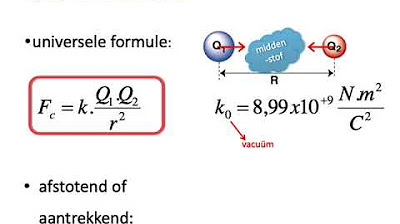
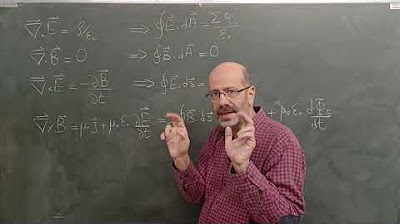LISTRIK MAGNET 14.3 Persamaan Maxwell dalam Bahan
Summary
TLDRThe video discusses Maxwell's equations in materials, focusing on concepts like polarization, magnetization, and bound charges. It explores the relationship between electric and magnetic fields in materials, emphasizing how changes in electric fields and currents lead to polarization and bound charges, affecting the behavior of the material. The speaker explains various physical phenomena like Gauss's law for polarization, conservation of bound charge, and Ampère's law in the context of materials. The lecture concludes with a reflection on the foundational knowledge required for advanced studies in physics.
Takeaways
- 😀 The script discusses Maxwell's equations in materials, with a focus on how electric and magnetic fields behave within materials.
- 😀 The concept of bound charges, which include volume and surface bound charges, is introduced and illustrated through examples like cubes.
- 😀 Polarization and magnetization are explained, with polarization corresponding to electric fields and magnetization related to magnetic fields in materials.
- 😀 The importance of bound charges in the form of surface and volume bound charges is emphasized, where surface charges are represented by sigma and volume charges by rho.
- 😀 Changes in electric and magnetic fields lead to variations in polarization and magnetization, which are essential to Maxwell's equations in materials.
- 😀 The script explains how changes in electric fields lead to polarization changes, and how this impacts the resulting bound charge density.
- 😀 Polarization currents are defined, arising from changes in polarization within materials, and are crucial for understanding the behavior of electric fields in materials.
- 😀 Gauss's law for polarization is introduced, demonstrating how polarization is related to changes in the electric field.
- 😀 The script elaborates on how the continuity equation and conservation laws apply to bound charges and currents, ensuring the consistency of Maxwell's equations in materials.
- 😀 The modified Ampère's law in the context of polarization currents is explained, showing how polarization currents are included in the equation alongside free and bound currents.
Q & A
What are the two types of bound charges mentioned in the lecture?
-The two types of bound charges mentioned in the lecture are bound volume charge and bound surface charge. The bound volume charge is distributed throughout the material, while the bound surface charge is located at the surface.
How is polarization related to the electric field within a material?
-Polarization in a material arises when an external electric field is applied. The electric field causes the dipoles within the material to align, leading to the creation of bound charges and polarization within the material.
What is meant by 'polarization current'?
-Polarization current refers to the current that arises due to the changing polarization within a material. It occurs when the polarization in the material varies over time, and it is related to the rate of change of the polarization.
What is the significance of Gauss's law for polarization?
-Gauss's law for polarization states that the divergence of the electric displacement field (D) is equal to the free charge density (ρ_F) minus the divergence of the polarization (P). This helps in understanding how polarization affects the electric field and is essential for solving Maxwell's equations in materials.
How does the concept of magnetization relate to electric polarization?
-Magnetization, like electric polarization, is a response of the material to an external field. While polarization refers to the alignment of electric dipoles in response to an electric field, magnetization refers to the alignment of magnetic dipoles (domains) in response to a magnetic field.
What happens to bound charges when the electric field inside a material changes?
-When the electric field inside a material changes, it leads to a variation in the polarization. This change in polarization generates bound charges, either on the surface or throughout the volume, depending on the nature of the material and the applied field.
How does Maxwell's equation change in a material compared to a vacuum?
-In a material, Maxwell's equations include terms that account for the material's response to electric and magnetic fields, such as the electric displacement field (D) and magnetization (M). These terms modify the equations to include the effects of polarization and magnetization, unlike in a vacuum where these effects are absent.
What is the role of the displacement field (D) in Maxwell's equations?
-The displacement field (D) represents the effects of both free and bound charges within a material. It is used in Maxwell's equations to replace the electric field (E) and incorporates the material's response to polarization. This helps describe the relationship between the electric field, charge distribution, and polarization in materials.
What is the connection between polarization and conservation of charge?
-Polarization plays a role in the conservation of charge by ensuring that the total charge, including bound charges, remains conserved within the material. The changes in polarization due to varying external fields lead to polarization currents, which are crucial for maintaining charge conservation in the material.
What does the lecture suggest about the beauty of Maxwell's equations?
-The lecturer expresses a sense of admiration for the beauty of Maxwell's equations, particularly their symmetry. The equations reflect elegant relationships between different fields (electric, magnetic) and charge densities, highlighting the interconnectedness of physical phenomena. This symmetry is both mathematically and physically appealing.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)