LISTRIK MAGNET 14 2 Penurunan persamaan Maxwell serta arti fisis Arus Perpindahan
Summary
TLDRThis video script dives into Maxwell's revision of Ampère's law, focusing on the mathematical and physical aspects of his work. The speaker explains how Maxwell identified inconsistencies in the original equations, particularly through the application of divergence and the concept of displacement current. Maxwell’s introduction of these ideas helped to resolve these inconsistencies, leading to a more unified understanding of electromagnetism. The script explores concepts like electric and magnetic fields, the role of capacitors, and the connection between changes in electric fields and the generation of magnetic fields, which ultimately led to the development of Maxwell's equations.
Takeaways
- 😀 Maxwell revised the Ampère equation to address inconsistencies in the original equations, especially with respect to symmetry.
- 😀 The four fundamental equations that Maxwell worked with are: Gauss's Law, Gauss's Law for magnetism, Faraday's Law, and Ampère's Law.
- 😀 A major issue identified by Maxwell was that the divergence of certain terms in the equations was zero, which created inconsistencies in the physical interpretation.
- 😀 Divergence of the electric field and magnetic field components must satisfy continuity conditions, meaning the amount of charge flowing in must equal that flowing out.
- 😀 Maxwell observed that there was no electric current between the plates of a capacitor, but the electric field changed when voltage was applied.
- 😀 The concept of 'displacement current' was introduced by Maxwell to explain how changes in the electric field could generate a magnetic field, even in the absence of actual current.
- 😀 This concept of displacement current resolved the inconsistency in Ampère's Law by allowing a changing electric field to induce a magnetic field, bridging the gap in classical electromagnetism.
- 😀 Maxwell's revisions also led to the discovery that electric fields can generate magnetic fields through changes in the electric field over time.
- 😀 The revised equations showed that electromagnetic waves are produced by oscillating electric and magnetic fields, and their speed is consistent with the speed of light.
- 😀 Maxwell's theories later enabled the prediction and experimental confirmation of electromagnetic waves, including radio waves, which were first demonstrated experimentally by Hertz.
Q & A
Why did Maxwell revise Ampère's law?
-Maxwell revised Ampère's law because he identified inconsistencies in the original formulation, particularly in terms of symmetry. The existing equations did not fully account for the behavior of changing electric fields, which Maxwell wanted to address.
What is the significance of the concept of 'displacement current' in Maxwell's revision of Ampère's law?
-The displacement current introduced by Maxwell accounts for the change in the electric field over time. It provides a way to explain how a varying electric field can generate a magnetic field, filling in a gap left by the original Ampère's law.
How does Maxwell's revision of Ampère's law connect to the concept of continuity?
