Telecurso 2000 - Metrologia - 05 Leitura no Sistema Métrico
Summary
TLDRThis educational video focuses on teaching viewers how to effectively read and interpret measurements using a caliper (paquímetro) in the metric system. It covers understanding the caliper's components, scales with different divisions (10, 20, 50), and how to read measurements accurately by combining readings from the main and auxiliary scales. The video emphasizes the importance of practice and understanding the resolution of the caliper for precise measurements. With real-world examples and clear explanations, viewers are encouraged to practice reading measurements to build confidence in using the caliper for accurate metric readings.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video focuses on teaching how to read and interpret measurements with a caliper in the metric system.
- 😀 The script explains the importance of understanding the components and functions of a caliper, which was covered in previous lessons.
- 😀 The main topic of today's lesson is how to read measurements accurately using a caliper with various scales.
- 😀 The video emphasizes the significance of practicing to improve your skills in interpreting measurements.
- 😀 The script provides examples of how to read measurements using calipers with 10, 20, and 50 divisions on the scale.
- 😀 It highlights that the number of divisions on the caliper's scale determines its resolution, which is the smallest measurable increment.
- 😀 A caliper with 10 divisions on the scale has a resolution of 1 mm per division, with 0.1 mm precision when reading between the divisions.
- 😀 For a caliper with 50 divisions, the resolution is 0.02 mm, offering more precise measurements, especially for smaller objects.
- 😀 The video demonstrates several examples, guiding the viewer to practice identifying exact measurements from the scale of the caliper.
- 😀 The lesson concludes with a reminder to review the material and practice the exercises in the workbook to retain the skills learned.
Q & A
What is the purpose of a caliper (paquímetro)?
-A caliper is a precision instrument used to measure the dimensions of objects, particularly internal and external measurements with high accuracy, often in millimeters.
How can you identify the resolution of a caliper?
-The resolution of a caliper is determined by the number of divisions on the movable scale. For example, a caliper with 10 divisions has a resolution of 0.1 mm, while one with 20 divisions has a resolution of 0.05 mm.
What should you check first when reading measurements with a caliper?
-First, you should check the fixed scale to identify the whole number value (in millimeters), and then examine the movable scale for the fractional measurement.
How do you read a measurement when the movable scale lines up with a fixed scale mark?
-When the movable scale's line aligns with a mark on the fixed scale, it indicates the fractional value. You count the divisions to determine the exact fractional measurement, which is then added to the whole number from the fixed scale.
What is the reading process when using a caliper with 10 divisions?
-For a caliper with 10 divisions, you look at the whole number on the fixed scale and then find the corresponding fractional value by looking at the movable scale. For instance, if the fixed scale shows 19 mm and the movable scale shows the fourth line, the measurement is 19.4 mm.
What is the smallest unit a caliper with 50 divisions can measure?
-A caliper with 50 divisions can measure the smallest unit of 0.02 mm, as it divides the 1 mm by 50.
How do you interpret a reading when the movable scale has 20 divisions?
-When using a caliper with 20 divisions, the smallest increment is 0.05 mm. For example, if the fixed scale shows 13 mm and the movable scale shows the fifth line, the total reading would be 13.5 mm.
What does it mean when the movable scale is aligned with the first division of the fixed scale?
-When the movable scale aligns with the first division of the fixed scale, it means the fractional value is equal to the smallest unit, which is determined by the caliper's division. For instance, if it's a 20-division caliper, the reading will include a fractional measurement like 0.05 mm.
Why is it important to practice reading a caliper regularly?
-Regular practice helps you become more familiar with the tool, making it easier and faster to interpret measurements accurately. It also reinforces the understanding of different resolutions and divisions in the caliper.
What key points should you review to understand caliper measurements better?
-To understand caliper measurements, review the different types of calipers, their resolutions (10, 20, and 50 divisions), and how to read both the fixed and movable scales. Practice using the tool with different readings to solidify your understanding.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Paquímetro analógico - como usar e como fazer a leitura

Cara Membaca Jangka Sorong Ketelitian 0.02 mm, 0.05 mm dan 0.1 mm

Cara Membaca Jangka Sorong [5 Menit Langsung Bisa]

Telecurso 2000 - Metrologia - 03 Régua Graduada, Metro e Trena

CARA MEMBACA JANGKA SORONG | KETELITIAN 0.02 mm | VERNIER CALIPER | SIGMAT
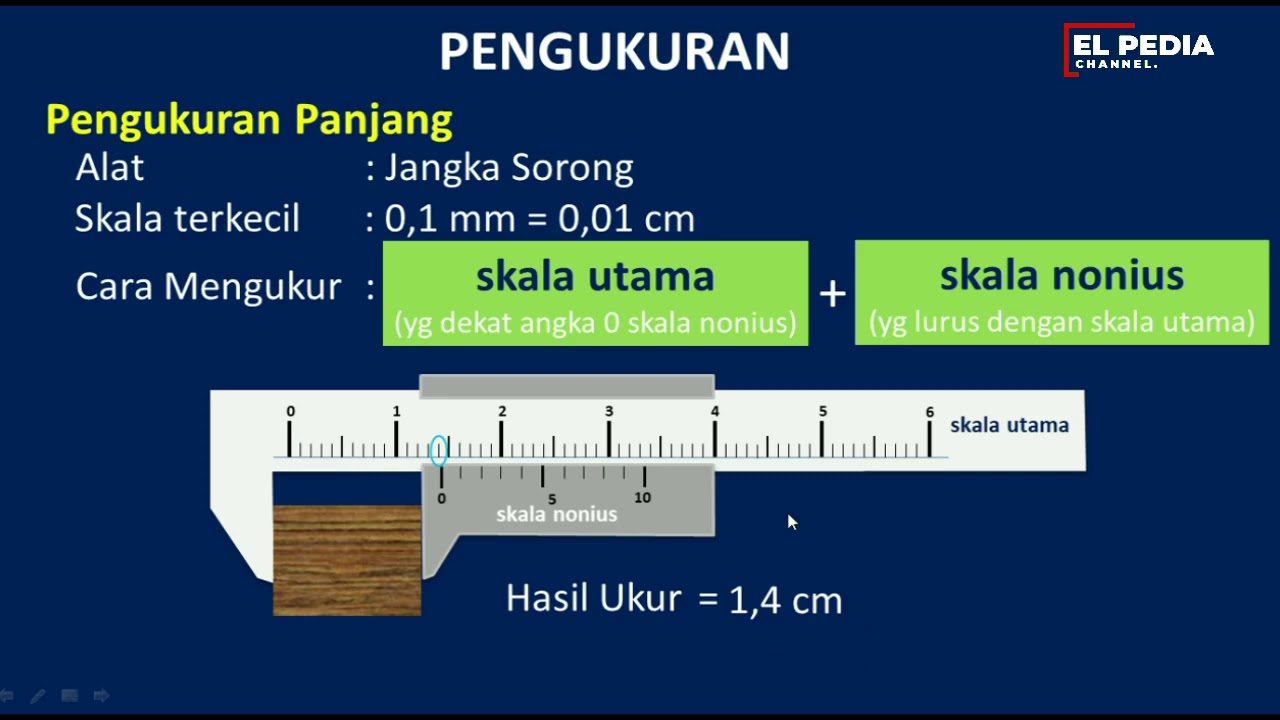
PENGUKURAN PANJANG : Cara Mengukur dgn Mistar, Jangka Sorong & Mikrometer Sekrup
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)