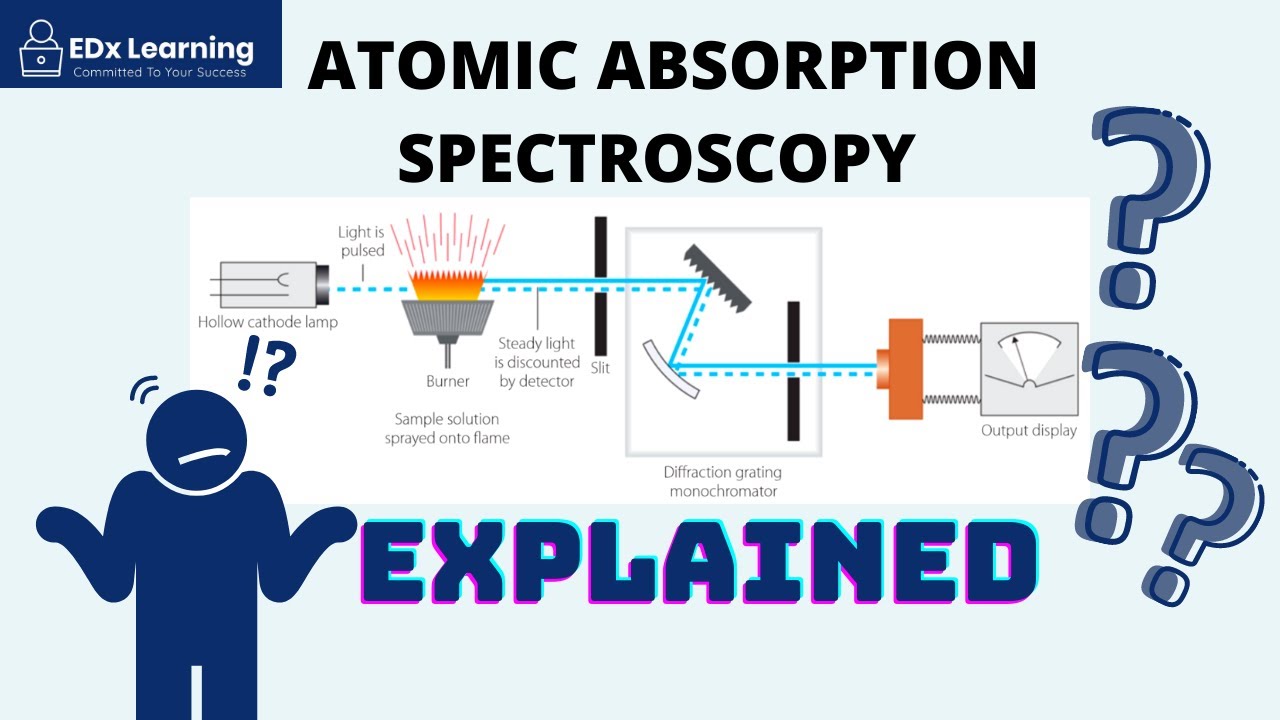
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) Explained - PART 1

Analisis Kadar Logam Besi (Fe) Pada Air Minum Dalam Kemasan Menggunakan Metode SSA

Determination of Zinc by Linear Calibration and Standard Addition Methods using AAS

analisis kandungan logam kadmium pada daging dengan metode AAS

PRAKTIKUM GEOKIMIA-Teknik Preparasi Sampel AAS
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)