-Maxwell's revision ensures the continuity of current and field interactions. He showed that for the laws of electromagnetism to be consistent, the electric displacement current must be accounted for, thus maintaining the continuity of charge conservation.
What is the relationship between electric and magnetic fields according to Maxwell's equations?
-Maxwell's equations show that changing electric fields produce magnetic fields and vice versa. A time-varying electric field can induce a magnetic field, and a time-varying magnetic field can induce an electric field, leading to the formation of electromagnetic waves.
What does the equation 'divergence of J = - ∂E/∂t' represent in Maxwell's revision?
-The equation 'divergence of J = - ∂E/∂t' represents the change in the current density due to a changing electric field. This is an expression of Maxwell's displacement current, highlighting how the changing electric field leads to the creation of a 'virtual' current in the absence of physical charges.
Why does Maxwell introduce the concept of 'displacement current' in relation to a capacitor?
-Maxwell introduces displacement current to explain the phenomenon in a capacitor where there is no physical current flowing between the plates, but the changing electric field between the plates can still produce a magnetic field. This concept resolves inconsistencies in Ampère's law, as it accounts for the varying electric field in situations like this.
How does Maxwell's revision address the issue of magnetic field generation in a capacitor?
-Maxwell's revision of Ampère's law includes the displacement current term, which ensures that even when there is no physical current in a capacitor, a changing electric field still produces a magnetic field, thus solving the problem of magnetic field generation in capacitors.
What is the physical interpretation of the 'displacement current' introduced by Maxwell?
-The displacement current is a theoretical current that accounts for the effect of a changing electric field on the creation of magnetic fields. It represents the rate of change of the electric field in regions where no physical current exists, like between the plates of a capacitor.
How does Maxwell's equation explain the continuity of electric charge?
-Maxwell's equations, particularly the modification of Ampère's law, ensure that the total electric charge is conserved. By introducing the displacement current, Maxwell ensures that the equation for the conservation of charge holds true even in situations involving changing electric fields.
What role does the 'epsilon naught' term play in Maxwell's revised equations?
-The 'epsilon naught' (ε₀) term represents the permittivity of free space in Maxwell's equations. It acts as a constant that describes how electric fields interact with the vacuum, influencing the magnitude of the displacement current and the propagation of electromagnetic waves.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
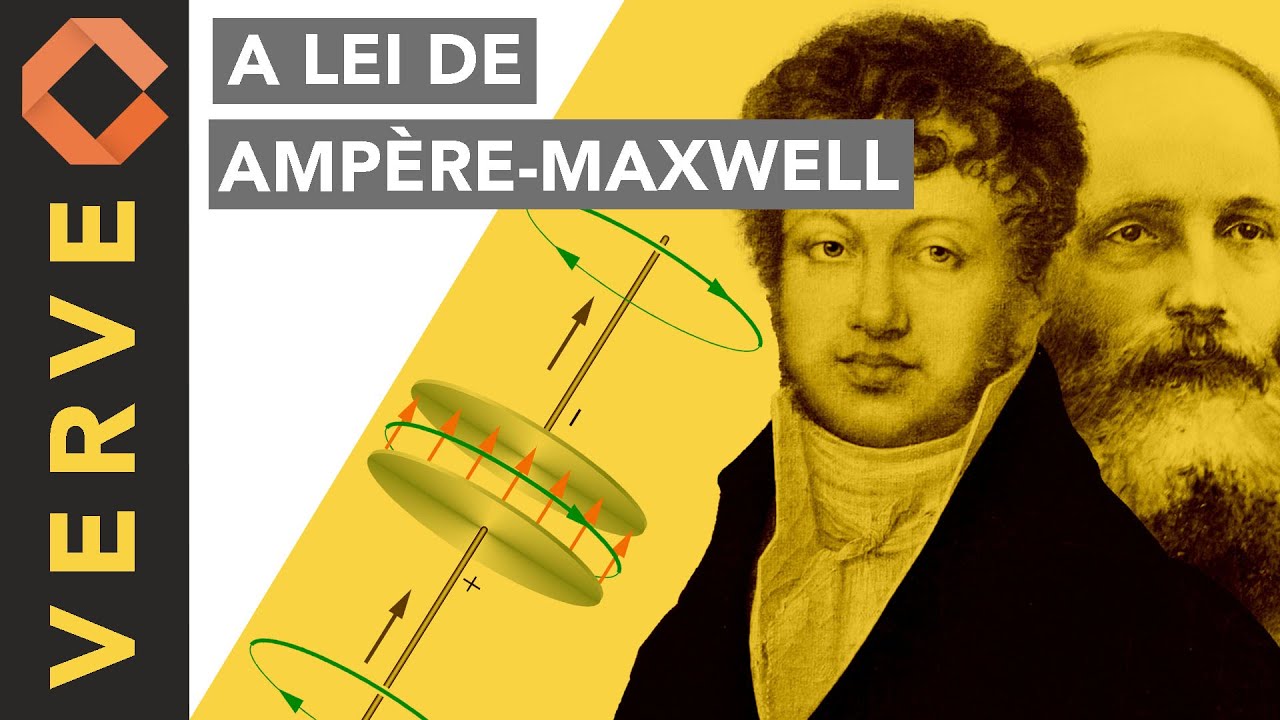
A Lei de Ampère-Maxwell: Campos elétricos induzem campos magnéticos.

MK Elektrodinamika - Persamaan Maxwell

LISTRIK MAGNET 14.3 Persamaan Maxwell dalam Bahan

Maxwell's Equations And Electromagnetic Theory: A Beginners Guide

マクスウェル電磁気学とニュートンからのアインシュタインの疑問
Physics - E&M: Ch 35.1 Coulumb's Law Explained (1 of 28) Why do Charged Objects Repel or Attract?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)